Gazebo是一种多机器人仿真器,可用于室内外机器人仿真。Gazebo在ROS中有良好的接口,包含ROS和Gazebo的所有控制。
若要实现ROS到Gazebo的通信,我们必须安装ROS-Gazebo接口。
应该安装以下软件包:
$ sudo apt install ros-melodic-gazebo-ros-pkgs ros-melodic-gazebo-msgs ros-melodic-gazebo-plugins ros-melodic-gazebo-ros-control
*gazebo_ros_pkgs : 它包含用于将ROS和Gazebo连接的封装和工具。
*gazebo-msgs : 它包含ROS和Gazebo交互的消息和服务的数据结构。
*gazebo-plugins : 它包含用于传感器、执行结构的Gazebo插件。
*gazebo-ros-control : 它包含用于在ROS和Gazebo之间通信的标准控制器。
安装后,请使用以下命令检查Gazebo是否安装正确:
$ roscore & rosrun gazebo_ros gazebo
一.为Gazebo创建机械臂仿真模型
我们可以通过添加仿真参数来更新现有的机器人描述,从而创建一个机械臂仿真模型。
我们需要去创建一个软件包:
$ catkin_create_pkg seven_dof_arm_gazebo gazebo_msgs gazebo_plugins gazebo_ros gazebo_ros_control mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg
也可以在相应的Git库中获得完整的软件包。如下:
$ git clone https://github.com/jocacace/seven_dof_arm_gazebo.git
可以在seven_dof_arm.xacro文件中看到机器人的完整仿真模型,上一章讲过。
该文件包含了URDF标签,这对于仿真是必要的,我们将定义碰撞、惯性、传动、关节、连杆、以及Gazebo。
我们可以使用seven_dof_arm_gazebo软件包来启动现有的仿真模型,启动文件为:seven_dof_arm_world.launch的启动文件。
代码如下:
1 <launch> 2 3 <!-- these are the arguments you can pass this launch file, for example paused:=t rue --> 4 <arg name="paused" default="false"/> 5 <arg name="use_sim_time" default="true"/> 6 <arg name="gui" default="true"/> 7 <arg name="headless" default="false"/> 8 <arg name="debug" default="false"/> 9 10 <!