题目1
编写程序,创建两个线程对象,一根线程循环输出“播放背景音乐”,另一根线程循环输出“显示画面”;
要求:
1: 1个线程使用Runnable接口的匿名内部类实现
2: 另一个线程使用lambda实现
效果:
参考答案:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("播放背景音乐...");
}
}
}).start();
//lambda
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
System.out.println("显示画面...");
}
}).start();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
题目2
3.请使用继承Thread类的方式定义一个线程类,在run()方法中循环10次,每1秒循环1次,每次循环按“yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”的格式打印当前系统时间。
请定义测试类,并定义main()方法,启动此线程,观察控制台打印。
要求:
1: 使用匿名内部类配合SimpleDateFormat和Date实现
2: 使用lambda配合LocalDateTime和DateTimeFormatter实现
效果: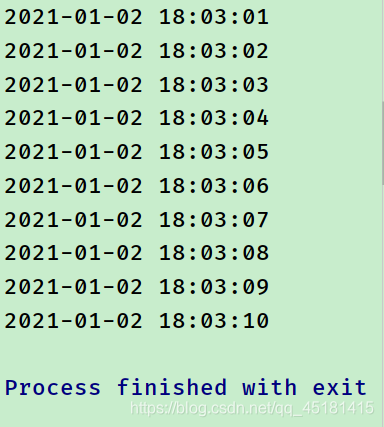
参考答案:
//方式1:
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String format = sdf.format(new Date());
System.out.println(format);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
//方式2:
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter f = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String format = f.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(format);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
题目3
请编写多线程应用程序,模拟多个人通过一个山洞:
(1).这个山洞每次只能通过一个人,每个人通过山洞的时间为1秒;
(2).创建10个线程,同时准备过此山洞,并且定义一个变量用于记录通过隧道的人数。显示每次通过山洞人的姓名,和通过顺序;
要求:
保证安全问题,不能出现多个人同时通过山洞的现象;(必须逐一通过)
效果:
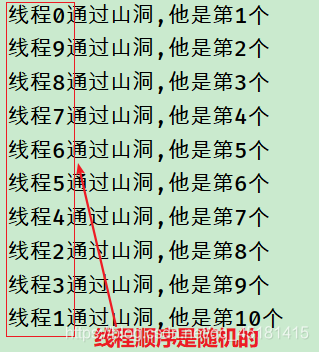
参考答案:
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(mr,"线程"+i).start();
}
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private int count = 1;
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"通过山洞,他是第"+count+"个");
count++;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
题目4
拼手速抽奖案例.
1.现有一个集合装了10个奖品在里面,分别是:{“电视机”,“电冰箱”,“电脑”,“游戏机”,“洗衣机”,“空调”,“手机”,“平板电脑”,“电动车”,“电饭煲”};
2.假如有3个人同时去抽这10个奖品.最后打印出来.三个人各自都抽到了什么奖品.
例如:
张三: “电视机”,”电冰箱”,”电脑”,”游戏机”,”洗衣机”
李四: ”空调”,”手机”,”平板电脑”,
王五: ”电动车”,”电饭煲
要求:
1:3个人同时开始抽奖,每次抽奖需要使用0.5秒才能完成抽奖;
2:需要控制住同一个奖项不能同时被多个人抽走;
效果:
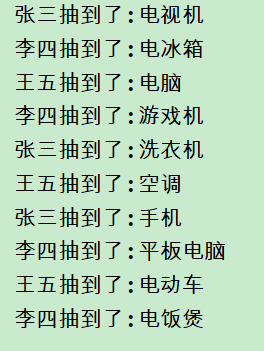
参考答案:
public class A { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建抽奖任务类对象 MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable(); //创建3个线程对象,都关联着任务对象, Thread t1 = new Thread(mr,"张三"); Thread t2 = new Thread(mr,"李四"); Thread t3 = new Thread(mr,"王五"); //开始抽奖 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } } class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private static ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); static { //初始化奖品,而且,只能初始化1次,所以使用了静态代码块 Collections.addAll(list,"电视机","电冰箱","电脑","游戏机","洗衣机","空调","手机","平板电脑","电动车","电饭煲"); } public void run() { while (list.size()>0){ try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (this) { if(list.size()==0){ return;//加这个if是确保安全的 } String r = list.remove(new Random().nextInt(list.size())); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抽到了:"+r); } } } }
原文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45181415/article/details/112107303