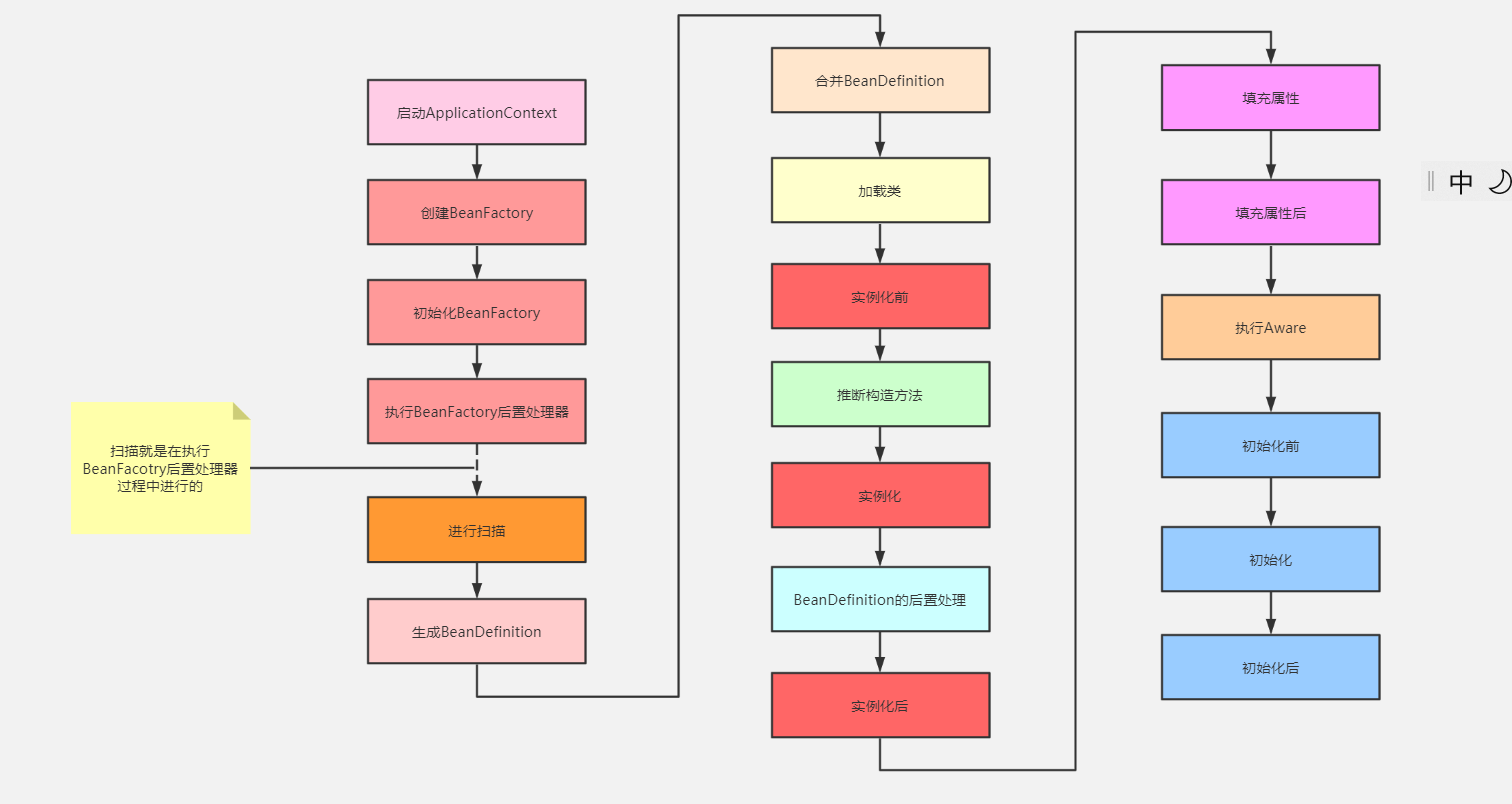
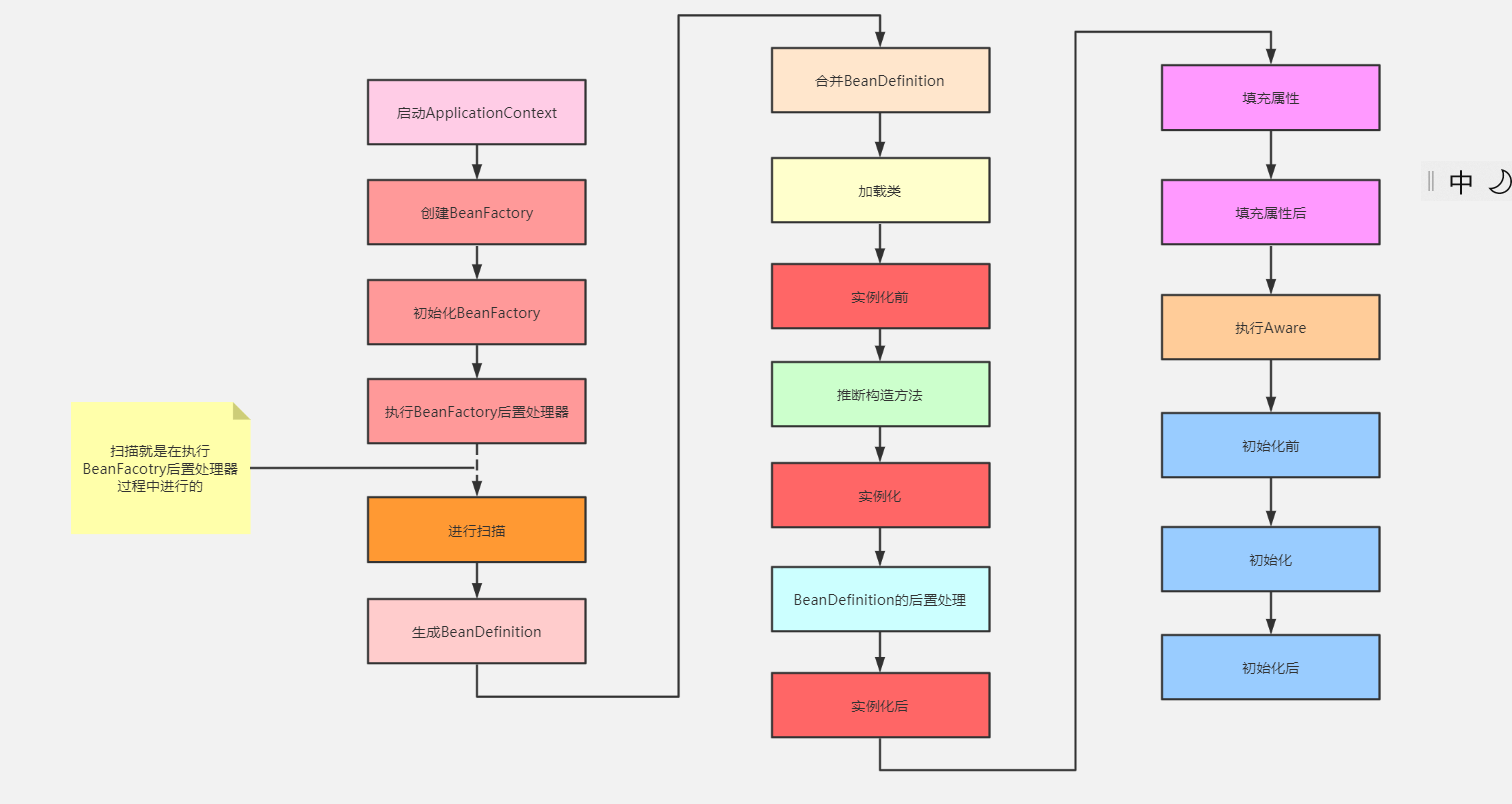
生命周期流程图镇楼
课前小demo 有关于推断构造函数的演示
UserService.java
@Component
public class UserService{
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
public UserService() {
System.out.println("无参");
}
public UserService(OrderService orderService) {
System.out.println("有参");
}
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.orderService);
}
}
OrderService.java
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
Test.java
public class Test(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService());
userService.test();
}
/**
无参
com.luban.service.OrderService@7722c3c3
com.luban.service.OrderService@7722c3c3
*/
1.getBean 的时候用UserService哪个构造函数生成bean呢?