-- We resume the logic in empty_world.launch --> 11 <include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch"> 12 <arg name="debug" value="$(arg debug)" /> 13 <arg name="gui" value="$(arg gui)" /> 14 <arg name="paused" value="$(arg paused)"/> 15 <arg name="use_sim_time" value="$(arg use_sim_time)"/> 16 <arg name="headless" value="$(arg headless)"/> 17 </include> 18 19 <!-- Load the URDF into the ROS Parameter Server --> 20 <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find ma stering_ros_robot_description_pkg)/urdf/seven_dof_arm.xacro'" /> 21 22 23 <!-- Run a python script to the send a service call to gazebo_ros to spawn a URDF robot --> 24 <node name="urdf_spawner" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" respawn="false" out put="screen" 25 args="-urdf -model seven_dof_arm -param robot_description"/> 26 27 28 </launch>
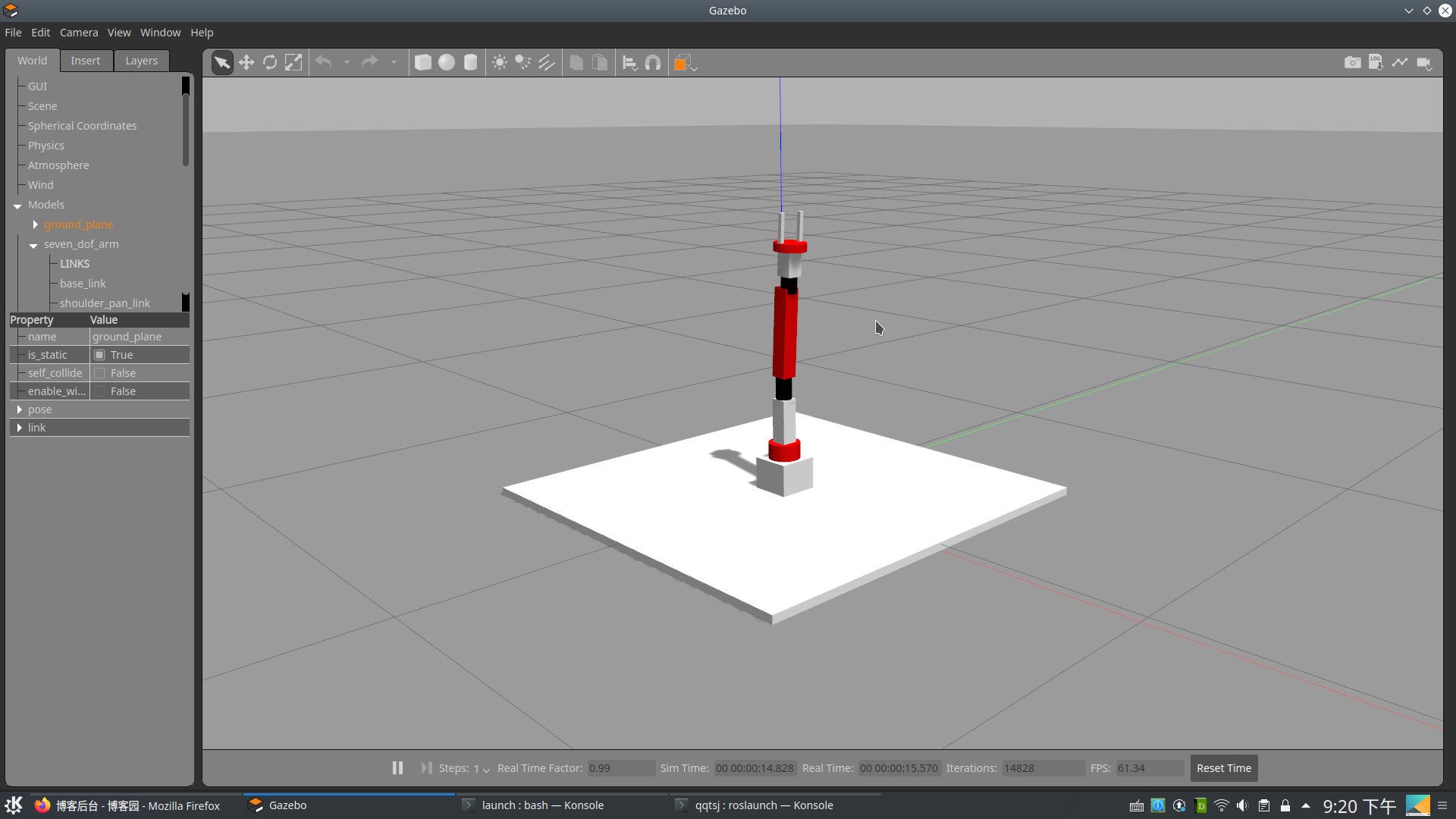
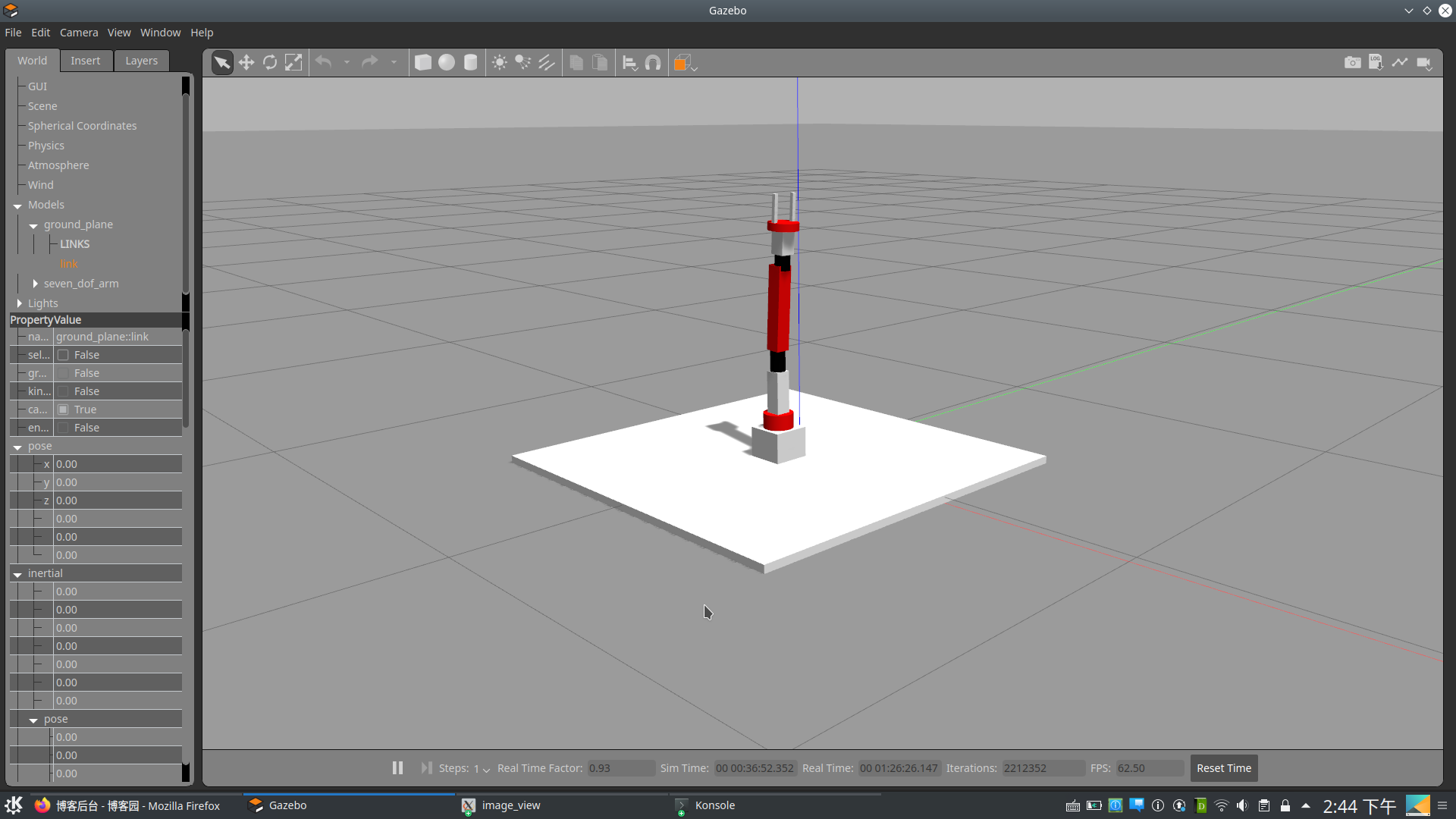
启动以下命令来显示仿真机械臂
$ roslaunch seven_dof_arm_gazebo seven_dof_arm_world.launch
模型如下:
接下来我们来详细的讨论一下机器人的仿真模型文件
1.为Gazebo机器人模型添加颜色和纹理
在机器人仿真中我们可以看到每个连杆都有不同的颜色和纹理。在xacro文件中,下面的标签可以为机器人的连杆提供纹理和颜色:
140 <gazebo reference="bottom_link"> 141 <material>Gazebo/White</material> 142 </gazebo> 172 <gazebo reference="base_link"> 173 <material>Gazebo/White</material> 174 </gazebo> 210 <gazebo reference="shoulder_pan_link"> 211 <material>Gazebo/Red</material> 212 </gazebo>
2.添加transmission标签来启动模型
