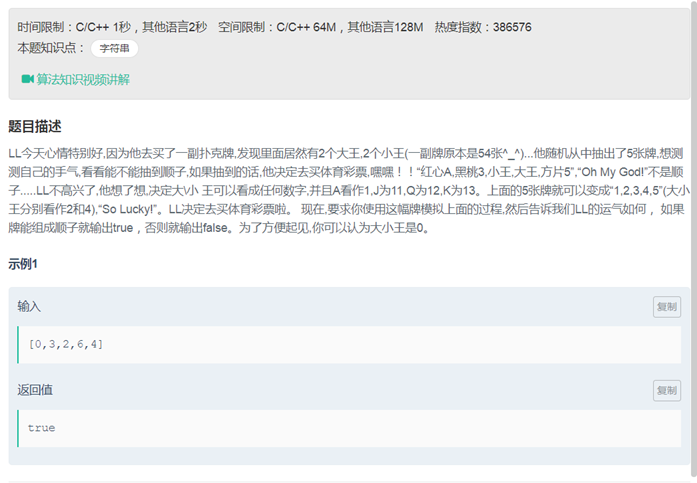
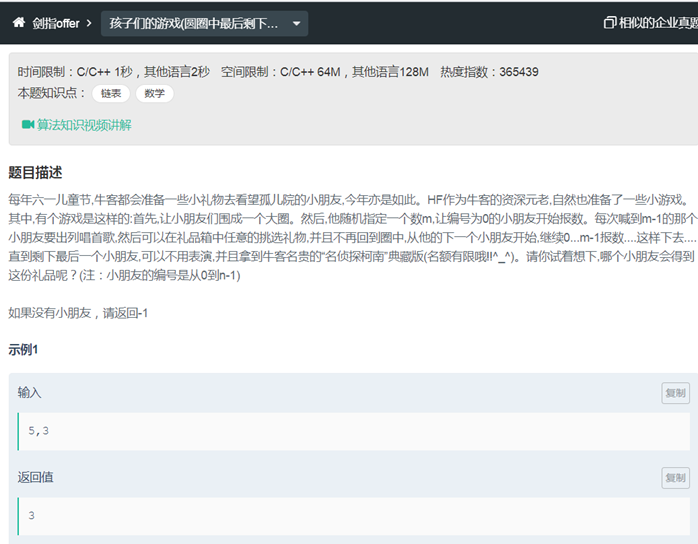
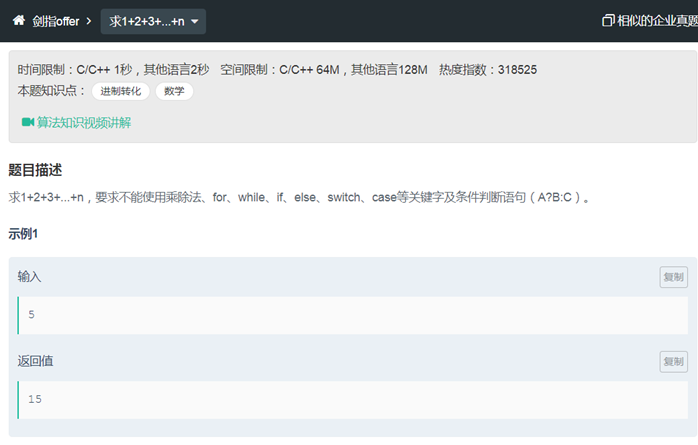
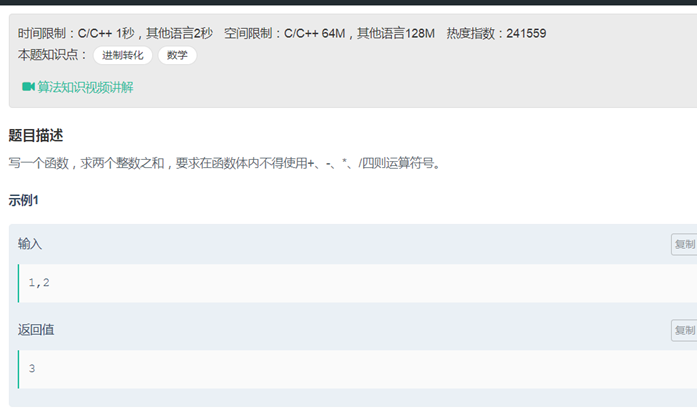
剑指offer记录
如何构造二叉搜索树
需要总结(全排列27/32,回溯,参考下载的ppt;记忆化遍历)
List、set、map、sort、unique、find、lowerBound、swap、remove、resize、count、reverse、find、count、replace、
swap(str[pos],str[i]);
for(auto i:nums) //可以是vector、set
int count = std::count(numbers.begin(),numbers.end(),i);
sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end());
next_permutation全排列;
to_string 数字转字符串;
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
auto it = unique(v.begin(),v.end());
v.erase(it,v.end());
int mark[rows][cols];
memset(mark, -1, sizeof(mark));
char* str = new char[s.length()+1];
strcpy(str,s.c_str());
priority_queue<int>q1;//大顶堆
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>q2;//小顶堆

01二维数组中的查找()
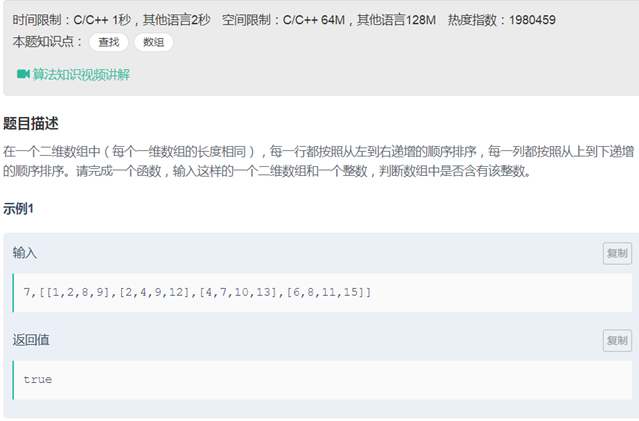

class Solution { public: bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array) { int row = array.size(); int col = array[0].size(); if(row ==0 ) return false; int i = 0; int j = col-1; while(i <= row-1 && j>=0) { if(array[i][j] == target) return true; else if(array[i][j] < target) i++; else j--; } return false; } }; |
02替换空格(换成string 再strcpy)
|
|
class Solution { public: void replaceSpace(char *str,int length) { if(str == NULL) return; //char* start =str; int count =0; while(*str != '�') { if(*str == ' ') count++; str++; } char* p =str; str = str + 2*count;//考虑长度是否足够,指针越界 while(p!=str) { if(*p == ' ') { *str-- = '0'; *str-- = '2'; *str-- = '%'; p--; } else { *str = *p; str--; p--; } }
} }; |
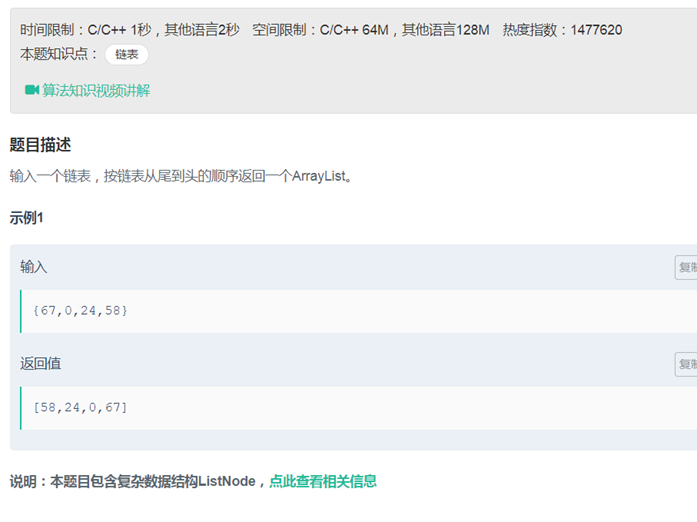
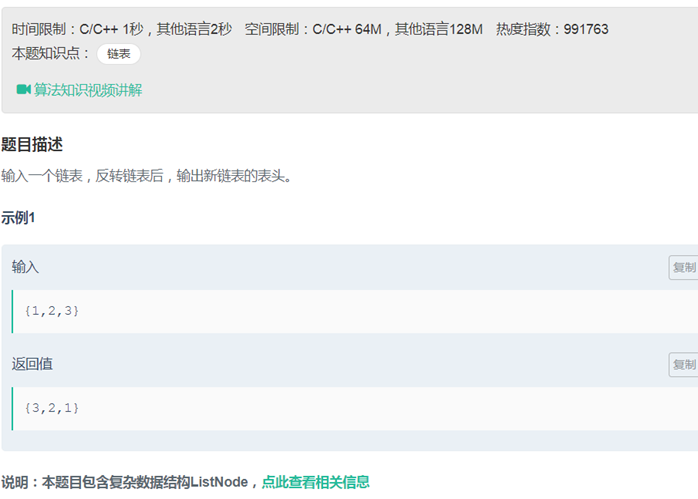
03从尾到头打印链表(递归,或者调用reverse)
|
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : * val(x), next(NULL) { * } * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> a; vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
if(head ==NULL) {
} else{ printListFromTailToHead(head->next); a.push_back(head->val); } return a; } }; |
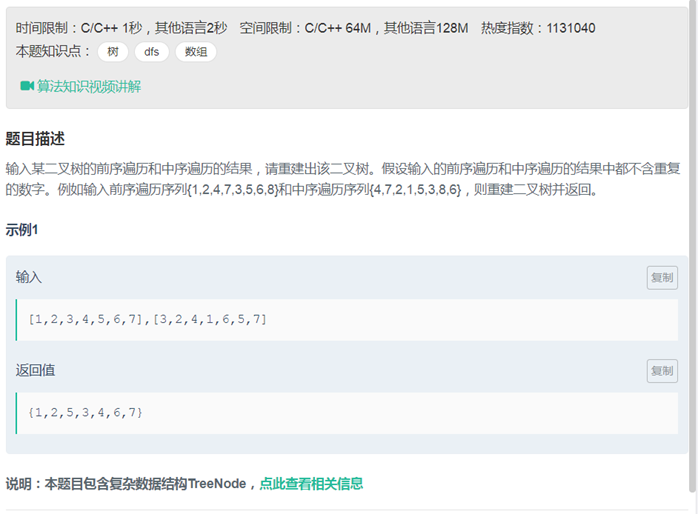
04重建二叉树(std::find 递归)***
|
/** * Definition for binary tree * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre,vector<int> vin) { if(pre.empty()) { return NULL; } auto it=std::find(vin.begin(),vin.begin()+vin.size(),pre.front()); int num = it-vin.begin(); vector<int> vec1(pre.begin()+1,pre.begin()+num+1); vector<int> vec2(vin.begin(),it); vector<int> vec3(pre.begin()+num+1,pre.end()); vector<int> vec4(it+1,vin.end());
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(pre.front()); node->left = reConstructBinaryTree(vec1,vec2); node->right = reConstructBinaryTree(vec3,vec4); return node; } }; |
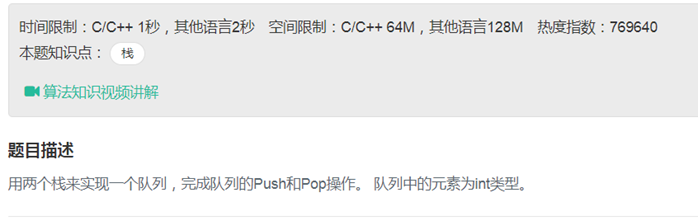
05用两个栈实现队列
|
class Solution { public: void push(int node) { stack1.push(node); }
int pop() { if(stack2.empty()) { if (stack1.empty()) return -1; while(!stack1.empty()) { stack2.push(stack1.top()); stack1.pop(); } int num = stack2.top(); stack2.pop(); return num; } else{ int num = stack2.top(); stack2.pop(); return num; } }
private: stack<int> stack1; stack<int> stack2; }; |
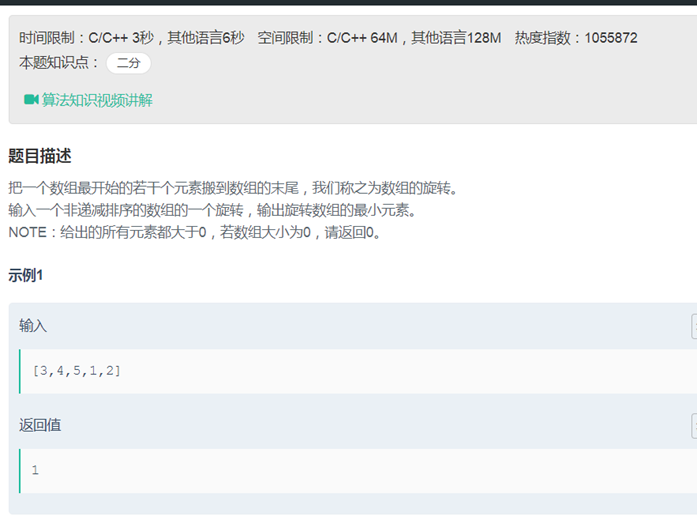
06旋转数组的最小数字(二分)
|
class Solution { public: int minNumberInRotateArray(vector<int> rotateArray) { int count = rotateArray.size(); if (count == 0) return 0; if (count == 1) return rotateArray.at(0); if (count == 2) return(rotateArray.at(0)>=rotateArray.at(1)?rotateArray.at(1):rotateArray.at(0)); //二分法 auto& nums = rotateArray; int first =0; int last = rotateArray.size()-1; // 如果是 1 0 1 1 1, arr[mid] = target = 1, 显然答案在左边 // 如果是 1 1 1 0 1, arr[mid] = target = 1, 显然答案在右边 while(last-first>1) { int mid = first + ((last-first)>>1); if(nums[mid]>nums[last]) { first = mid + 1; } else if(nums[mid]<nums[last]) { last =mid; } else{ last--; } } return(rotateArray.at(first)>=rotateArray.at(last)? rotateArray.at(last):rotateArray.at(first)); // int minnum =rotateArray.at(0); // if(rotateArray.at(count-1)>rotateArray.at(0)) // { // minnum = rotateArray.at(0); // } // int i =0; // for(i =1; i<count;i++) // { // if(rotateArray.at(i-1)>rotateArray.at(i)) // { // minnum =rotateArray.at(i); // break; // } // } // return minnum;
} }; |
07斐波那契数列
|
class Solution { public: int Fibonacci(int n) { if(n == 0) return 0; if(n ==1) return 1; int a =0; int b= 1; int num =0; for(int i =2; i<=n;i++) { num =a+ b; a =b; b =num; } return num;
} }; |
08跳台阶(递归)
|
class Solution { public: int jumpFloor(int number) { if(number == 1) return 1; if(number == 2) return 2; return jumpFloor(number -1)+jumpFloor(number -2); } }; |
09变态跳台阶
|
class Solution { public: int jumpFloorII(int number) { if(number == 1) return 1; if(number == 2) return 1 + 1; int mm =1; for(int i =1;i<number;i++) { mm+=jumpFloorII(i); } return mm; } }; |
int jumpFloorII(int n) { if (n==0 || n==1) return 1; vector f(n+1, 0); f[0] = f[1] = 1; for (int i=2; i<=n; ++i) { for (int j=0; j<i; ++j) { f[i] += f[j]; } } return f[n]; } |
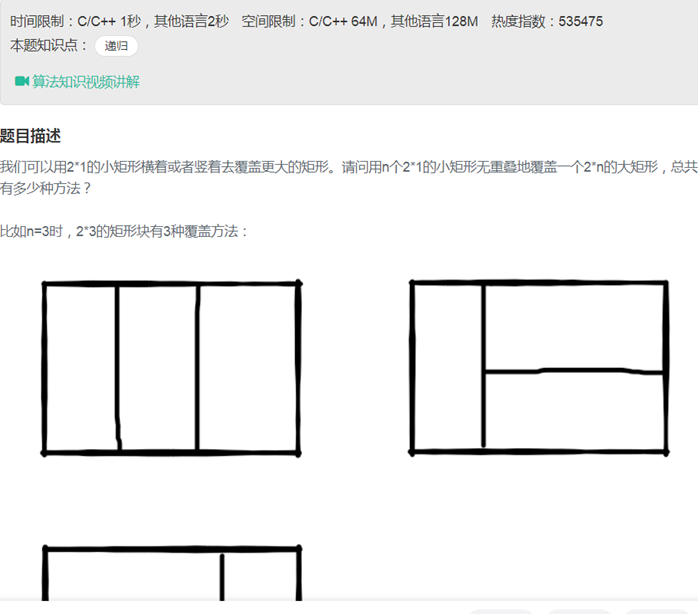
10矩形覆盖(递归)
|
class Solution { public: int rectCover(int number) { if(number == 1 || number == 0) return number; if(number == 2) return 2; int a = 1, b = 2, c; for(int i = 3; i <= number; i++){ c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return c; } }; |
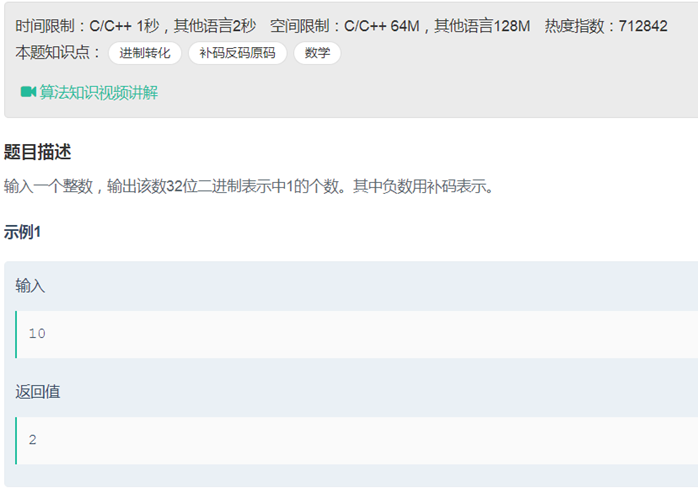
11二进制中1的个数(位运算)
|
class Solution { public: int NumberOf1(int n) { int ans =0; int mark = 1; while(mark) { ans+=(n & mark?1:0); mark<<=1; } return ans; // if( n ==0)return 0; // if(n >0) // { // int i =31; // int num =0; // while(i--) // { // num+= n&1; // n=n>>1; // } // return num; // } // else // { // int i =31; // int num =0; // while(i--) // { // num+= n&1; // n=n>>1; // } // return num+1; // }
} }; |
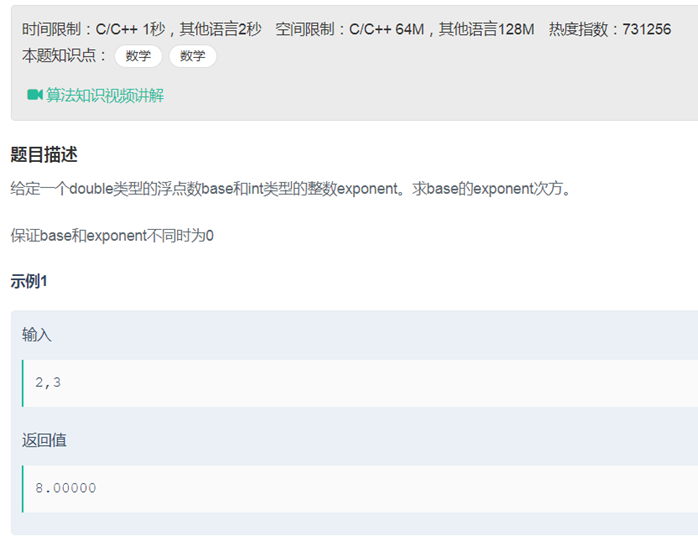
12数值的整数次方(递归)
|
class Solution { public: double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if(exponent <0) { exponent =-exponent; base = 1.0/base; } if(exponent ==0) { return 1; } if(exponent ==1) { return base; }
if(exponent %2 == 0) { return Power(base,exponent/2)*Power(base,exponent/2); } else{ return Power(base,exponent/2)*Power(base,exponent/2)*base; } } }; |
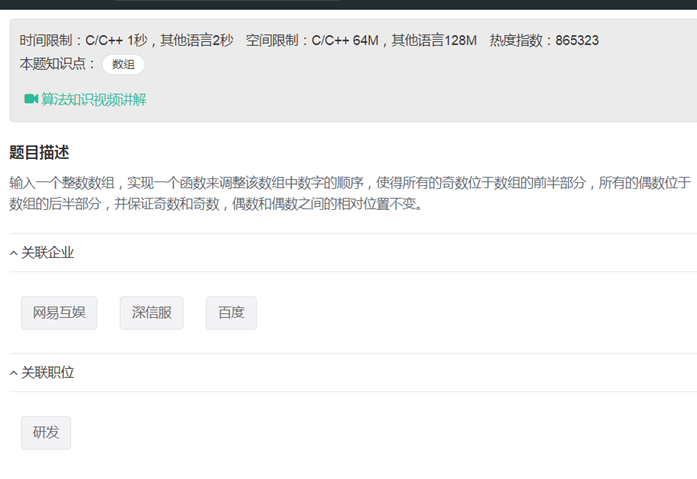
13调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面(双指针或者开辟新的数组)
|