结论:
applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService()); 使用有参的构造函数生成Bean
applicationContext.getBean("userService"); 使用无参的构造函数生成Bean
执行Test的main方法确实打印无参,这是因为UserService是在AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); 生成的。 spring容器启动了,就能把bean创建完,所以后面 UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService()); 是去单例池拿userService
我们把UserService改成原型的时候,此时实例化userservice对象的时候,执行有参构造函数
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class UserService{
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
public UserService() {
System.out.println("无参");
}
public UserService(OrderService orderService) {
System.out.println("有参");
}
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.orderService);
}
}
OrderService.java
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
Test.java
public class Test(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService());
userService.test();
}
/**
无参
com.luban.service.OrderService@7722c3c3
com.luban.service.OrderService@7722c3c3
*/
/**
有参
com.luban.service.OrderService@5119fb47
com.luban.service.OrderService@5119fb47
*/
课前小demo2 关于bean的别名
问题:我们如何给bean设置别名呢?
1.在@Component 上无法设置别名
@Component
public class UserService{
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
2.使用@Bean注解生成别名
- 分析代码1 :
Appconfig.java
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean("userService") // 单单只有”userService“并不算是别名 userService就是该bean真正的名字
public UserService userService(){
return new UserService();
}
}
Test.java
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService());
userService.test();
userService.test();
}
@Bean("userService") 单单只有”userService“并不算是别名 userService就是该bean真正的名字,它真正的名字就是@Bean注解标记的方法名userService,如下所示
- 分析代码2
Appconfig.java
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean({"userService","userService1","userService2"})
public UserService userService(){
return new UserService();
}
}
Test.java
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService",new OrderService());
userService.test();
userService.test();
}
@Bean({"userService","userService1","userService2"}) 中 userService就是bean真正的名字,userService1、userService2 就是别名了
此时this.aliasMap 中就存在键值对 <"userService1","userService"> ,<"userService2","userService">
3.使用
<bean id="userService" name = "userService11123" class="com.luban.service.UserService" >
</bean>
4.如何查看bean的别名呢,可以查看this.aliasMap表这张表记录了 真实名字和别名的映射关系。 查看此文章我们知道:Spring源码解析(五)-解析alias标签] key 为别名 vlue为真实名字
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
补充AbstractBeanFactroy#doGetBean()方法
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 对beanName进行转换 name如果是"&lubanFactoryBean",那么beanName就是"lubanFactoryBean"
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); // Map<>
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
//省略
}
else {
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 原型bean正在创建中
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
//前// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 原型bean正在创建中
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}面省略
// 创建Bean
try {
// 得到合并后的BeanDefinition
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 加载DependsOn的bean
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); //=========================================(1)
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
// 判断beanName是不是也被dep依赖了,如果是,就是相互依赖
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 存在在两个map中
// 1. dependentBeanMap,key为dep, value是一个LinkedHashSet,表示dep被哪些bean依赖了
// 2. dependenciesForBeanMap,key为beanName,value是一个LinkedHashSet,表示beanName依赖了哪些bean
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
// 先去生成所依赖的bean
getBean(dep); // getBean("xxx")
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
} // ========================================================================(2)
// 根据Scope去创建bean
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 获取单例bean,如果获取不到则创建一个bean,并且放入单例池中
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
// sharedInstance可能是一个FactoryBean,所以需要单独再去factoryBeanObjectCache中去获取对应的对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 其他作用域的
else { //==========================================================(3)
String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); // request, session
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}//===========================================================================(4)
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
// 根据beanName获取到的bean的类型是否和requiredType匹配,如果不配则进行类型转化
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { // 转换异常则报错
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
为什么会涉及到这段代码呢??大都督说这段代码等讲到循环依赖的时候会讲清楚。迟点我可以自己搞清楚。。
// 原型bean正在创建中
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
循环依赖:
(1)与(2)之间的代码段主要是判断:判断两个Bean是否有@dependOn相互依赖:即a depends on b , b depends on a 无法创建bean
@component
@dependson("orderService")
public class UserService(){
}
@component
@dependson("userService)
public class OrderService(){
}
存在在两个map中
-
dependentBeanMap,表示dep被哪些bean依赖了 (key为dep, value是一个LinkedHashSet)
-
dependenciesForBeanMap,表示dep依赖了哪些bean(key为dep,value是一个LinkedHashSet)
先去生成dep所依赖的bean
创建单例bean
// 根据Scope去创建bean
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 获取单例bean,如果获取不到则创建一个bean,并且放入单例池中
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
// sharedInstance可能是一个FactoryBean,所以需要单独再去factoryBeanObjectCache中去获取对应的对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
会调用DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton()方法
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); // 双重校验机制
// 如果不存在实例,则创建单例bean实例
if (singletonObject == null) {
// 当前单例正在销毁中..