为了使用ROS控制器来启动机器人,我们需要定义<transmission>(传动)标签来连接执行机构和关节,以下是为传动的宏:
92 <xacro:macro name="transmission_block" params="joint_name">
93 <transmission name="tran1">
94 <type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
95 <joint name="${joint_name}">
96 <hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface</hardwareIn terface>
97 </joint>
98 <actuator name="motor1">
99 <hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface</hardwareIn terface>
100 <mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
101 </actuator>
102 </transmission>
103 </xacro:macro>
在这里<joint name="">是连接启动器的关节。<type>标签是传动类型。目前,仅支持简单的传动transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission. <hardwareInterface>
标签是要加载的硬件接口类型(位置、速度或力度),在该示例中,使用了位置控制硬件接口。这个硬件接口由gazebo_ros_control插件加载,下一节将看到。
3.添加gazebo_ros_control插件
在添加传动标签后,我们应该在仿真模型中添加gazebo_ros_control插件来解析传动标签并分配适当的硬件接口和控制管理器。代码如下:
563 <gazebo> 564 <plugin name="gazebo_ros_control" filename="libgazebo_ros_control.so"> 565 <robotNamespace>/seven_dof_arm</robotNamespace> 566 </plugin> 567 </gazebo> 568
<plugin>标签指定了要加载的插件名是libgazebo_ros_control.so。可以将<robotNamespace>标签作为机器人的名称,
如果我们没有指定名称,它将从URDF 自动加载机器人的名称。我们还可以在参数服务器(<robotParam>)上指定控制器刷新速率(<control-Period>),robot_description(URDF)
的位置以及机器人硬件接口的类型(<robotSimType>).默认的硬件接口可以是:JointStateInerface、EffortJointInterface或VelocityJointInterface.