class Solution { public: void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) { int m = array.size(); int k = 0;//记录已经摆好位置的奇数的个数 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { if (array[i] % 2 == 1) { int j = i; while (j > k) {//j >= k+1 int tmp = array[j]; array[j] = array[j-1]; array[j-1] = tmp; j--; } k++; } } } }; |
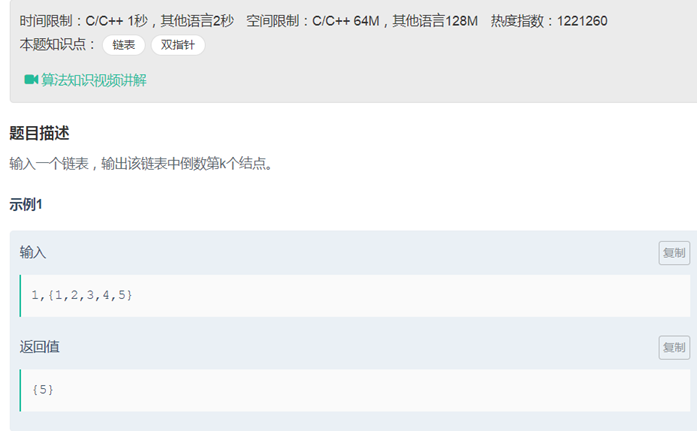
14链表中倒数第k个结点(双指针)
|
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
ListNode *p= pListHead, *q= pListHead; int i=0; while(p!=NULL) { p = p->next; i++; if(i>k) { q = q->next; }
} if(i<k)return NULL; return q; } }; |
15反转链表
|
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(!pHead) return NULL; ListNode* p =pHead,*q=NULL,* temp; while(p)//循环结束时,指针指向哪里 { temp = p->next; p->next = q; q = p; p = temp; } return q; } }; |
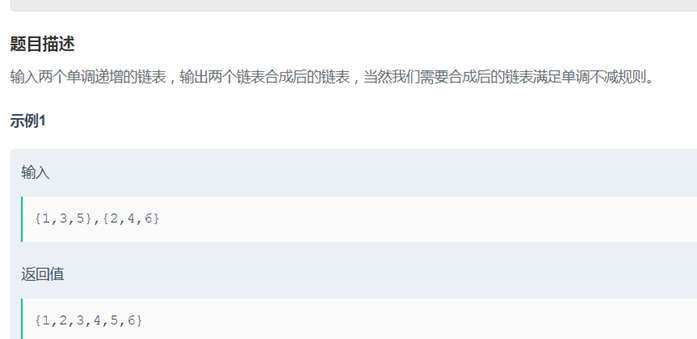
16合并两个排序的链表
|
/*将第二个链表中的元素插入到第一个里面;还可以逐一比较两个链表的头一个元素重建链表更简单 struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ static bool compare(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { if(pHead1->val <= pHead2->val) { return true; } else return false; } class Solution { public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { list<ListNode*>ls; while(pHead1) { ls.push_back(pHead1); pHead1 = pHead1->next; } while(pHead2) { ls.push_back(pHead2); pHead2 = pHead2->next; } ls.sort(compare); pHead1 = ls.front(); ls.pop_front(); pHead2 = pHead1; while(!ls.empty()) { pHead2->next=ls.front(); pHead2 = pHead2->next; ls.pop_front(); } pHead2->next=NULL;//一定要加上这一句,不然链表就可能有环 return pHead1; // ListNode* p= pHead1,*q =pHead2,*temp;
// while(q) // { // while(1) // { // if(q->val<p->val) // { // temp = q; // q=q->next; // temp->next = p; // p = temp; // break; // } // else if( p->next && q->val>=p->val && q->val<=p->next->val) // { // temp = q; // q=q->next; // temp->next = p->next; // p->next = temp; // p = temp; // break;
// } // else if(!p->next && q->val>=p->val) // { // temp = q; // q=q->next; // temp->next = p->next; // p->next = temp; // p = temp; // break; // } // else{ // p=p->next; // } // }
// } // return pHead1; } }; |
class Solution { public: ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { if(pHead1==nullptr)return pHead2; if(pHead2==nullptr)return pHead1; ListNode* pHead=nullptr; if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){ pHead=pHead1; pHead1=pHead1->next; }else{ pHead=pHead2; pHead2=pHead2->next; } ListNode* cur=pHead; while(pHead1!=nullptr && pHead2!=nullptr){ if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){ cur->next=pHead1; pHead1=pHead1->next; }else{ cur->next=pHead2; pHead2=pHead2->next; } cur=cur->next; } while(pHead1!=nullptr){ cur->next=pHead1; pHead1=pHead1->next; cur=cur->next; } while(pHead2!=nullptr){ cur->next=pHead2; pHead2=pHead2->next; cur=cur->next; } return pHead; } }; |
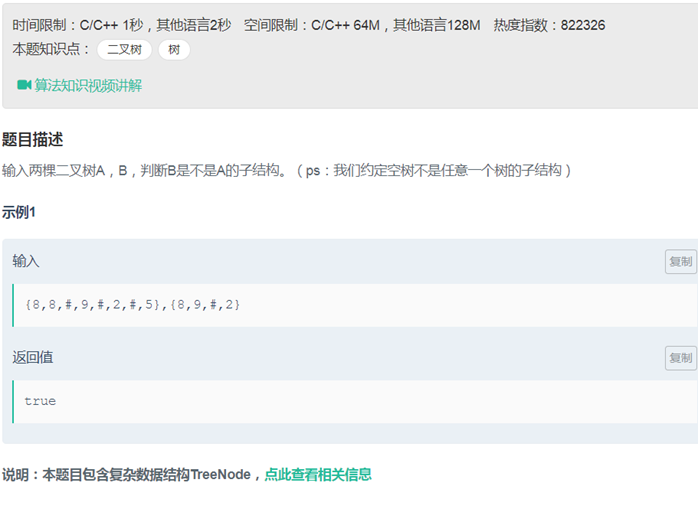
17树的子结构
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) { bool has = false; if(pRoot2 == NULL)//不写这个就会提示段错误!!!uuuups return false; dfs(pRoot1,pRoot2,has); return has; } void dfs(TreeNode* node,TreeNode* pRoot2,bool& has) { if (node == NULL){ return; } if(node->val == pRoot2->val) { has = has || isEqual(node,pRoot2); if(has) return; } dfs(node->left,pRoot2,has); if(has) return; dfs(node->right,pRoot2,has); } bool isEqual(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) { if(pRoot2 == NULL) return true; if(pRoot1 == NULL) return false; return pRoot1->val == pRoot2->val && isEqual(pRoot1->left, pRoot2->left)&& isEqual(pRoot1->right, pRoot2->right); } }; |
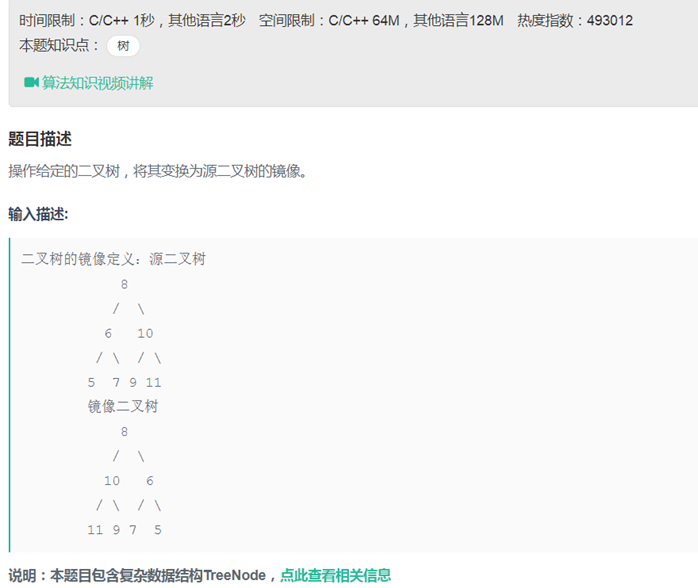
18二叉树的镜像(递归)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: void Mirror(TreeNode *pRoot) { if(pRoot == NULL)return; TreeNode *temp=pRoot->left; pRoot->left=pRoot->right; pRoot->right = temp; Mirror(pRoot->left); Mirror(pRoot->right); } }; |
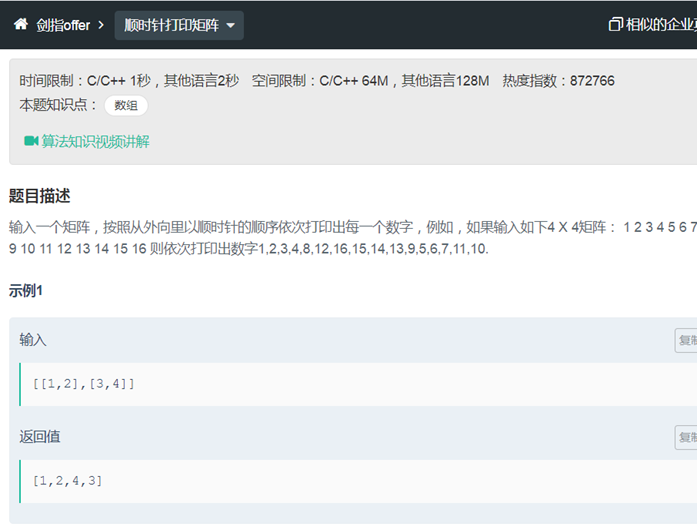
19顺时针打印矩阵
|
class Solution { public: // 1 2 3 4 // 5 6 7 8 // 9 10 11 12 // 13 14 15 16 vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) { vector<int> res; if (matrix.empty()) return res; int rows =matrix.size(); int cols = matrix.at(0).size(); // bool isodd = false; // if(rows%2 == 1) // isodd = true; //只有一行 if(rows == 1) { for(int j =0;j<cols;j++ ) res.push_back(matrix[0][j]); return res; } if(cols == 1) { for(int j =0;j<rows;j++ ) res.push_back(matrix[j][0]); return res; } int cc= min(cols,rows)/2; int up ; int down ; int left ; int right ; for(int i=0; i<cc;i++) { up = i; down = rows -up-1; left = up; right = cols -left-1; for(int j= left; j<right; j++) { res.push_back(matrix[up][j]); } for(int j= up; j<down; j++) { res.push_back(matrix[j][right]); } for(int j= right; j>left; j--) { res.push_back(matrix[down][j]); } for(int j= down; j>up; j--) { res.push_back(matrix[j][left]); } } if(down-up == 1 || right-left ==1 ) return res; if(down-up == 2)//还有横着的一行 { for(int j =left+1;j<right;j++ ) { res.push_back(matrix[up+1][j]); } return res; } else{//还有竖着的一列 for(int j =up+1;j<down;j++ ) { res.push_back(matrix[j][left+1]); } return res; } /*不一定是正方形 int cc= rows/2; for(int i=0; i<cc;i++) { int up = i; int down = rows -up-1; int left = up; int right = rows -up-1; for(int j= left; j<=right; j++) { res.push_back(matrix[up][j]); } for(int j= up; j<=down; j++) { res.push_back(matrix[j][right]); } for(int j= right; j>=left; j--) { res.push_back(matrix[j][down]); } for(int j= down; j>=up; j++) { res.push_back(matrix[j][left]); } } if(rows%2 == 1) res.push_back(matrix[rows%2][rows%2]); return res; */ /* int left =0-1; int right= cols; int up = 0-1; int down = rows; // enum Car {PORSCHE, FERRARI, JAGUAR}; //enum D {UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT} ; enum Dir {U, D, L, R}; Dir dir =R; int i=0,j=0;//试探标记 while(1) { if(dir == R) { if(j<right) { res.push_back(matrix.at(i).at(j)); j++;//试探 } else { j--; i++; dir = D; up++; if(i == down)//到达下边界 break; } } else if (dir == D) { if(i<down) { res.push_back(matrix.at(i).at(j)); i++; } else { i--; j--; dir = L; right--; if(j == left)//到达边界 break; } } else if (dir == L) { if(j>left) { res.push_back(matrix.at(i).at(j)); j--; } else { j++; i--;
dir = U; down--; if(i == up)//到达边界 break; } } else if (dir == U) { if(i>up) { res.push_back(matrix.at(i).at(j)); i--; } else { i++; j++; dir = R; left++; if(j == right)//到达边界 break; } } } return res; */ } };
|
20包含min函数的栈
|
class Solution { public: void push(int value) { s.push(value); if(smin.empty()) { smin.push(value); } else if(value <=smin.top()) { smin.push(value); } } void pop() { if(s.top()==smin.top()) smin.pop(); s.pop();