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 把当前正在创建的beanName添加到singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中,singletonsCurrentlyInCreation是一个Set
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// singletonFactory是外面传进来的lambda表达式,执行lambda表达式
// 创建单例bean
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); // createBean()
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// 将刚刚正在创建的beanName从singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中移除
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
// 将创建好的单例bean添加到单例池singletonObjects中
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
把当前正在创建的beanName添加到singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中,singletonsCurrentlyInCreation是一个Set
protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
// inCreationCheckExclusions中的beanName,表示如果是这些bean正在创建中,重复创建也没关系
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中的beanName,表示这些bean正常创建中,在没创建完时不能重复创建
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
}
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); // createBean()
执行lambda表达式,createBean
() -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
scope其他作用域
(3)与(4)之间的代码段,主要是解决scope等于session、或request的情况,详解如下
"request" ,UserService -->>Bean对象 request.getAttribute().get("beanName")
"session" ,UserService -->>Bean对象 session.getAttribute().get("beanName")
-
String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); // 获取scopeName: request 或者session
-
获取scope的作用域
-
获取scopeInstance
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } });我们看一下scope.get方法,首先scope 是一个接口,有两个重要的是实现类RequestScope和SessionScope
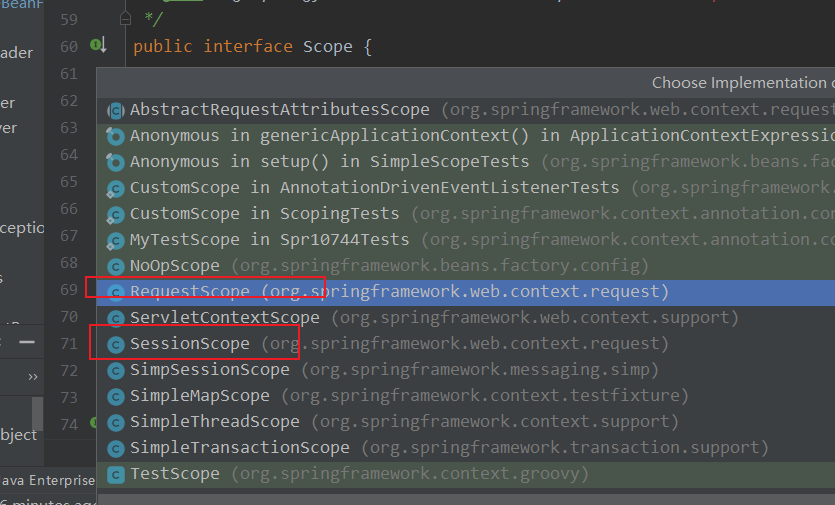
scope.get 其实是调用父类AbstractRequestAttributesScope#get 方法
public abstract class AbstractRequestAttributesScope implements Scope {
@Override
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
RequestAttributes attributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
//
Object scopedObject = attributes.getAttribute(name, getScope());
if (scopedObject == null) {
scopedObject = objectFactory.getObject();
attributes.setAttribute(name, scopedObject, getScope());
// Retrieve object again, registering it for implicit session attribute updates.
// As a bonus, we also allow for potential decoration at the getAttribute level.
Object retrievedObject = attributes.getAttribute(name, getScope());
if (retrievedObject != null) {
// Only proceed with retrieved object if still present (the expected case).
