在前边的文章中,和小伙伴一起认识了异步执行的好处,以及如何进行异步开发,对,就是使用@Async注解,在使用异步注解@Async的过程中也存在一些坑,不过通过正确的打开方式也可以很好的避免,今天想和大家分享下@Async的原理,开始前先温习下之前的文章哦,
springboot:使用异步注解@Async获取执行结果的坑
springboot:嵌套使用异步注解@Async还会异步执行吗
一、引言
在前边说到在使用@Async的时候,在一个类中两个@Async的方法嵌套使用会导致异步失败,下面把场景重现下,
AsyncContoller.java
package com.example.myDemo.controller;
import com.example.myDemo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
@Controller
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/aysnc")
@ResponseBody
public String asyncMethod(){
try {
Long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
//调用method3方法,该方法中嵌套了一个异步方法
String str3=asyncService.method3().get();
Long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时长:"+(end-start));
} catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello @Async";
}
}
下面是method3方法
package com.example.myDemo.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
@Async
public class AsyncService {
/**
* 第一个异步方法,睡眠10s返回字符串
*
* @return
*/
public Future<String> method() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult("I am method");
}
/**
* 第三个异步方法,在该异步方法中调用了另外一个异步方法
* @return
*/
public Future<String> method3(){
try{
//睡眠10s
Thread.sleep(10*1000);
System.out.println(this);
//method方法也是睡眠10s
this.method();
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<>("two async method");
}
}
上面便是method3方法,以及嵌套在method3方法中的method方法,这两个方法体上均没有标注@Async,只是在这个类上使用了@Async注解,那么该类中的所有方法都是异步的。
执行结果如下,
2022-04-30 15:29:47.711 INFO 16836 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 4 ms
com.example.myDemo.service.AsyncService@7e316231
执行时长:20028
从上面可以看到整个方法的执行时长是20多秒,那么就说明这种同一个类中的嵌套调用,@Async是失效的。
二、解决方式
1、把嵌套方法抽到另一个类中
这种方式就是把嵌套的异步方法method抽取到另外一个类中,下面我们来看下,
OtherService.java
package com.example.myDemo.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
@Async
public class OtherAsyncService {
public Future<String> method() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult("I am method");
}
}
那么AsyncService.java则变成下面的样子
package com.example.myDemo.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
@Async
public class AsyncService {
//注入OtherService
@Autowired
private OtherAsyncService otherAsyncService;