} int top() { return s.top(); } int min() { return smin.top(); } private : stack<int> s; stack<int> smin; }; |
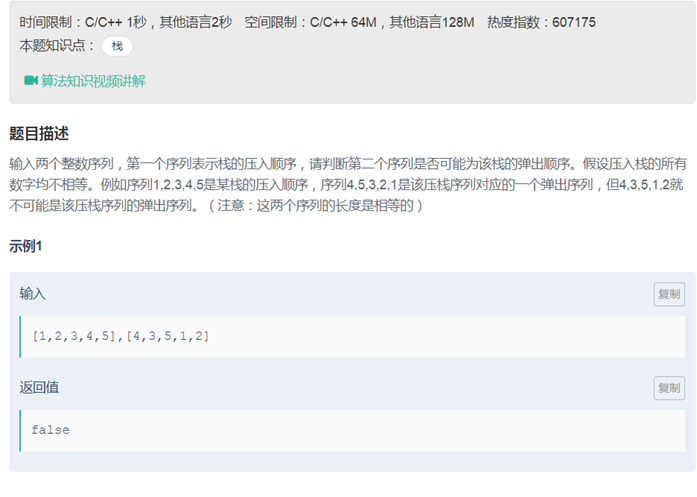
21栈的压入、弹出序列
|
class Solution { public: bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) { int m=pushV.size(); int n=popV.size(); int i=0; int j=0; if(m == 0) { return false; } for(;i<m;i++) { s.push(pushV.at(i)); while(!s.empty() && s.top() == popV.at(j))//注意j的范围 { s.pop(); j++; } } return s.empty(); } private: stack<int> s; }; |
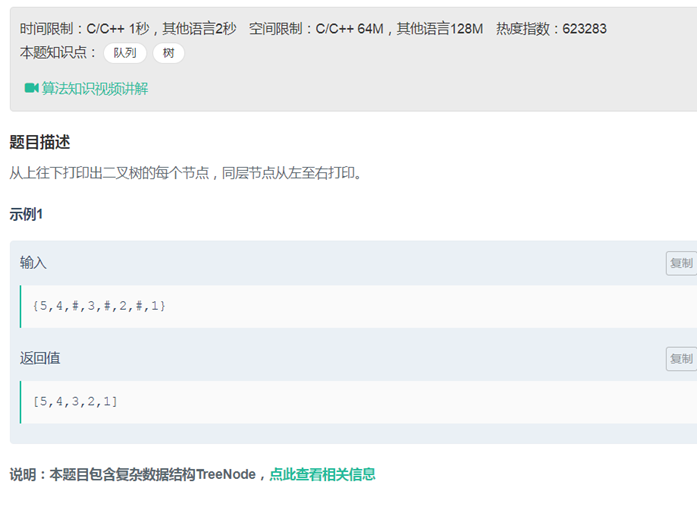
22从上往下打印二叉树(层序遍历)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: vector<int> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) { queue <TreeNode*>q; vector<int> vec; if(root == NULL) return vec; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()) { TreeNode * temp = q.front(); q.pop(); vec.push_back(temp->val); if(temp->left) q.push(temp->left); if(temp->right) q.push(temp->right); } return vec; } private: }; |
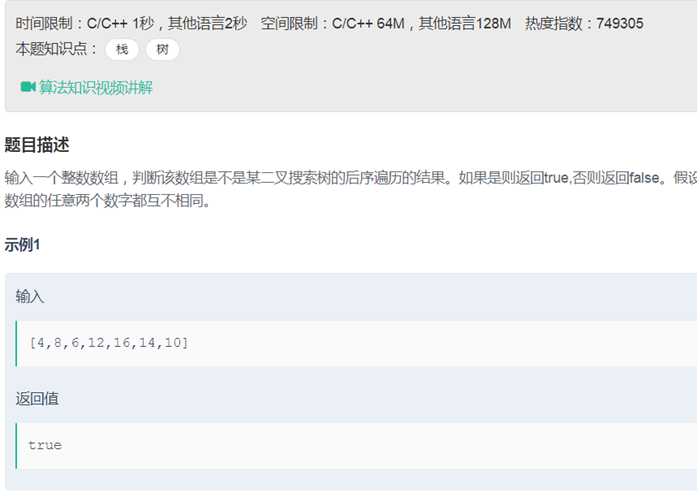
23二叉树的后序遍历序列(分治法 递归)
|
class Solution { public: bool VerifySquenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) { if(sequence.empty()) return false; int size = sequence.size(); return verify(sequence, 0, size-1); } bool verify(vector<int>& sequence,int start,int end) { if(start >= end) return true; int key = sequence[end]; int i; for(i = start; i<=end-1; i++) { if(sequence[i]>key) break; } int ind = i; for(; i<=end-1; i++) { if(sequence[i]<key) return false; } return verify(sequence, start, ind-1)&&verify(sequence, ind, end-1); } }; |
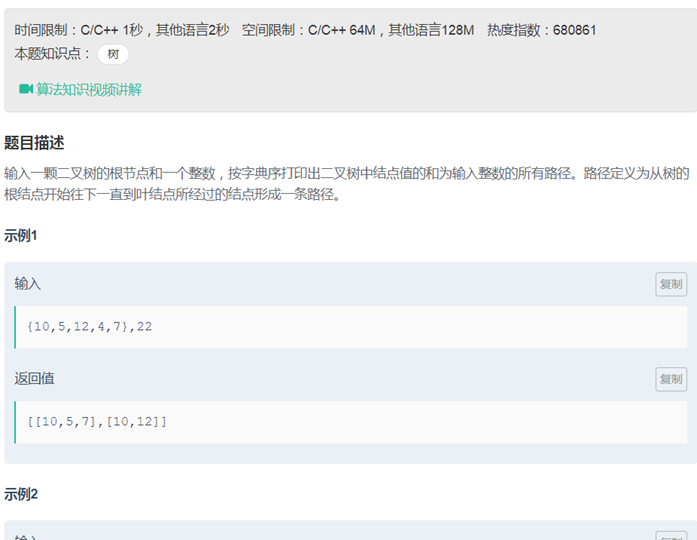
24二叉树中和为某一值的路径(记忆化dfs)
|
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> >res; vector<int> path; void find(TreeNode * root, int sum) { if(root == NULL) return; path.push_back(root->val); if(sum == root->val&&!root->left && !root->right) res.push_back(path); else{ if(root->left) find(root->left,sum-root->val); if(root->right) find(root->right,sum-root->val); } path.pop_back(); } vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) { find(root,expectNumber); return res; } }; |
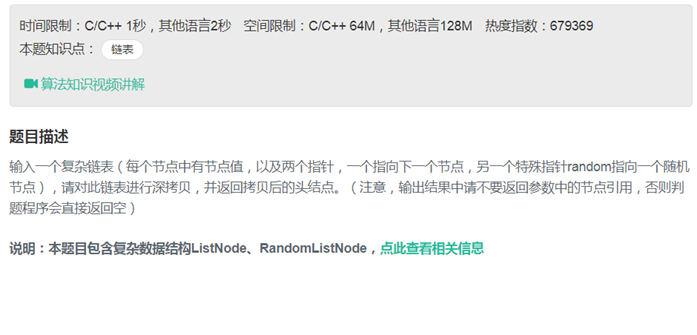
25复杂链表的复制
|
/* struct RandomListNode { int label; struct RandomListNode *next, *random; RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead) { if(pHead == NULL) return NULL; RandomListNode* p =pHead; while(p) { RandomListNode* temp = new RandomListNode(p->label); temp->next = p->next; p->next =temp; p=temp->next; } p=pHead; while(p) { if(p->random) p->next->random = p->random->next; p = p->next->next; } p = pHead; RandomListNode * res = pHead->next; while(p) { RandomListNode * temp = p->next->next; RandomListNode * temp2 = p->next; p->next = temp; if(temp) temp2->next =temp->next; p=temp; } return res; } }; |
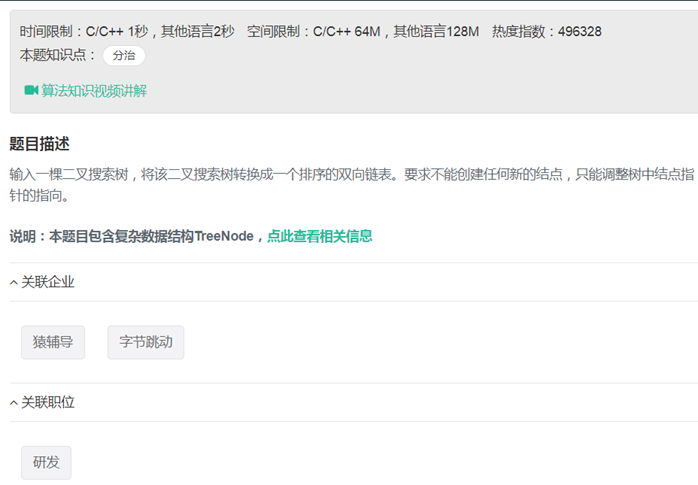
26二叉搜索树与双向链表(分治法 递归)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: TreeNode* head; TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode*& node = pRootOfTree; if(node == NULL) return node; traverse(node); return head; // TreeNode *node1; // TreeNode *node2; // serial(node, node1, node2); // return node1; } void traverse(TreeNode* node) { static int num = 0; static TreeNode* last = NULL; if(node == NULL) return; traverse(node->left); num++; if(num==1) { last = node; head = node; } else{ last->right = node; node->left=last; last = node; } traverse(node->right); } /* void serial(TreeNode* node,TreeNode*& node1,TreeNode*& node2)//返回tail { // if(node->left == NULL &&) TreeNode* head ; TreeNode* tail ; if(node->left) { serial(node->left,head,tail); tail->right = node; node->left=tail; } else{ head=node; } node1 = head; if(node->right) { serial(node->right,head,tail); node->right=head; head->left=node; node2 = tail; } else{ node2=node; } } */
}; |
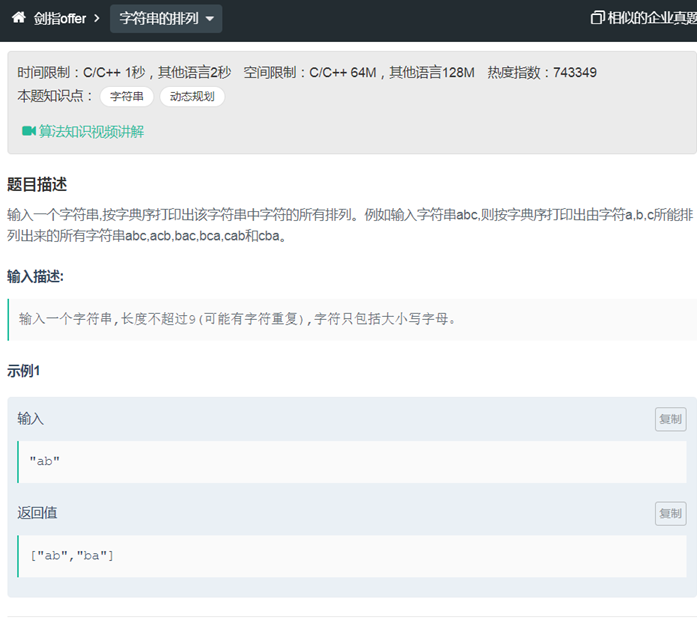
27字符串的排列(递归,dfs)
|
class Solution { public: vector<string> Permutation(string str) { size = str.length(); vector<string> res; if(size == 0) { return res; } dfs(str,0); return vector<string>(ans.begin(),ans.end()); } void dfs(string str,int pos) { if(pos == size-1) { ans.insert(str); } for(int i=pos; i<size;i++) { swap(str[pos],str[i]); dfs(str,pos+1); swap(str[pos],str[i]);//交换回来 } } set<string> ans; int size; }; |
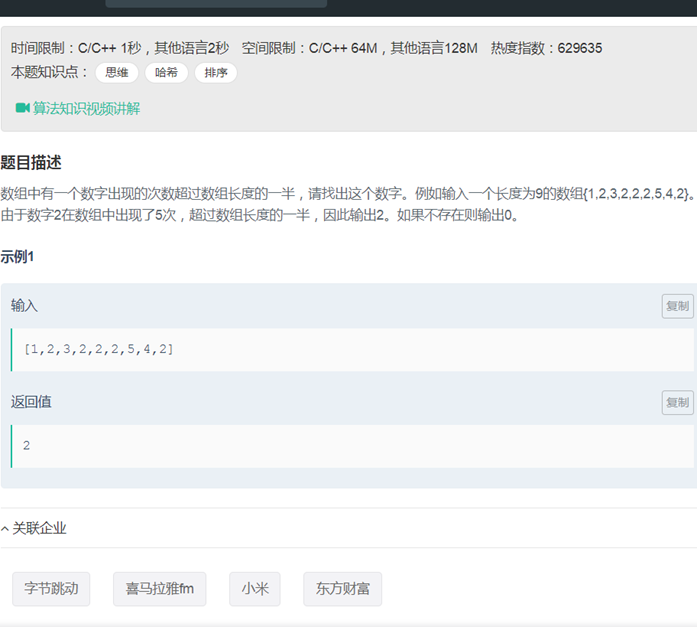
28数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
|
class Solution { public: int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { // vector<int> numbers2; sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); // numbers2 = numbers; // unique(numbers) set<int> nums(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); // for(set<int>::iterator i=nums.begin();i!=nums.end();i++) for(auto i:nums) { int count = std::count(numbers.begin(),numbers.end(),i); if(count>numbers.size()/2) return i; } return 0; } }; |
class Solution { public: int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); int mid = numbers.size()/2; int target = numbers.at(mid); int count =0; for(auto k:numbers) { if(k == target) count++; } if(count>numbers.size()/2) return target; else return 0; } }; |
class Solution { public: int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) { // 这道题,最直白的解法是使用一个 map 来记录各个数字出现的次数,最后取出现次数最多的作为解。但这个方法需要消耗额外的空间,不是最优。下面是最优解法: // 我们做这样的想象,现在有来自不同阵营的多支部队,他们互为敌人。每个士兵都容不得敌人,宁愿与敌人同归于尽。可以想象,如果某个阵营的士兵数量超过所有阵营士兵总数的一半,该阵营士兵一换一带走一个其他阵营的,最终剩下的就是该阵营的士兵了,该阵营就获胜了。 // 这和本题有什么关系呢?且看下面的故事:// 现在要打仗了,所有士兵依次进入战场,如果战场上有其他阵营的士兵,他就与其中一个同归于尽。否则,他就留在战场上。容易想象,战场上要么没有人,要么是同一阵营的。所有士兵都进入战场后,最终战场上剩下的只会是同一阵营的,而该阵营就是人数过半的那个。 // 我们要模拟这个过程,找到那个获胜的阵营。数组中每个元素就是士兵,元素的值,就是这个士兵所属阵营。 int win; int count=0; for(auto k:numbers) { if(count == 0) { win = k; count++; } else{ if(k == win) count++; else count--; } } count=0; for(auto k:numbers) { if(k== win) count++; } if(count>numbers.size()/2) return win; else return 0;
/* sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); int mid = numbers.size()/2; int target = numbers.at(mid); int count =0; for(auto k:numbers) { if(k == target) count++; } if(count>numbers.size()/2) return target; else return 0;*/ } }; |
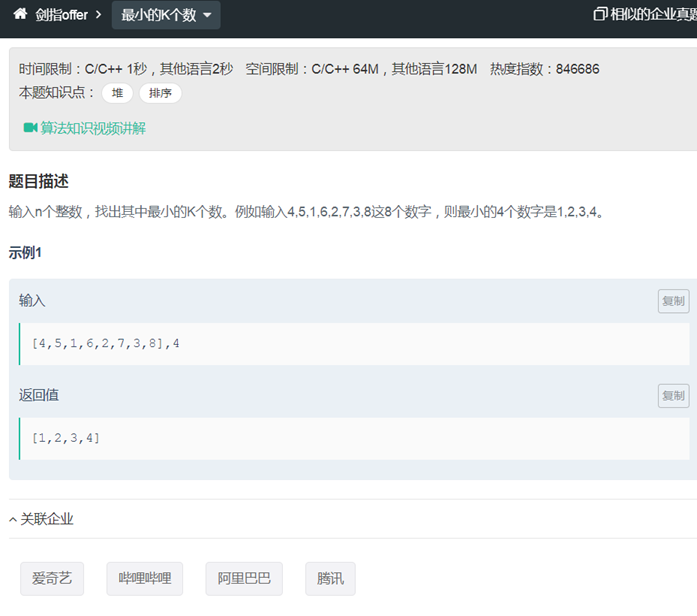
29最小的k个数(大顶堆priority_queue)
|