// If it disappeared concurrently, we return our locally created instance.
scopedObject = retrievedObject;
}
}
return scopedObject;
}
RequestScope 、 SessionScope 都属于AbstractRequestAttributesScope的子类。
子类执行父类的方法,attributes.getAttribute(name, getScope())等价于
request.getAttribute().get("beanName")、或者是 session.getAttribute().get("beanName")
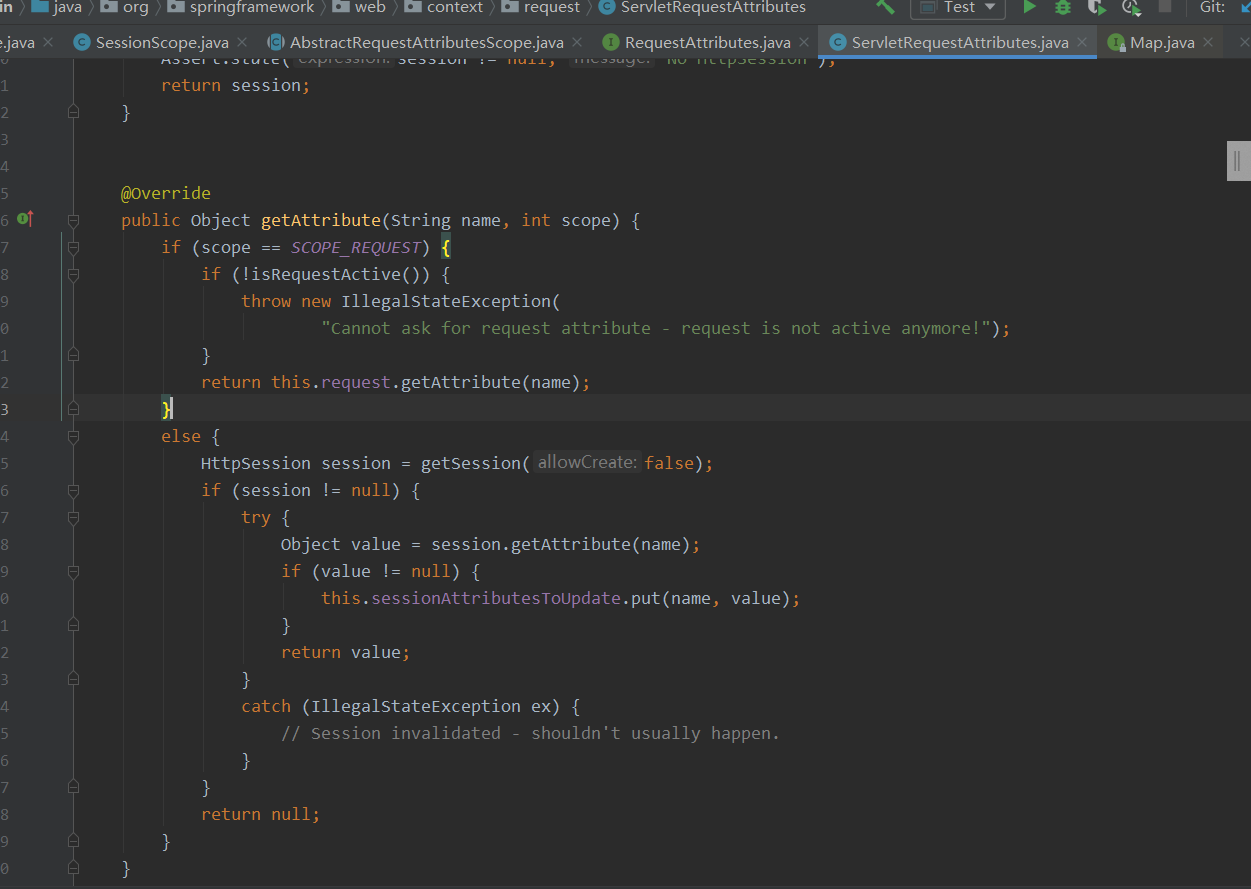
attributes.getAttribute(name, getScope())为null则执行objectFactory.getObject方法,创建bean
() -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
AbstractBean#createBean()
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
// 对通过XML定义的bean中的look-up方法进行预处理
// 对于@Lookup注解标注的方法不在这里进行处理,@AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor会处理@Lookup注解
// 不研究了
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 1、实例化前 null 开发者不用spring自带的创建bean的方法 自定义创建bean的方法然后返回bean 跳过了实例化 实例化后 初始化前后 还有 注入属性 等直接进入初始化后的逻辑
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); // 对象
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 创建bean Spring自带的创建bean的方法
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
3. 加载类
BeanDefinition合并之后,就可以去创建Bean对象了,而创建Bean就必须实例化对象,而实例化就 必须先加载当前BeanDefinition所对应的class,
在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的 createBean()方法中,一开始就会调用
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
这行代码就是去加载类,该方法是这么实现的:
protected Class<?> resolveBeanClass(final RootBeanDefinition mbd, String beanName, final Class<?>... typesToMatch)
throws CannotLoadBeanClassException {
try {
// 直接返回beanClass
if (mbd.hasBeanClass()) {
return mbd.getBeanClass();
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
return AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Class<?>>) () ->
doResolveBeanClass(mbd, typesToMatch), getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 加载BeanDefinition中beanClass中所指定的类名对应的类 //根据mbd中拿到的"com.xx.xx"的字符串然后去加载这个类
return doResolveBeanClass(mbd, typesToMatch);
}
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
ClassNotFoundException ex = (ClassNotFoundException) pae.getException();
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), err);
}
}
private Class<?> doResolveBeanClass(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 根据mbd中的beanClassName来加载类并返回
// 拿到类加载器
ClassLoader beanClassLoader = getBeanClassLoader();
ClassLoader dynamicLoader = beanClassLoader;
boolean freshResolve = false;
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(typesToMatch)) {
// When just doing type checks (i.e. not creating an actual instance yet),
// use the specified temporary class loader (e.g. in a weaving scenario).
ClassLoader tempClassLoader = getTempClassLoader();
if (tempClassLoader != null) {
dynamicLoader = tempClassLoader;
freshResolve = true;
if (tempClassLoader instanceof DecoratingClassLoader) {
DecoratingClassLoader dcl = (DecoratingClassLoader) tempClassLoader;
for (Class<?> typeToMatch : typesToMatch) {
dcl.excludeClass(typeToMatch.getName());
}
}
}
}
// 获取BeanDefinition中所指定的beanClass属性的值,beanClass属性的类型为Object,可以指定为某个类名 //根据mbd中拿到的"com.xx.xx"的字符串然后去加载这个类
String className = mbd.getBeanClassName(); // 字符串 #{xxx}
if (className != null) {
// className可以有SpEL,所以需要解析
Object evaluated = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(className, mbd);
if (!className.equals(evaluated)) {