/**
* 第三个异步方法,在该异步方法中调用了另外一个异步方法
* @return
*/
public Future<String> method3(){
try{
Thread.sleep(10*1000);
System.out.println(this);
//调用OtherAsyncService的method方法
otherAsyncService.method();
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<>("two async method");
}
}
下面看执行的结果,
2022-04-30 15:44:18.914 INFO 16768 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 5 ms
com.example.myDemo.service.AsyncService@689927ef
执行时长:10016
执行时长10s多点,符合预期。
2、自己注入自己
这种方式很有意思,我斗胆给它取名为“自己注入自己”,在AsyncService类中注入一个AsyncService的实例,如下
package com.example.myDemo.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
@Async
public class AsyncService {
//这里注入的是AsyncService的实例
@Lazy
@Autowired
private AsyncService otherAsyncService;
/**
* 第一个异步方法,睡眠10s返回字符串
*
* @return
*/
public Future<String> method() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult("I am method");
}
/**
* 第三个异步方法,在该异步方法中调用了另外一个异步方法
* @return
*/
public Future<String> method3(){
try{
Thread.sleep(10*1000);
System.out.println(this);
otherAsyncService.method();
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<>("two async method");
}
}
小伙伴们注意,我是在AsyncService类中又注入了一个AsyncService的实例,在method3方法中调用的是AsyncSerevice的方法method,要区别于下面的调用方式
this.method();
下面看下执行结果,
2022-04-30 15:55:30.635 INFO 9788 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 5 ms
com.example.myDemo.service.AsyncService@2ac186f8
执行时长:10015
好了,我们看到执行时长为10s多点,也就是说异步是生效的,在这种方式中要注意注入的对象必须添加@Lazy注解,否则启动会报错哦。
三、原理揭秘
上面已经把嵌套使用的误区和解决方式已经总结完了,下面到了要揭开@Async面纱的时候了,最好的方式是debug,看下面@Async的debug的过程
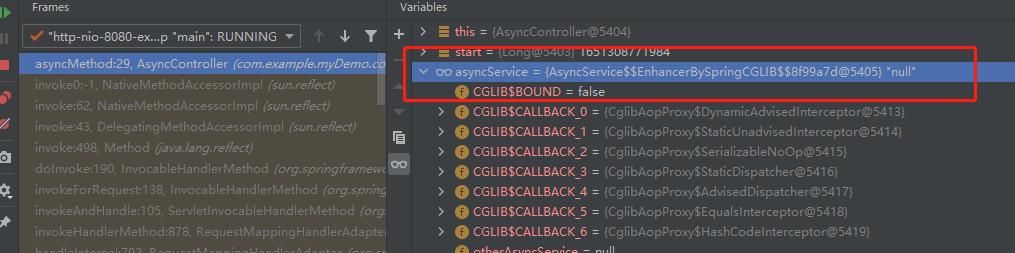
可以看到在AsyncController中asyncService是一个代理对象,且使用的方式是cglib,那么也就是会把其中的方法进行代理,类似下面的代码
before();
method3();
after();
也就是对method3进行了代理,这里的代理指的是把mthod3方法封装成一个task,交给线程池去执行,那么在method3中的this.method()这句调用,也就是普通调用了,是同步的,为什么这样说,因为这里的this代表的是AsyncService这个实例对象,
但是如果换成"自己注入自己的方式",例如下图,
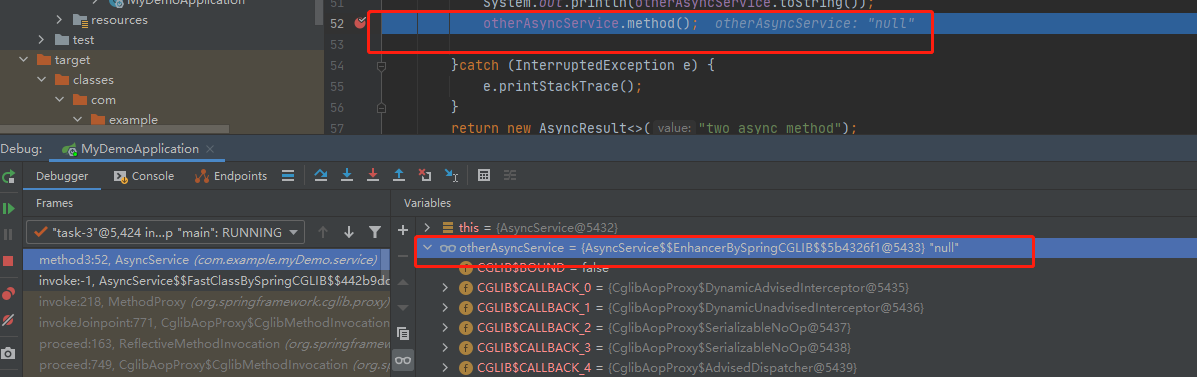
可以看到还是一个AsyncService的cglib代理对象,所以完美解决了嵌套调用的问题。
四、总结
本文分析了@Async注解的实现原理及如何使用正确使用嵌套调用,
1、@Async注解底层使用的是代理,标记为@Async所在的类在实际调用时是一个代理类;
2、合理使用@Async方法的嵌套,可以把嵌套方法抽到另外一个类中;
3、如果在本类中使用嵌套方法,那么需要自己注入自己,切记加上@Lazy注解;
推荐阅读
springboot:使用异步注解@Async获取执行结果的坑
springboot:嵌套使用异步注解@Async还会异步执行吗