class Solution { public: vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) { priority_queue<int> res; int size = input.size(); vector<int> ans; if(input.empty()) return ans; if(k>size) return ans; if(k<=0) return ans; for(auto i:input) { if(res.size()<k) { res.push(i); } else if(res.top()>i) { res.pop(); res.push(i); } } while(!res.empty()) { ans.push_back(res.top()); res.pop(); } reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end()); return ans; } }; |
class Solution { public: vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) { vector<int> ret; if (k==0 || k>input.size()) return ret; sort(input.begin(), input.end()); return vector<int>({input.begin(), input.begin()+k}); } }; |
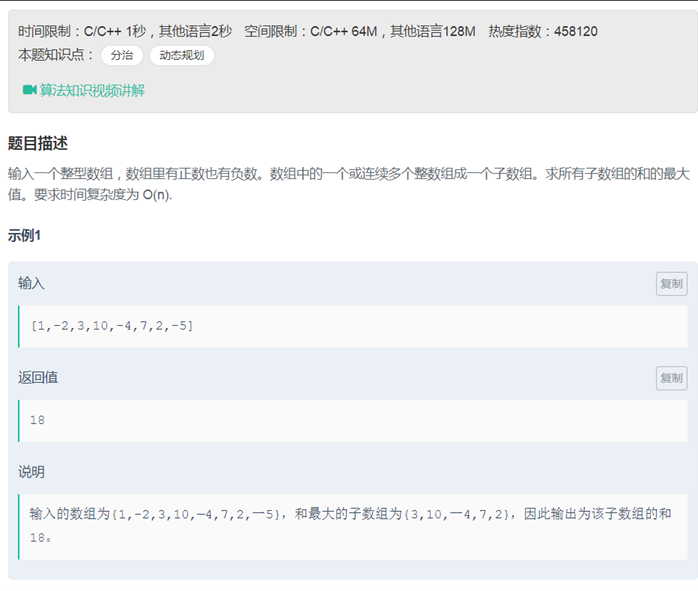
30连续子数组的最大和
|
class Solution { public: int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector<int> array) { int ans=array[0]; vector<int> vec(array.size(),0); if(array.empty()) return 0; if(array.size() == 1) return ans; vec[0]=ans; for(int i=1; i<array.size();i++) { vec[i]=max(array[i],array[i]+vec[i-1]); ans = max(ans,vec[i]); } return ans; } }; |
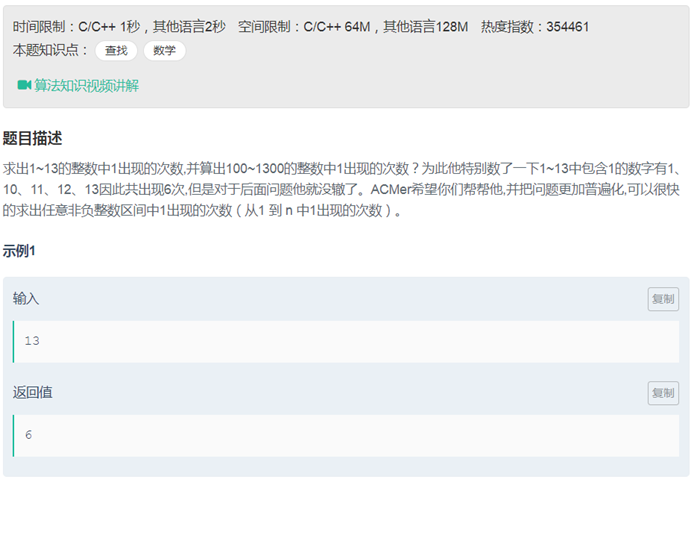
31整数中1出现的次数
|
class Solution { public: int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) { int ans=0; for(int i =1;i<=n;i++) { int j = i; while(j>0) { if(j%10 == 1) ans++; j=j/10; } } return ans; } }; |
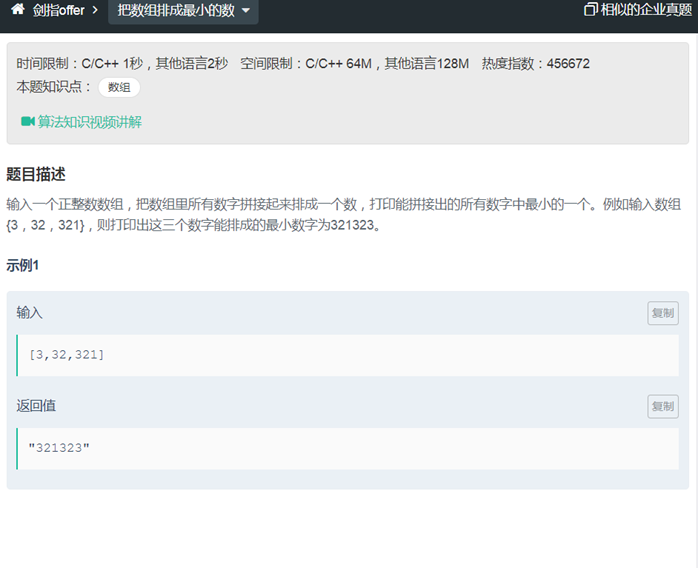
32把数组排成最小的数(全排列next_permutation)
|
class Solution { public: string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) { vector<string> vec; for(auto k:numbers) { vec.push_back(to_string(k)); } sort(vec.begin(),vec.end()); string ans=""; for(auto k:vec) { ans+=k; } do{ string temp=""; for(auto k:vec) { temp+=k; } ans = min(ans,temp); }while(next_permutation(vec.begin(), vec.end())); return ans; } }; |
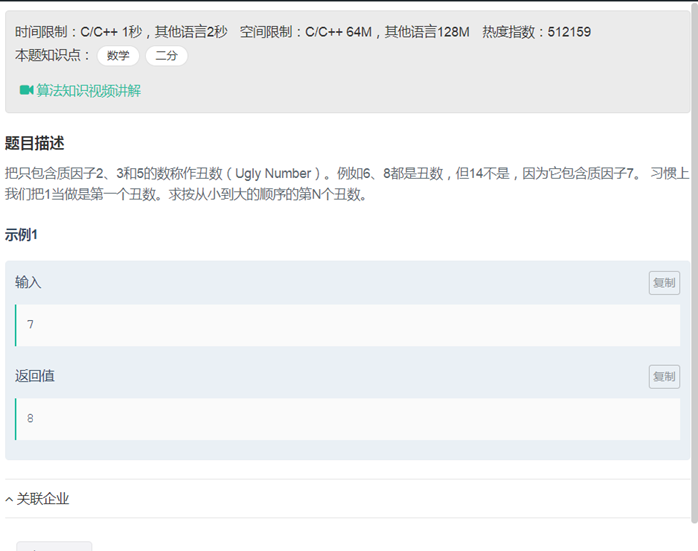
33丑数***(没有搞懂)
|
public class Solution { public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) { if(index <= 0)return 0; int p2=0,p3=0,p5=0;//初始化三个指向三个潜在成为最小丑数的位置 int[] result = new int[index]; result[0] = 1;// for(int i=1; i < index; i++){ result[i] = Math.min(result[p2]*2, Math.min(result[p3]*3, result[p5]*5)); if(result[i] == result[p2]*2)p2++;//为了防止重复需要三个if都能够走到 if(result[i] == result[p3]*3)p3++;//为了防止重复需要三个if都能够走到 if(result[i] == result[p5]*5)p5++;//为了防止重复需要三个if都能够走到
} return result[index-1]; } } |
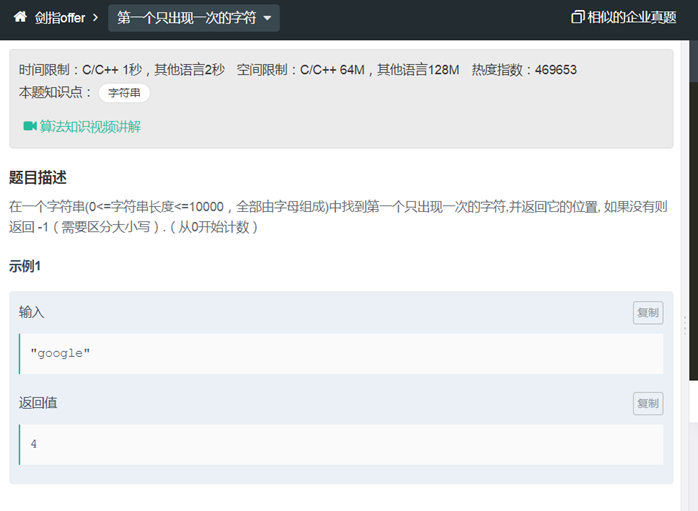
34第一个只出现一次的字符位置(map)
|
class Solution { public: int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) { map<char,int>mp; map<char,int>index; for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++) {
mp[str[i]] = mp[str[i]] +1; if(mp[str[i]]==1) { index[str[i]]=i; } } // int ans =0; int res=-1; for(auto i:mp) { if(i.second == 1) { static int ans = index[i.first]; ans = min(ans,index[i.first]) ; res = ans; } } return res; } }; |
class Solution { public: int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) { vector<char> vec; map<char,int>mp; int len = str.length(); if(len<1) return -1; // str.at(i) for(int i=0; i<len; i++) { vec.push_back(str.at(i)); mp[str.at(i)]=mp[str.at(i)]+1; } for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++) { if(mp[vec.at(i)]==1) return i; } return -1; } }; |
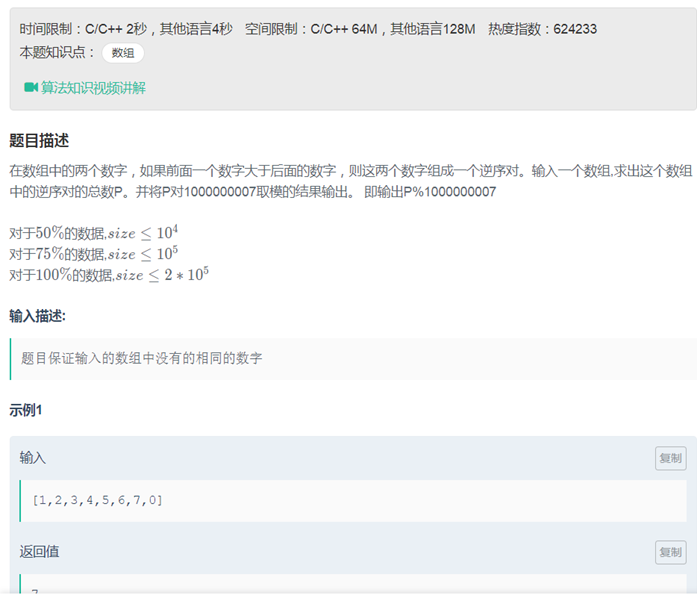
35数组的逆序对(递归 归并排序)
|
class Solution { public: int InversePairs(vector<int> data) { count = 0; if(data.size()<2) return count; divide(data,0,data.size()-1); return (count%1000000007);//这里count会越过最大值!!! } //每一次递归返回的都是合并后的数组 private: void divide(vector<int> &data,int start,int end) { if(start >=end) return; int mid =start +((end-start)>>1); divide(data,start,mid); divide(data,mid+1,end);//不写加一会有无限循环2 5 3 merge(data,start,mid,end); } void merge(vector<int> &data,int start,int mid,int end) { vector<int> temp=vector<int>(data.begin()+start,data.begin()+end+1);//这里一定要加上一 int i = start; int j= mid+1; int ind =0; while(i<=mid && j<=end) { if(data[i]>data[j]) { // count=(mid-i+1) + count%1000000007;//不能写成 count=(mid-i+1) + count; temp[ind]=data[j]; j++; ind++; } else { temp[ind]=data[i];//不存在以data[i]开头的逆序对 i++; ind++; } } //剩下的都是较大的数,直接拷贝到temp while(i<=mid) temp[ind++]=data[i++]; while(j<=end) temp[ind++]=data[j++]; //合并后的数组 for(int k=0;k<temp.size();k++) { data[start+k]=temp[k]; } } private: int long long count;//改成long long 之后就可以了; }; |
public class Solution { //统计逆序对的个数 int cnt; public int InversePairs(int [] array) { if(array.length != 0){ divide(array,0,array.length-1); } return cnt; }
//归并排序的分治---分 private void divide(int[] arr,int start,int end){ //递归的终止条件 if(start >= end) return; //计算中间值,注意溢出 int mid = start + (end - start)/2;
//递归分 divide(arr,start,mid); divide(arr,mid+1,end);
//治 merge(arr,start,mid,end); }
private void merge(int[] arr,int start,int mid,int end){ int[] temp = new int[end-start+1];
//存一下变量 int i=start,j=mid+1,k=0; //下面就开始两两进行比较,若前面的数大于后面的数,就构成逆序对 while(i<=mid && j<=end){ //若前面小于后面,直接存进去,并且移动前面数所在的数组的指针即可 if(arr[i] <= arr[j]){ temp[k++] = arr[i++]; }else{ temp[k++] = arr[j++]; //a[i]>a[j]了,那么这一次,从a[i]开始到a[mid]必定都是大于这个a[j]的,因为此时分治的两边已经是各自有序了 cnt = (cnt+mid-i+1)%1000000007; } } //各自还有剩余的没比完,直接赋值即可 while(i<=mid) temp[k++] = arr[i++]; while(j<=end) temp[k++] = arr[j++]; //覆盖原数组 for (k = 0; k < temp.length; k++) arr[start + k] = temp[k]; } } |
36两个链表的第一个公共节点
|
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { ListNode* node=NULL; if(pHead1== NULL)return node; if(pHead2== NULL)return node; ListNode* p1=pHead1; ListNode* p2=pHead2; while(!(p1==NULL||p2==NULL)) { p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next; } if(p1==NULL)//p1指向短一些的链表 { p1=pHead2; while(p2) { p2=p2->next; p1=p1->next; } p2=pHead1; } else{ // p2=p1; // p1=NULL; p2=pHead1; while(p1) { p2=p2->next; p1=p1->next; } p1=pHead2; } while(p2) { if(p1==p2) return p1; p2=p2->next; p1=p1->next; } return node; } }; |
37数字在升序数组中出现的次数(二分查找)
|
class Solution { public: int GetNumberOfK(vector<int> data ,int k) { ////方法1 // auto it1 = lower_bound(data.begin(), data.end(), k); // if(it1 == data.end()) // return 0; // auto it2 = upper_bound( data.begin(), data.end(), k); // return it2-it1; ////方法2 // if(data.size() == 0) // return 0; // if(data.size() == 1) // return data[0]==k?1:0; // int left= 0; // int right =data.size()-1; // int ind =-1; // while(left < right) // { // int mid = (left + right)/2; // if(data[mid] >k) // right =mid-1; // else if(data[mid] <k) // left =mid+1; // else // { // ind = mid; // break; // } // } // if(left>=right) // return 0; // left =ind; // while(left >=0 && data[left] == k) // left--; // left++; // right =ind; // while(right <=data.size()-1 && data[right] == k) // right++; // right--; // return right-left+1; //方法3 if(data.size() == 0) return 0; if(data.size() == 1) return data[0]==k?1:0; int num =data.size(); int left=0; int right =num-1;