// A dynamically resolved expression, supported as of 4.2...
if (evaluated instanceof Class) {
return (Class<?>) evaluated;
}
else if (evaluated instanceof String) {
className = (String) evaluated;
freshResolve = true;
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid class name expression result: " + evaluated);
}
}
if (freshResolve) {
// When resolving against a temporary class loader, exit early in order
// to avoid storing the resolved Class in the bean definition.
if (dynamicLoader != null) {
try {
return dynamicLoader.loadClass(className);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not load class [" + className + "] from " + dynamicLoader + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
return ClassUtils.forName(className, dynamicLoader);
}
}
// Resolve regularly, caching the result in the BeanDefinition...
return mbd.resolveBeanClass(beanClassLoader);
}
*/
@Nullable
public Class<?> resolveBeanClass(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String className = getBeanClassName();
if (className == null) {
return null;
}
Class<?> resolvedClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader);
this.beanClass = resolvedClass;
return resolvedClass;
}
public boolean hasBeanClass() {
return (this.beanClass instanceof Class);
}
如果beanClass属性的类型是Class,那么就直接返回
如果不是,则会根据类名进行加载(doResolveBeanClass方法所做的事情)
-
使用BeanFactory所设置的类加载器来加载类
- context.getBeanFactory().setBeanClassLoader(customerClassLoader)
-
BeanFactory没有设置类加载器
-
则默认使用 ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()所返回的类加载器来加载。
-
ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()
-
优先获取当前线程中的ClassLoader(正常情况下,就是AppClassLoader)
-
线程中类加载器为null的情况下,则获取加载ClassUtils类的类加载器(正常情况下,就是AppClassLoader,但是如果是在Tomcat中运行,那么则会是Tomcat中为每个应用所创建的WebappClassLoader,tomcat会在前面设置)
-
如果ClassUtils类的类加载器为空,那么则是bootstrap类加载器加载的ClassUtils类,那则获取系统类加载器进行加载 系统类加载器默认返回的是appClassLoader
-
-
如何生成Class对象
public String getBeanClassName() {
Object beanClassObject = this.beanClass;
if (beanClassObject instanceof Class) {
return ((Class<?>) beanClassObject).getName();
}
else {
return (String) beanClassObject;
}
}
AbstractBeanDefinition 的
@Nullable
private volatile Object beanClass; // String Class
获取BeanDefinition中所指定的beanClass属性的值,beanClass属性的类型为Object,可以指定为某个类名
根据mbd中拿到的"com.xx.xx"的字符串然后使用类加载器去加载这个类, 而前面使用asm技术解析字节码生成bd文件,已经已经给beanClass属性赋值为字符串,这边需要把beanClass 真正的赋值成一个Class对象,这个Class对象通过类加载器加载.class字节码获取。
Object evaluated = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(className, mbd);
className可以有SpEL,所以需要解析Object evaluated = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(className, mbd);
如下所示:
我们知道:mbd中的beanClass设置是在扫描类生成bean定义的时候生成,让我们查看spring生命周期上篇1.3spring为beanDefintion设置beanName属性,其中value属性中设置的值可以用来作为beanClass的属性值
@Component
public class UserService(){
@value("#{orderService}") // 可以注入成功
private OrderService orderService;
public void test (){
sout(orderService;)}
}
@value("#{orderService}") 取beanName为orderService的类
@value("#{orderService1}") 取beanName为orderService1的类,此时会报错
@value("${LunbanXX}") 取名字为LunbanXX的环境变量的值 (如properties里面设置的)
-
$表示是占位符 需要填充 用什么填充呢 ,用的是spring的Enviroment
1、定义properties
2、vm options 的时候指定 -D LunbanXX=123
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
获取resolvedClass之后对mbd重新赋值beanClass 使得属性值为Class对象
4. 实例化前
当前BeanDefinition对应的类成功加载后,就可以实例化对象了,但是createBean方法中继续走:
