【C# vs C++/CLI 析构】
For example, the following is a declaration of a finalizer
class Car { ~Car() // finalizer { // cleanup statements... } }
概念:1、Finalize 2、Dispose
Difference:
1、C#中析构函数会被编译器替换为Finalize,代码永远不可以直接调用Finalize。
2、C#中可以实现IDisposable接口来主动释放资源。
3、C#中可以使用using语句来主动调用Dispose()。
1、C++/CLI中析构函数被编译器替换为Dispose()函数。
2、局部变量作用域结束、使用delete,会调用该Dispose()函数。
3、!ClassName()函数被编译器替换为Finalize()函数,代码无法直接调用,只能通过GC调用。
【Finalize详细信息】
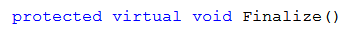
对象变为不可访问后将自动调用此方法,除非已通过 SuppressFinalize 调用使对象免除了终结。在应用程序域的关闭过程中,对没有免除终结的对象将自动调用 Finalize,即使那些对象仍是可访问的。对于给定的实例仅自动调用 Finalize 一次,除非使用 ReRegisterForFinalize 这类机制重新注册该对象并且后面没有调用 GC.SuppressFinalize。
Because the C# compiler does not allow you to directly implement the Finalize method, a C# destructor automatically calls the destructor of its base class.
C# 析构函数自动调用基类析构函数。
public virtual void Finalize()
A type must implement Finalize when it uses unmanaged resources such as file handles or database connections that must be released when the managed object that uses them is reclaimed.
1、Finalize方法在哪个线程中运行是未定义的。
2、Finalize方法调用的时间不确定。
3、如果A引用了B,并不意味着A.Finalize会先于B.Finalize调用。
4、如果一个Finalizer被阻塞,则会阻碍其它的Finalizer的调用。
参考:http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.object.finalize(v=vs.90).aspx
【Finalizer Example】
The class First is the base class, Second is derived from First, and Third is derived from Second. All three have finalizers.
1 class First 2 { 3 ~First() 4 { 5 System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("First's destructor is called."); 6 } 7 } 8 9 class Second : First 10 { 11 ~Second() 12 { 13 System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("Second's destructor is called."); 14 } 15 } 16 17 class Third : Second 18 { 19 ~Third() 20 { 21 System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("Third's destructor is called."); 22 } 23 } 24 25 class TestDestructors 26 { 27 static void Main() 28 { 29 Third t = new Third(); 30 } 31 32 } 33 /* Output (to VS Output Window): 34 Third's destructor is called. 35 Second's destructor is called. 36 First's destructor is called. 37 */