while(left<right) { int mid = (right + left)/2; if(data[mid] >=k) right = mid; else left = mid+1; } if(data[right] != k) return 0; int ind_left = left;
left = 0; right =num-1; while(left < right) { int mid =left+(right-left+1)/2; if(data[mid]<=k) left = mid; else right =mid -1; // if(right -left ==1) // break; } int ind_right =right; return ind_right-ind_left+1;
} }; |
38二叉树的深度(分治法 dfs回溯)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot) { //method 1 // if(!pRoot) // return 0; // int n1=TreeDepth( pRoot->left); // int n2=TreeDepth( pRoot->right); // return 1+(n1>n2?n1:n2);
//method 2 // if(!pRoot) // return 0; // int n=0; // int max=0; // travel(pRoot,n,max); // return max; //method 3 int n =0; travel(pRoot,n); return n; } //method 2 // void travel(TreeNode* node,int & n,int & max) // { // if(!node) // { // return; // } // n++; // if(n>max) // max =n; // travel(node->left,n,max); // travel(node->right,n,max); // n--; // } //method 3 void travel(TreeNode *node,int & depth) { if(!node) { return; } int num1 =0; int num2 =0; travel(node->left, num1); travel(node->right,num2); depth = (num1>num2?num1:num2)+1;
} }; |
39平衡二叉树(dfs后序遍历 剪枝)
|
class Solution { public: bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot) {
int num = dfs(pRoot); if(num<0) return false; return true; } int dfs(TreeNode* pRoot) { if(pRoot == NULL) return 0; int num1 = dfs(pRoot->left); if(num1<0) return -1; int num2 = dfs(pRoot->right); if(num2<0) return -1; if(num1 == num2||abs(num1-num2)==1) return max(num1,num2)+1; else return -1; } }; |
40数组中只出现一次的数字(哈希表set或者map)
|
class Solution { public: void FindNumsAppearOnce(vector<int> data,int* num1,int *num2) { set<int>ans; // ans.clear() for(auto k:data) { if(ans.count(k)==0) ans.insert(k); else ans.erase(k); } int a[]={0,0}; int i=0; for(auto k:ans) { a[i++]=k; } *num1 = a[0]; *num2 = a[1]; } }; |
class Solution { public: void FindNumsAppearOnce(vector<int> data,int* num1,int *num2) { std::map<int,int> m; int size=data.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) { int num = data[i]; m[num] = m[num] + 1; if(m.at(num)== 2) m.erase(num); } map<int,int>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); *num1 = it->first; map<int,int>::const_reverse_iterator it2=m.crbegin(); *num2 = it2->first; } }; |
41和为s的连续正数序列(双指针 双下标 滑动窗口)
|
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) { vector<vector<int> >ans; if(sum <2) return ans; int mid = sum%2 == 1? sum/2:sum/2-1; int start =1; int end =1; int temp =1; while(start<=mid) { while( 1) { // temp = (start+end)*(end-start+1)/2; if(temp > sum) break; if(sum == temp) { bingo(ans,start,end); break; } end++; temp+=end; } temp-=start; start++; } return ans; } void bingo(vector<vector<int> >& ans,int start,int end) { vector<int>temp; for(int i=start;i<=end;i++) temp.push_back(i); ans.push_back(temp); } }; |
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) { vector<vector<int> > res; int left=1; int right = 1; for(left = 1; left <=sum/2; left++) { int total = 0; total+=left; right = left; while(total<sum) { right=right+1; total+=right; } if(total == sum) { vector<int> ans; for(int t=left; t<=right; t++) { ans.push_back(t); } res.push_back(ans); } } return res; } }; |
42 和为s的两个数字(双指针 双指针+二分查找 和前一题不一样)
|
class Solution { public: vector<int> FindNumbersWithSum(vector<int> array,int sum) { vector<int> ans; if(array.empty()) return ans; int min; int max; int mul; bool found =false; int i=0; int j=array.size()-1; while(i<array.size()-1) { while(j>i) { int temp = array[i]+array[j]; if(temp==sum) { if(found == false) { min = array[i]; max =array[j]; mul = min*max; found = true; } else if(array[i]*array[j]<mul){ min = array[i]; max =array[j]; mul = min*max; } break; } if(temp<sum) { break; } j--; } i++; } if(found) { ans.push_back(min); ans.push_back(max); return ans; } return ans; } }; |
43左旋转字符串(string::substr)
|
class Solution { public: string LeftRotateString(string str, int n) { int size = str.length(); if(size == 0) return str; if(n == 0) return str; if(n>size)n=n%size; if(n == 0) return str; return str.substr(n)+str.substr(0,n); } }; |
444 |
44翻转单词顺序
|
class Solution { public: string ReverseSentence(string str) { //假设不会有连续的 空格 int size = str.length(); vector<string> res; int i=-1; int j =0; // str.npos if(str.find(' ') == str.npos) return str; while(str.find(' ',1+i) != str.npos ) { j = str.find(' ',1+i); res.push_back(str.substr(i+1,j-i-1)); i=j; } res.push_back(str.substr(j+1)); // reverse(res.begin(),res.end()); string ans; for(int i =res.size()-1; i>=0; i--) { ans+=res[i]; if(i>0) ans+=" "; } // ans.erase(ans.end()-1, ans.end()); return ans; } }; |
45 |
45扑克牌顺子(sort)
|
class Solution { public: bool IsContinuous( vector<int> numbers ) { // find_first_of() if(numbers.empty()) return false; int num = count(numbers.begin(),numbers.end(),0); int size = numbers.size(); sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end()); if(size-num == 0 || size-num ==1 ) return true; for(int i = num+1; i<size; i++) { if(numbers[i]==numbers[i-1]) return false; if(numbers[i]-numbers[i-1] -1>num) return false; if(numbers[i]-numbers[i-1] -1 == num) num=0; if(numbers[i]-numbers[i-1] -1 < num) num =num-(numbers[i]-numbers[i-1]-1); } return true; } }; |
46圆圈中最后剩下的数(list::erase)
|
class Solution { public: int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) { if(n==0) return -1; if(m==0) return n-1; list<int> ls; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) ls.push_back(i); list<int>::iterator it= ls.begin(); while(ls.size()>1) { for(int i=0; i<m-1; i++) { it++; it= it==ls.end()?ls.begin():it; } list<int>::iterator rm =it; it++; it= it==ls.end()?ls.begin():it; ls.erase(rm); } return ls.front();
/*方法2 if(n<1)return -1; if(n==1)return 0; vector<bool>nums(n,true); int now; now =0; for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++) { int last; for(int j=0; j<m; j++) { if(nums[now]==true) { last =now; now++; now=now%n; } else { while(!nums[now]) { now++; now=now%n; } last =now; now++; now=now%n; } } nums[last]=false;