4.在Gazebo中添加3D视觉传感器
在Gazebo中,我们可以仿真机器人的运动和物理特征,也可以对传感器进行仿真。
要在Gazebo中创建一个传感器,我们就必须对Gazebo中传感器的行为进行建模。
Gazebo中有一些预先创建的传感器模型,可以直接在代码中使用而无需编写新模型。
这里,我们在Gazebo中添加了一个名为Asus Xtion Pro模型的3D视觉传感器(通常称为RGB-D传感器)。传感器已经在gazebo_ros_pkgs/gazebo_plugins的ROS软件包中实现。
Gazebo中的每个模型都可以作为Gazebo_ROS插件实现,可以将其插入URDF文件来加载。
以下是我们如何在seven_dof_arm_with_rgbd.xacro机器人的xacro文件中把Gazebo定义和Xtion Pro的物理机器人模型包含进来的:
<xacro:include filename="$(find mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg)/urdf/sensor s/xtion_pro_live.urdf.xacro"/>
在xtion_pro_live.urdf.xacro文件内部,我们可以看到以下代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0"?>
2 <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro">
3
4 <xacro:include filename="$(find mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg)/urdf/sensors /xtion_pro_live.gazebo.xacro"/>
5
6 <xacro:macro name="dummy_inertial">
7 <inertial>
8 <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
9 <mass value="0.001"/>
10 <inertia ixx="0.00001" ixy="0" ixz="0"
11 iyy="0.00001" iyz="0"
12 izz="0.00001"/>
13 </inertial>
14 </xacro:macro>
15
16 <xacro:macro name="xtion_pro_live" params="name parent *origin *optical_origin">
17
18 <!-- frames in the center of the camera -->
19 <joint name="${name}_joint" type="fixed">
20 <xacro:insert_block name="origin"/>
21 <parent link="${parent}_link"/>
22 <child link="${name}_link"/>
23 </joint>
24
25 <link name="${name}_link">
26 <inertial>
27 <origin xyz="-0.00936000000 -0.00003000000 -0.00273000000" rpy="0 0 0"/>
28 <mass value="0.21970000000"/>
29 <inertia ixx="0.00000429247" ixy="0.00000000000" ixz="0.00000002565"
30 iyy="0.00000008027" iyz="0.00000000000"
31 izz="0.00000427339"/>
32 </inertial>
33 <visual>
34 <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
35 <geometry>
36 <mesh filename="package://mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg/meshes/sens ors/xtion_pro_live/xtion_pro_live.dae"/>
37 </geometry>
38 <material name="DarkGrey"/>
39 </visual>
40 </link>
41
42 <joint name="${name}_optical_joint" type="fixed">
43 <xacro:insert_block name="optical_origin"/>
44 <parent link="${name}_link"/>
45 <child link="${name}_optical_frame"/>
46 </joint>
47
48 <link name="${name}_optical_frame">
49 <dummy_inertial/>
50 </link>
51
52 <!-- Depth sensor frames -->
53 <joint name="${name}_depth_joint" type="fixed">
54 <origin xyz="0.0 0.049 0.0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
55 <parent link="${name}_link"/>
56 <child link="${name}_depth_frame"/>
57 </joint>
58
59 <link name="${name}_depth_frame">
60 <dummy_inertial/>
61 </link>
62
63 <joint name="${name}_depth_optical_joint" type="fixed">
64 <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${-90.0 * deg_to_rad} 0.0 ${-90.0 * deg_to_rad}"/>
65 <parent link="${name}_depth_frame"/>
66 <child link="${name}_depth_optical_frame"/>
67 </joint>
68
69 <link name="${name}_depth_optical_frame">
70 <dummy_inertial/>
71 </link>
72
73 <!-- RGB sensor frames -->
74 <joint name="${name}_rgb_joint" type="fixed">
75 <origin xyz="0.0 0.022 0.0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
76 <parent link="${name}_link"/>
77 <child link="${name}_rgb_frame"/>
78 </joint>
79
80 <link name="${name}_rgb_frame">
81 <dummy_inertial/>
82 </link>
83
84 <joint name="${name}_rgb_optical_joint" type="fixed">
85 <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${-90.0 * deg_to_rad} 0.0 ${-90.0 * deg_to_rad}"/>
86 <parent link="${name}_rgb_frame"/>
87 <child link="${name}_rgb_optical_frame"/>
88 </joint>
89
90 <link name="${name}_rgb_optical_frame">
91 <dummy_inertial/>
92 </link>
93
94 <xacro:xtion_pro_live_rgbd_camera_gazebo name="${name}"/>
