原文 http://tecdat.cn/?p=3364
加载R包和数据集
上述症状数据集包含在R-package 中,并在加载时自动可用。 加载包后,我们将此数据集中包含的12个心情变量进行子集化:
对象mood_data是一个1476×12矩阵,测量了12个心情变量:
time_data包含有关每次测量的时间戳的信息。数据预处理需要此信息。
该数据集中的一些变量是高度偏斜的,这可能导致不可靠的参数估计。 在这里,我们通过计算自举置信区间(KS方法)和可信区间(GAM方法)来处理这个问题,以判断估计的可靠性。 由于本教程的重点是估计时变VAR模型,因此我们不会详细研究变量的偏度。 然而,在实践中,应该在拟合(时变)VAR模型之前始终检查边际分布。
估计时变VAR模型
通过参数lags = 1,我们指定拟合滞后1 VAR模型,并通过lambdaSel =“CV”选择具有交叉验证的参数λ。 最后,使用参数scale = TRUE,我们指定在模型拟合之前,所有变量都应缩放为零和标准差1。 当使用“1正则化”时,建议这样做,因为否则参数惩罚的强度取决于预测变量的方差。 由于交叉验证方案使用随机抽取来定义折叠,因此我们设置种子以确保重现性。
在查看结果之前,我们检查了1476个时间点中有多少用于估算,这在调用控制台中的输出对象时打印的摘要中显示
估计的VAR系数的绝对值存储在对象tvvar_obj $ wadj中,该对象是维度p×p×滞后×estpoints的数组。
参数估计的可靠性
res_obj $ bootParameters包含每个参数的经验采样分布。
计算时变预测误差
函数predict()计算给定mgm模型对象的预测和预测误差。
预测存储在pred_obj $预测中,并且所有时变模型的预测误差组合在pred_obj中:
可视化时变VAR模型
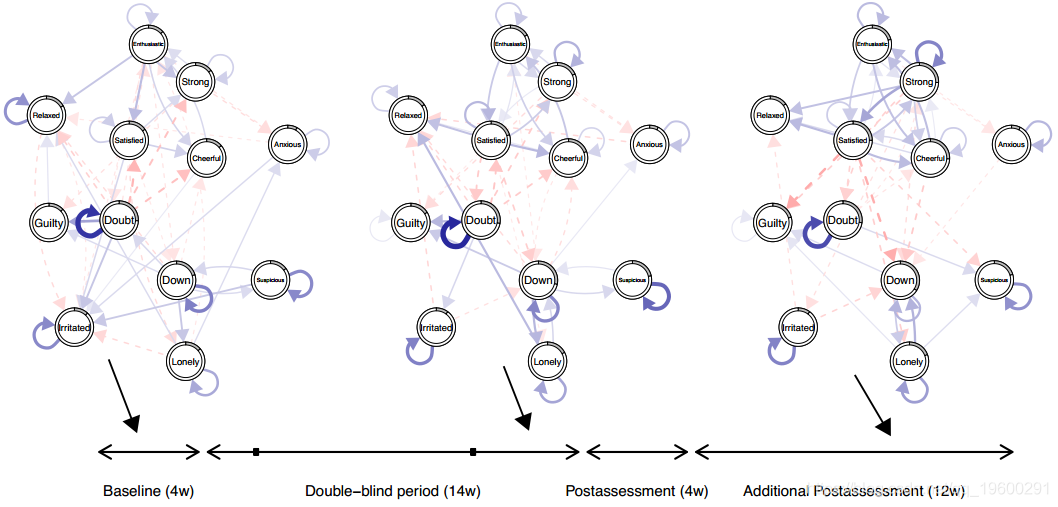
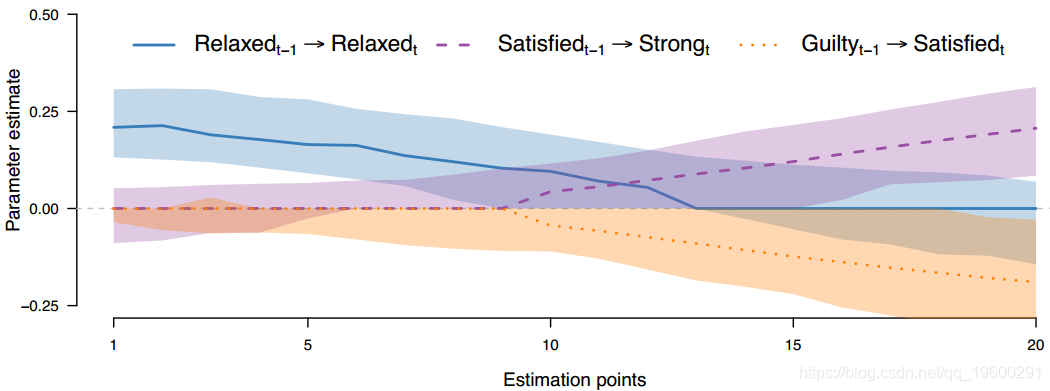
可视化上面估计的一部分随时间变化的VAR参数:
图 显示了上面估计的时变VAR参数的一部分。 顶行显示估计点8,15和18的VAR参数的可视化。蓝色实线箭头表示正关系,红色虚线箭头表示负关系。 箭头的宽度与相应参数的绝对值成比例。