} for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++) { if(nums[i]==true) return i; } */ } }; |
47求1+2+3+...+n(递归)
|
class Solution { public: int Sum_Solution(int n) { int sum=n; n&&(sum+=Sum_Solution(n-1)); return sum; } }; |
48不用加减乘除做加法
|
class Solution { public: int Add(int num1, int num2) { return num2 ? Add(num1^num2, (num1&num2)<<1) : num1;
} }; /* 首先看十进制是如何做的: 5+7=12,三步走 第一步:相加各位的值,不算进位,得到2。 第二步:计算进位值,得到10. 如果这一步的进位值为0,那么第一步得到的值就是最终结果。 第三步:重复上述两步,只是相加的值变成上述两步的得到的结果2和10,得到12。 同样我们可以用三步走的方式计算二进制值相加: 5-101,7-111 第一步:相加各位的值,不算进位, 得到010,二进制每位相加就相当于各位做异或操作,101^111。 第二步:计算进位值,得到1010,相当于各位做与操作得到101,再向左移一位得到1010,(101&111)<<1。 第三步重复上述两步, 各位相加 010^1010=1000,进位值为100=(010&1010)<<1。 继续重复上述两步:1000^100 = 1100,进位值为0,跳出循环,1100为最终结果 */ |
49把字符串转换成整数
|
class Solution { public: int StrToInt(string str) { if(str.empty()) return 0; int size = str.length(); // remove(str.begin(), str.end(), ' '); int res =0; int i=0; int flag = 1; if(str[i]=='+') {flag =1;i++;} if(str[i]=='-') {flag =-1;i++;} for(;i<size; i++) { if(str[i]>='0'&&str[i]<='9') { res = res*10+(str[i]-'0'); if(res*flag > INT_MAX) return INT_MAX; if(res*flag < INT_MIN) return INT_MIN;
} else{ res=0; return res; } } return res*flag;
} }; |
50数组中重复的数字(set)
|
class Solution { public: // Parameters: // numbers: an array of integers // length: the length of array numbers // duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number // Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number // otherwise false bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) {
int num =0; set<int> m; for(int i=0; i<length; i++) { if(m.find(numbers[i])==m.end()) m.insert(numbers[i]); else{ *duplication =numbers[i]; return true; }
} if(m.empty()) return false; } }; |
51构建乘积数组
|
class Solution { public: vector<int> multiply(const vector<int>& A) { vector<int> B (A.size(),1); for(int i =1; i<A.size();i++) { B[i] = B[i-1] * A[i-1]; } int ret=1; for(int i = A.size()-2;i>-1;i--) { ret = ret*A[i+1]; B[i] = B[i]*ret; } return B;
} }; |
52正则表达式匹配(分类讨论 递归 动态规划)
|
class Solution { public: bool match(char* s, char* p) { if(*s == '�'&&*p=='�') return true; if(*p=='�') return false; if(*s == '�') { if(*(p+1)!='*') return false; return match(s,p+2); } else{ if(*(p+1)!='*') { return *s==*p||*p=='.'?match(s+1,p+1):false; } else{ //注意相等的时候可能*后面和*s相等;所以要把s保留; return *s==*p||*p=='.'?(match(s+1,p)||match(s,p+2)):match(s,p+2); } } } }; |
53表示数值的字符串(**分类讨论)
|
class Solution { public: int cnt1 = 0,cnt2 = 0; //cnt1是.计数器,cnt2是'+'和'-计数器' bool isNumeric(char* string) { if (*string == '�') return true; //截止符号,停止检测,则返回true if ((*string < '0' || *string > '9') && *string != '.' && *string != '+' && *string != 'e' && *string != '-' && *string != 'E') return false; //情况7 if (*string == '.') cnt1 ++; if (*string ==+ '+' || *string == '-') if (*(string - 1) != 'E' && *(string - 1) != 'e') cnt2 ++; if (cnt1 == 2 || cnt2 == 2) return false; //情况6 if (*string == 'e') if(*(string - 1) < '0' || *(string - 1) > '9' || *(string + 1) == '�' || *(string + 3) == '.') return false; //情况4,情况8,情况9 if (*string == '+' || *string == '-') if(*(string - 1) > '0' && *(string - 1) < '9') return false; return isNumeric(string + 1); } }; |
54字符流中第一个不重复的字符(map[ch]++、map::find==map::end())
|
class Solution { public: //Insert one char from stringstream void Insert(char ch) { str+=ch; size++; res[ch]++;//注意查找到时候用find } //return the first appearence once char in current stringstream char FirstAppearingOnce() { for(auto k:str) { if(res.find(k)!=res.end()&&res[k]==1) return k; }
return '#'; } private: string str; int size; map<char,int>res; }; |
55链表中环的入口结点(双指针 快慢指针)
|
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { if(pHead == NULL) return NULL; if(pHead->next == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* p1=pHead; ListNode* p2=pHead; bool hasCircle=false; while(p1->next&&p1->next->next) { p1=p1->next->next; p2=p2->next; if(p1==p2) { hasCircle = true; break; } } if(hasCircle == false) return NULL; p1=pHead; while(p1!=p2) { p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next; } return p2; } }; |
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { ListNode* pslow; ListNode*pfast; pslow = pHead; pfast =pHead; while(!(pfast == NULL || pfast->next ==NULL)) { pfast = pfast->next->next; pslow = pslow->next; if(pslow == pfast) break; } if(pfast == NULL || pfast->next ==NULL) return NULL; pfast =pHead; while(pfast != pslow) { pfast = pfast->next; pslow =pslow->next; } return pfast; //return NULL; } }; |
56删除链表中重复的结点(多指针)
|
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* node) { if(node == NULL) return node; if(node->next == NULL) return node; ListNode* Head = new ListNode(0); Head->next=node; ListNode* prev = Head; ListNode* move; int val; while(node) { if(node->next == NULL) break; val = node->val; move = node; do{ move = move->next; }while(move&&val == move->val); if(node->next==move)//没找到相同的结点 { prev =node; node=node->next; continue; } ListNode* temp1 = node; //删除相同的结点 while(temp1!=move) { ListNode* temp2 = temp1->next; delete temp1; temp1=temp2; } prev->next=move; node=move; // node=node->next; } prev=Head; Head = Head->next; delete prev; return Head; } }; |
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) {
ListNode* nodefront=pHead; ListNode* node=pHead; if(node ==NULL ||node->next == NULL) return pHead; bool mopfirst =false; if(nodefront->val ==nodefront->next->val) mopfirst =true;
while(node->next!=NULL) { ListNode* node1=node->next; ListNode* node2=node->next;//从第二个开始 get(node1,node2); if(node1==node2) node=node->next; else node->next= node2; } if(mopfirst) { if(nodefront->next!=NULL && nodefront->val ==nodefront->next->val) { ListNode* temp = nodefront->next; delete nodefront; nodefront = temp; temp = nodefront->next; delete nodefront; nodefront = temp; } else{ ListNode* temp = nodefront->next; delete nodefront; nodefront = temp; } } return nodefront;
} void get(ListNode*& node1,ListNode*& node2) { if(node1->next!=NULL && node1->next->val==node1->val) { node2=node1->next; while(node2->next!=NULL && node2->next->val==node2->val) { node2=node2->next; } ListNode*& node =node1; while(node1 !=node2) { ListNode* temp=node1->next; delete node1; node1=temp; } delete node1; node1 =node; node2=node2->next; } else { // node2=node1; } } }; |
57二叉树的下一个结点(中序遍历,存储上一次遍历的结点)
|