95 </xacro:macro>
96
97 </robot>
在这里,我们可以看到它包含另一个名为xtion_pro_live.gazebo.xacro的文件,该文件包含Xtion Pro在Gazebo中的完整定义。
我们还可以看到一个名为xtion_pro_live的宏定义,其中包含Xtion Pro的完整模型定义,包括连杆和关节:
<mesh filename="package://mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg/meshes/sens ors/xtion_pro_live/xtion_pro_live.dae"/>
在宏定义中,我们将导入一个Asus Xtion Pro的网格文件该文件将在Gazebo中显示为相机连杆。
在mastering_ros_robot_description_pkg/urdf/sensors/xtion_pro_live.gazebo.xacro文件中,
我们可以设置Xtion Pro的Gazebo-ROS插件,我们将插件定义为宏,并支持RGB和深度相机,插件的定义如下:
67 <plugin name="${name}_frame_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_openni_kine ct.so">
68 <alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
69 <updateRate>6.0</updateRate>
70 <cameraName>${name}</cameraName>
71
72 <imageTopicName>rgb/image_raw</imageTopicName>
73 <cameraInfoTopicName>rgb/camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName>
74 <pointCloudTopicName>rgb/points</pointCloudTopicName>
75
76 <depthImageTopicName>depth/image_raw</depthImageTopicName>
77 <depthImageCameraInfoTopicName>depth/camera_info</depthImageCameraInfoTop icName>
78
79 <frameName>${name}_optical_frame</frameName>
80 <pointCloudCutoff>0.05</pointCloudCutoff>
81 <pointCloudCutoffMax>5</pointCloudCutoffMax>
82 <rangeMax>1.5</rangeMax>
83
84 </plugin>
Xtion Pro的插件文件名是libgazebo_ros_openni_kinect.so,我们可以定义插件参数,例如相机名称,图像话题等。
二.仿真装有Xtion Pro的机械臂
现在已经了解了Gazebo中相机插件的定义,我们可以使用以下命令启动完整的仿真:
$ roslaunch seven_dof_arm_gazebo seven_dof_arm_with_rgbd_world.launch
我们就可以看到一个机器人模型,在机械臂顶部装有一个传感器,如图所示:
可视化三维传感器数据
使用上述命令启动仿真后,我们可以检查由传感器插件生成的话题,如图所示:
命令:qqtsj � ~ � catkin_ws � :rostopic list /clock /gazebo/link_states /gazebo/model_states /gazebo/parameter_descriptions /gazebo/parameter_updates /gazebo/set_link_state /gazebo/set_model_state /image_view_1581403067208774218/output /image_view_1581403067208774218/parameter_descriptions /image_view_1581403067208774218/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/depth/camera_info /rgbd_camera/depth/image_raw /rgbd_camera/depth/points /rgbd_camera/ir/camera_info /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressed /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressed/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressed/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressedDepth /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressedDepth/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/compressedDepth/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/theora /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/theora/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw/theora/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/rgb/camera_info /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressed /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressed/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressed/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressedDepth /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressedDepth/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/compressedDepth/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/theora /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/theora/parameter_descriptions /rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw/theora/parameter_updates /rgbd_camera/rgb/points /rosout /rosout_agg
我们使用名为image_view的工具来查看3D视觉传感器的图像数据:
*查看RGB原始图像:
$ rosrun image_view image_view image:=/rgbd_camera/rgb/image_raw
*查看IR原始图像:
$rosrun image_view image_view image:=/rgbd_camera/ir/image_raw
*查看深度图像
$rosrun image_view image_view image:=/rgbd_camera/depth/image_raw
如下为以上的截图: