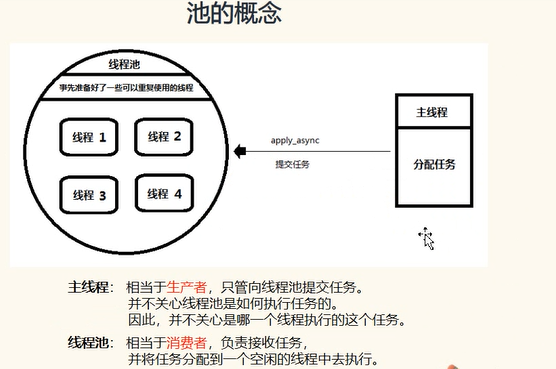
池:存任务的空间,存入多个线程就叫线程池。(每个线程开启关闭耗费资源,线程池统一管理,线程可重复使用)
重复利用的线程池,代码实现:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ 重复利用的线程池 """ from threading import Thread, current_thread from queue import Queue import time class MyThreadPool: def __init__(self, n): self.queue = Queue() # 生成线程池 for i in range(n): Thread(target=self.run, args=(self.queue, ), daemon=True).start() def run(self, queue): while True: task, args, kwargs = self.queue.get() task(*args, **kwargs) print(current_thread(), task) # 打印当前线程 self.queue.task_done() # 计数器 -1 def join(self): # queue计数为0时终止程序 self.queue.join() # 重写thread join方法,调用queue join def apply_async(self, func, args=(), kwargs={}): self.queue.put((func, args, kwargs)) # 计数器 +1 def apply1(n, m): # print('apply1: n+m=', n+m) time.sleep(3) def apply2(n, m): # print('apply2: n+m=', n+m) time.sleep(3) if __name__ == '__main__': my_thread_pool = MyThreadPool(3) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply1, args=(1, 1)) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply2, args=(2, 2)) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply1, args=(1, 1)) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply2, args=(2, 2)) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply1, args=(1, 1)) my_thread_pool.apply_async(apply2, args=(2, 2)) # 主线程先执行到这儿,此时queue计数器 +1 *6 my_thread_pool.join() # 等待计数器为0时结束队列queue阻塞程序