走到Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
调用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#resolveBeforeInstantiation 方法
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
// beforeInstantiationResolved为null或true
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
// 实例化前
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
在Spring中,实例化对象之前,Spring提供了一个扩展点,允许用户来控制是否在某个或某些Bean实例化之前做一些启动动作。这个扩展点叫InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()。比如:
@Component
public class ZhouyuBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userService".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("实例化前");
}
return null;
}
}
如上代码会导致,在userService这个Bean实例化前,会进行打印。
值得注意的是,postProcessBeforeInstantiation()是有返回值的,如果这么实现:
@Component
public class ZhouyuBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userService".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("实例化前");
return new UserService();
}
return null;
}
}
userService这个Bean,在实例化前会直接返回一个由我们所定义的UserService对象。如果是这样,表示不需要Spring来实例化了,并且后续的Spring依赖注入也不会进行了,会跳过一些步骤,直接执行初始化后这一步。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法 (为了给程序员自定义的bean 执行aop生成动态代理)
直接执行beanPostProcess类的postProcessAfterInitialization 初始化后方法:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
意义:让程序员自己返回一个bean 实现方法用bean的后置处理器
spring在创建bean的过程中,我们可以设置一些bean的后置处理器去干涉spring创建bean的过程
实例化之前的bean后置处理器 返回bean 则再执行初始化后的bean后置处理器(目的是为了aop)我们必须保留对一个bean进行aop的权利
如下图所示:

题外话:如果想知道项目组中哪里有用到实例化前返回程序员自定义的bean,可以找到InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()的方法,查看方法在哪里有实现
没有实现上述接口的话那么会使用spring自己的创建bean的逻辑如下:
spring自己创建bean的代码就很牛逼了,涵盖了各种拓展点
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// factoryBeanObjectCache:存的是beanName对应的FactoryBean.getObject()所返回的对象
// factoryBeanInstanceCache:存的是beanName对应的FactoryBean实例对象
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 2、实例化
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建bean实例 new USerSerive()
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 原始对象
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 运行修改合并好了的BeanDefinition
// 这里会查找@Autowired的注入点(InjectedElement),并把这些注入点添加到mbd的属性externallyManagedConfigMembers中
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 如果当前创建的是单例bean,并且允许循环依赖,并且还在创建过程中,那么则提早暴露
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 此时的bean还没有完成属性注入,是一个非常简单的对象
// 构造一个对象工厂添加到singletonFactories中
// 第四次调用后置处理器
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)); // AService
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
// 对象已经暴露出去了
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 3、填充属性 @Autowired
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //
// 4、 初始化 和 BeanPostProcessor 正常AOP BeanPostProcessor
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// 在解决循环依赖时,当AService的属性注入完了之后,从getSingleton中得到AService AOP之后的代理对象
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); // earlySingletonObjects
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// 如果提前暴露的对象和经过了完整的生命周期后的对象相等,则把代理对象赋值给exposedObject
// 最终会添加到singletonObjects中去
if (exposedObject == bean) { //
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
// 如果提前暴露的对象和经过了完整的生命周期后的对象不相等
// allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping表示在循环依赖时,只能
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