/* struct TreeLinkNode { int val; struct TreeLinkNode *left; struct TreeLinkNode *right; struct TreeLinkNode *next; TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
} }; */ class Solution { public: TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) { TreeLinkNode* head; TreeLinkNode* node=pNode; while(node) { head = node; node = node->next; } last=NULL; target = pNode; inorderTraverse(head); return next; } void inorderTraverse(TreeLinkNode* node) { if(last == target) { next = node; // return; } if(node == NULL) return; inorderTraverse(node->left); if(last == target) { next = node; // return; } last = node; inorderTraverse(node->right); } private: TreeLinkNode* last; TreeLinkNode* target; TreeLinkNode* next; }; |
/* struct TreeLinkNode { int val; struct TreeLinkNode *left; struct TreeLinkNode *right; struct TreeLinkNode *next; TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
} }; */ class Solution { public: vector<TreeLinkNode*> vec; // int n=0; TreeLinkNode* NODE; TreeLinkNode* ans ; // bool isFound; TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) { NODE =pNode; ans =NULL; // isFound =false; TreeLinkNode* head=pNode; while(head->next) { head = head->next; } inorder(head); for(int i =0;i<vec.size();i++){ if(vec[i]==pNode && i+1<vec.size()) return vec[i+1]; } return ans; // void inorder(TreeLinkNode*); } void inorder(TreeLinkNode* node) { if(node==NULL) return; inorder(node->left); vec.push_back(node); // n++; inorder(node->right); } }; |
58对称的二叉树(中序和反中序同时遍历,队列层序遍历)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) { isright = true; if(pRoot == NULL) return true; traverse(pRoot->left,pRoot->right); return isright; }
void traverse(TreeNode* node1,TreeNode* node2) { if(node1==NULL&&node2==NULL) { return; } if(node1==NULL || node2==NULL) { isright = false; return; } traverse(node1->left,node2->right); if(node1->val!=node2->val) isright = false; traverse(node1->right, node2->left); } bool isright; }; |
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) { if(pRoot == NULL) return true; queue<TreeNode*> s; s.push(pRoot->left); s.push(pRoot->right); while(!s.empty()) { TreeNode* n1 = s.front(); s.pop(); TreeNode* n2 = s.front(); s.pop(); if(n1 == NULL && n2 ==NULL) continue; else if(n1 == NULL || n2 == NULL) { return false; } else if(n1->val != n2->val) { return false; } s.push(n1->left); s.push(n2->right); s.push(n1->right); s.push(n2->left);
} return true; } }; |
59 |
59按之字形打印二叉树(层序遍历)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* node) { vector<vector<int> > ans; if(node == NULL) return ans; vector<int> res; // vector<int> res2; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(node); int order =1; while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++) { res.push_back(q.front()->val); if(q.front()->left) q.push(q.front()->left); if(q.front()->right) q.push(q.front()->right); q.pop(); } if(order == -1) { reverse(res.begin(),res.end()); } order =-order; ans.push_back(res); res.clear(); } return ans; }
}; |
60把二叉树打印成多行
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* node) { vector<vector<int> > ans; if(node == NULL) return ans; vector<int> res; // vector<int> res2; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(node); // int order =1; while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++) { res.push_back(q.front()->val); if(q.front()->left) q.push(q.front()->left); if(q.front()->right) q.push(q.front()->right); q.pop(); } // if(order == -1) // { // reverse(res.begin(),res.end()); // } // order =-order; ans.push_back(res); res.clear(); } return ans; }
}; |
61序列化二叉树(**前序遍历、层序遍历【看成是入队和出队】,指针的引用)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: //线序遍历相当于进入队列 char* Serialize(TreeNode *root) { if(root == NULL) return "#"; string res = to_string(root->val); res+=","; char* left = Serialize(root->left); char* right = Serialize(root->right); // res+=string(left)+string(right); // return const_cast<char*> (res.c_str()); char* ret = new char[strlen(left)+strlen(right)+res.size()]; // 如果是string类型,直接用operator += ,这里char* 需要用函数 strcpy(ret,res.c_str()); strcat(ret,left); strcat(ret,right);
return ret; } //反序列化也按照先序遍历的顺序递归进行,相当于出队列 TreeNode* Des(char *& s) { if(*s == '#') { s++; return NULL; } int num =0; while(*s!=',') { num = num*10 +(*s-'0'); s++; } s++; TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(num); node->left=Des(s); node->right=Des(s); return node; } TreeNode* Deserialize(char *str) { // if() return Des(str); } }; |
62二叉搜索树的第k个结点(中序遍历)
|
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, int k) { TreeNode* ans; int i=0; TreeNode* n=NULL; in_order(pRoot,n,i,k); return n; }
void in_order(TreeNode* node,TreeNode* &n,int &i,int &k) { if(node == nullptr) return; in_order(node->left,n,i,k); i++; if(i==k) n=node; in_order(node->right,n,i,k); } }; |
63数据流中的中位数(大顶堆和小顶堆)
|
class Solution { public: void Insert(int num) { if(q1.empty()) { q1.push(num); num1++; return; } if(q2.empty()) { if(num>=q1.top()) { q2.push(num); num2++; } else{ q2.push(q1.top()); num2++; q1.pop(); q1.push(num); } return; } if(num<=q1.top()) { q1.push(num); num1++; } else{ q2.push(num); num2++; } }
double GetMedian() { while(num1>num2) { q2.push(q1.top()); q1.pop(); num1--; num2++; } while(num2-num1>1) { q1.push(q2.top()); q2.pop(); num1++; num2--; } if(num1==num2) return (q1.top()+q2.top())/2.0; return q2.top(); } int num1=0; int num2=0; priority_queue<int>q1;//大顶堆 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>q2;//小顶堆
}; |
64滑动窗口的最大值(大顶堆)
|
class Solution { public: vector<int> maxInWindows(const vector<int>& num, unsigned int size) { vector<int> ans; if(num.empty()) return ans; if(size>num.size()) return ans; if(size ==1) return vector<int> (num); if(size<=0) return ans; priority_queue<int>ls; int i=0; for(;i<size;i++) { ls.push(num[i]); } ans.push_back(ls.top()); // i++; while(i<num.size()) { if(ls.top() == num[i-size]) ls.pop(); ls.push(num[i]); ans.push_back(ls.top()); i++; } return ans; } }; |
65矩阵中的路径
|
66机器人的运动范围(dfs bfs使用队列 )
|
class Solution { public: int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) { //这种方式不好,最好还是mark作为局部变量; mark = vector<vector<int>>(rows,vector<int>(cols,0));
ans =0; r=rows; c=cols; thresh = threshold; dfs(0,0); return ans; } private: vector<vector<int>> mark; // static constexpr int dir[4][2]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; void dfs(int x, int y) { if (x < 0 || x >= r || y < 0 || y >= c || mark[x][y] == 1) { return; } if(overthresh(x,y)) return; mark[x][y]=1; ans++; for(auto k:dir) { dfs(x+k[0],y+k[1]); } } bool overthresh(int x, int y) { int sum =0; while(x) { sum +=x%10; x=x/10; } while(y) { sum +=y%10; y=y/10; } return sum>thresh?true:false; } int ans; int r; int c; int thresh; }; |
class Solution { public: using pii = pair<int,int>; int dir[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; int check(int n) { int sum = 0;
while (n) { sum += (n % 10); n /= 10; }
return sum; } int movingCount(int sho, int rows, int cols) { if (sho <= 0) { return 0; }
int ret = 0; int mark[rows][cols]; memset(mark, -1, sizeof(mark)); queue<pii> q; q.push({0, 0}); mark[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) { auto node = q.front(); q.pop(); // 每次保证进队列的都是满足条件的坐标 ++ret;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int x = node.first + dir[i]; int y = node.second + dir[i + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < rows && y >= 0 && y < cols && mark[x][y] == -1) { if (check(x) + check(y) <= sho) { q.push({x, y}); mark[x][y] = 1; } } } }
return ret; } }; |
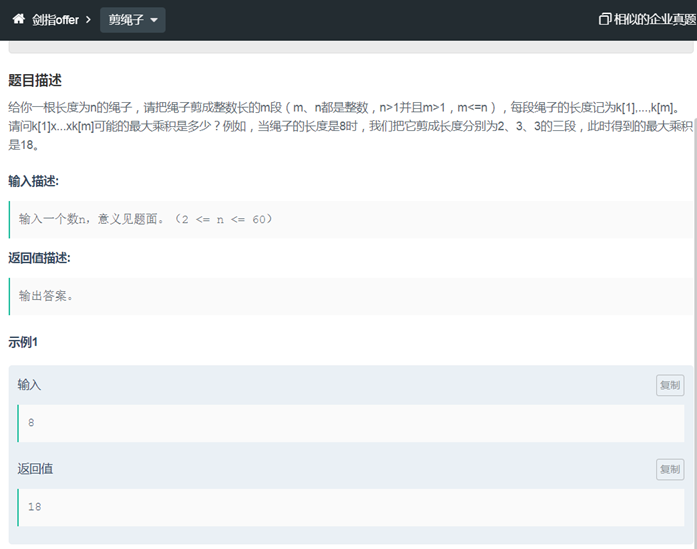
67剪绳子(递归 记忆化递归去重 动态规划)
|
class Solution { public: int cutRope(int number) { if (number == 2) { return 1; } else if (number == 3) { return 2; } vector<int> f(number+1,-1); for (int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i) { f[i] = i; } for (int i = 5; i <= number; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) { f[i] = max(f[i], j * f[i - j]); } } return f[number]; } }; |
//递归 class Solution { public: int back_track(int n) { // n <= 4, 表明不分,长度是最大的 if (n <= 4) { return n; } int ret = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { ret = max(ret, i * back_track(n - i)); } return ret; } int cutRope(int number) { // number = 2 和 3 时,分 2 段和分 1 段的结果是不一样的,所以需要特判一下 if (number == 2) { return 1; } else if (number == 3) { return 2; } return back_track(number); } }; |
//记忆化递归 class Solution { public: int back_track(int n, vector<int> &mark) { if (n <= 4) { return n; } // 在方法一的基础上添加 if (mark[n] != -1) { return mark[n]; }
int ret = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { ret = max(ret, i * back_track(n - i)); } // 添加部分 return mark[n] = ret; } int cutRope(int number) { if (number == 2) { return 1; } else if (number == 3) { return 2; } // 添加部分 vector<int> mark(number, -1); return back_track(numberm, mark); } }; |
经典必刷题库
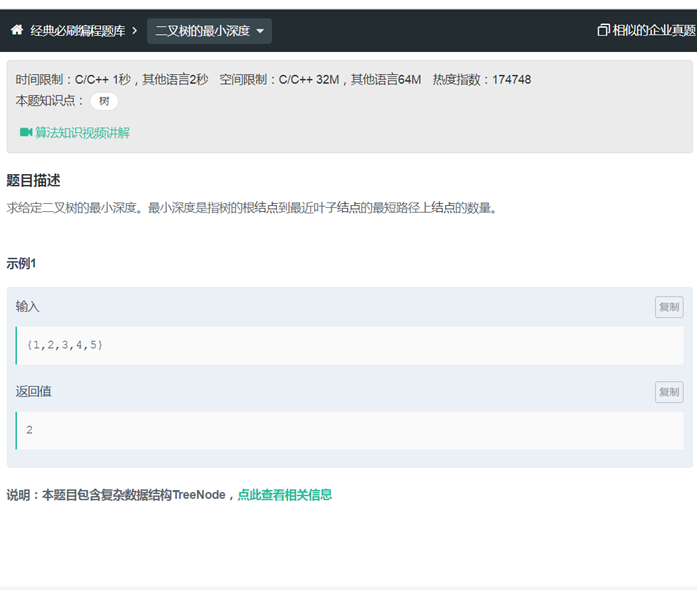
LC1二叉树的最小深度(递归 dfs 层序遍历)
|
/** * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
class Solution { public: /** * * @param root TreeNode类 * @return int整型 */ int run(TreeNode* node) { // write code here if(node ==nullptr) return 0; return depth(node); /* int num =1; int d =0; dfs(node,num,d); return d; */ } int depth(TreeNode* node) { if(node == NULL) { return -1; } if(node->left==NULL && node->right==NULL) return 1; if(node->left==NULL) return 1+depth(node->right); if(node->right==NULL) return 1+depth(node->left); return 1+min(depth(node->left),depth(node->right)); } /* void dfs(TreeNode* node,int & num,int & d) { if(node==NULL) return; if(node->left==NULL&&node->right==NULL) { d= (d==0?num:min(d,num)); return; }
num++; dfs(node->left,num,d); dfs(node->right,num,d); num--; } */ }; |
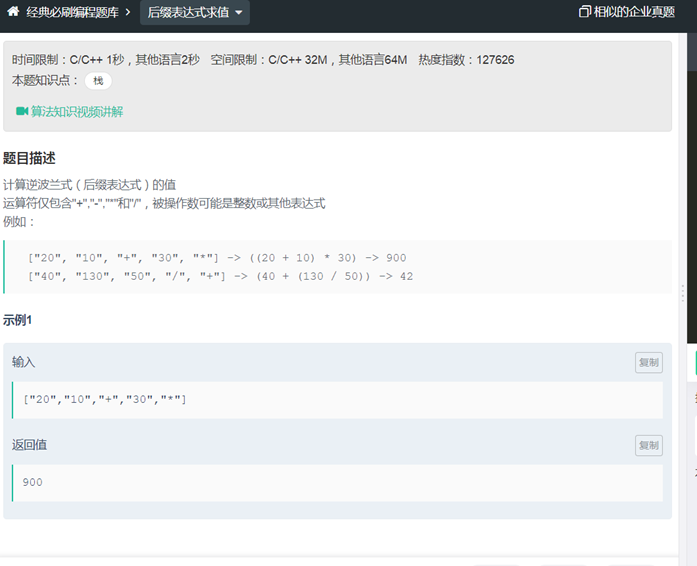
LC2后缀表达式求值(堆栈)
|
class Solution { public: /** * * @param tokens string字符串vector * @return int整型 */ int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { // write code here stack<int> res; for(auto k:tokens) { if(k=="+"||k=="-"||k=="*"||k=="/") { if(res.size()<2) return 0; int a=res.top(); res.pop(); int b=res.top(); res.pop(); int c=0;//用c表示每次运算的结果 if(k=="+") c=b+a; if(k=="-") c=b-a; if(k=="*") c=b*a; if(k=="/") c=b/a; res.push(c); } else { res.push(atoi(k.c_str())); } } return res.top(); } }; |
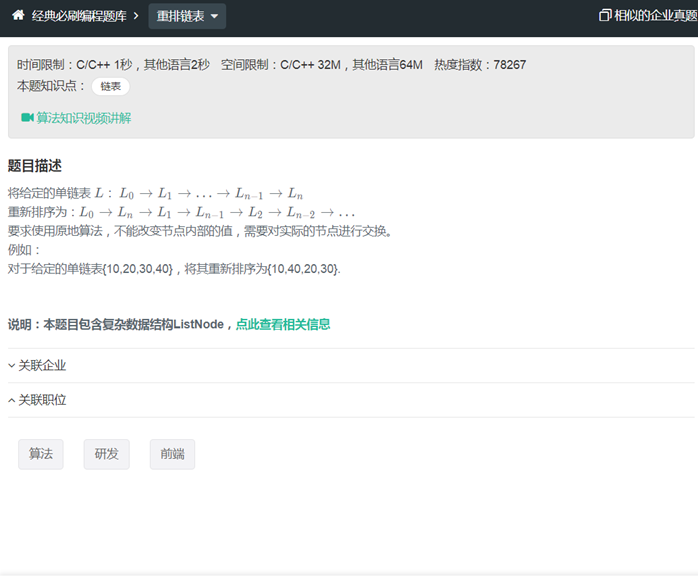
LC8重排链表(快慢指针,反转链表,注意最后一个结点的next为NULL)
|
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr) return; if(head->next == nullptr) return; if(head->next->next==nullptr) return; ListNode* slow=head; ListNode* fast =head; while(fast->next!=NULL && fast->next->next!=NULL) { fast=fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } ListNode* node=slow->next; ListNode* temp = NULL; ListNode* head2=temp; while(node) { temp=node; node = node->next; temp->next=head2; head2=temp; } temp=head; // head2; while(temp!=slow) { node = head2->next; head2->next=temp->next; temp->next=head2; temp=head2->next; head2=node; } if(head2!=NULL) { slow->next=head2; } else slow->next=NULL; } }; |
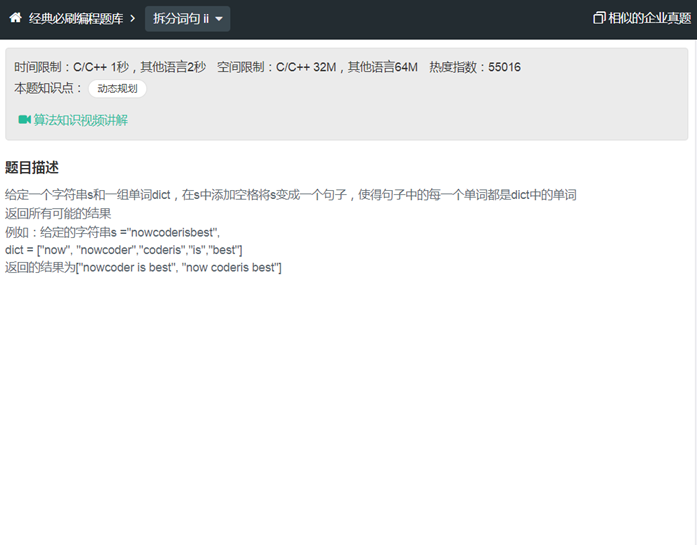
LC11拆分词句
|
#include<unordered_set> #include<vector> #include<string>
class Solution11 { public: vector<string> wordBreak(string s, unordered_set<string> &dict) { int size = s.size(); vector<string>ans; // for() if (s.empty() || dict.empty()) return ans; for(auto k:dict) { if(startwith(s, k)) { string res; // res+=" ";
res+=k; get(string(s.begin()+k.size() ,s.end()),dict,ans,res); } } return ans; }
bool startwith(string s,string d) { if(s.length()<d.length()) return false; return string(s.begin(),s.begin()+d.length()) == d ; } void get(string s,unordered_set<string> &dict,vector<string>&ans,string &res) { if(s=="") { ans.push_back(res); } for(auto k:dict) { if(startwith(s, k)) { res+=" "; res+=k; get(string(s.begin()+k.size() ,s.end()),dict,ans,res); } } } };
|
LC
LC
LC
LC
LC
LC
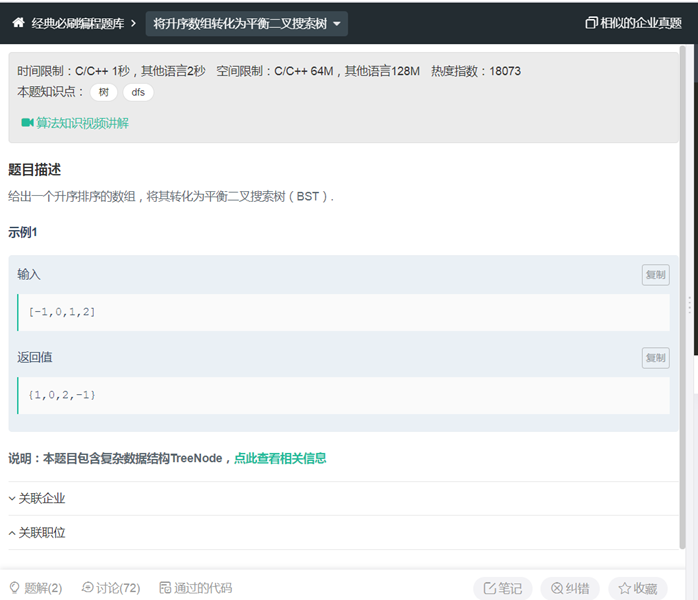
LC41将升序数组转化为平衡二叉树
|
/** * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
class Solution { public: /** * * @param num int整型vector * @return TreeNode类 */ TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& num) { // write code here int size = num.size(); if(size ==0) return nullptr; int mid = size/2; // vector<int> vec1 = vector<int>(num.begin(),num.begin()+mid); // vector<int> vec2 = vector<int>(num.begin()+mid,num.end()); TreeNode*node = new TreeNode(num[mid]); node->left=get(num,0,mid-1); node->right=get(num,mid+1,size-1) ; return node; } TreeNode* get(vector<int>& num,int start, int end) { if(start > end) return nullptr; if(start == end) { TreeNode*node = new TreeNode(num[start]); node->left=NULL; node->right=NULL; return node; } int mid =start+(end-start+1)/2; TreeNode*node = new TreeNode(num[mid]); node->left=get(num,start,mid-1); node->right=get(num,mid+1,end) ; return node; } }; |