// AService的原始对象被注入给了其他bean,但是AService最后被包装了
// 也就是说其他bean没有用到AService的最终版本
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
5. 实例化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
在这个步骤中就会根据BeanDefinition去创建一个对象了。
5.1 Supplier创建对象
首先判断BeanDefinition中是否设置了Supplier,如果设置了则调用Supplier的get()得到对象。
得直接使用BeanDefinition对象来设置Supplier,比如:
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition().getBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setInstanceSupplier(new Supplier<Object>() {
@Override
public Object get() {
return new UserService();
}
});
context.registerBeanDefinition("userService", beanDefinition);
5.2 工厂方法创建对象
如果没有设置Supplier,则检查BeanDefinition中是否设置了factoryMethod,也就是工厂方法,有两种方式可以设置factoryMethod,比如:
方式一:
<bean id="userService" class="com.zhouyu.service.UserService" factory-method="createUserService" />
对应的UserService类为:
public class UserService {
public static UserService createUserService() {
System.out.println("执行createUserService()");
UserService userService = new UserService();
return userService;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
方式二:
<bean id="commonService" class="com.zhouyu.service.CommonService"/>
<bean id="userService1" factory-bean="commonService" factory-method="createUserService" />
对应的CommonService的类为:
public class CommonService {
public UserService createUserService() {
return new UserService();
}
}
Spring发现当前BeanDefinition方法设置了工厂方法后,就会区分这两种方式,然后调用工厂方法得到对象。
值得注意的是,我们通过@Bean所定义的BeanDefinition,是存在factoryMethod和factoryBean的,也就是和上面的方式二非常类似,@Bean所注解的方法就是factoryMethod,AppConfig对象就是factoryBean。如果@Bean所所注解的方法是static的,那么对应的就是方式一。
5.3 推断构造方法
createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
推断完构造方法后,就会使用构造方法来进行实例化了。
额外的,在推断构造方法逻辑中除开会去选择构造方法以及查找入参对象意外,会还判断是否在对应的类中是否存在使用@Lookup注解了方法。如果存在则把该方法封装为LookupOverride对象并添加到BeanDefinition中。
在实例化时,如果判断出来当前BeanDefinition中没有LookupOverride,那就直接用构造方法反射得到一个实例对象。如果存在LookupOverride对象,也就是类中存在@Lookup注解了的方法,那就会生成一个代理对象。
@Lookup注解就是方法注入,使用demo如下:
@Component
public class UserService {
private OrderService orderService;
public void test() {
OrderService orderService = createOrderService();
System.out.println(orderService);
}
@Lookup("orderService")
public OrderService createOrderService() {
return null;
}
}
6. BeanDefinition的后置处理
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
1.执行BeanDefinition的后置处理
2.Object exposedObject = bean; 没有进行依赖注入的bean;
3.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
3.1 实例化后 --》 bpp InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 只有他有 postProcessAfterInstantiation
作用就是填充属性然后返回Bean,使得Bean不经历下面的填充属性方法
3.2填充属性 --》 使用spring自带的方法 autowireByType 、autoWireByName填充属性
3.3 填充属性后 --》 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 中的 postProcessPropertyValues 、
postProcessProperties 进行依赖注入 @AutoWire 和@Resource
4.exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
initializeBean(){
4.1、执行Aware : invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
4.2、初始化前 : wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
4.3、初始化: invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
4.3.1 执行initLuBan 方法
4.4、初始化后 AOP wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
doCreateBean中的代码片段:
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 运行修改合并好了的BeanDefinition
// 这里会查找@Autowired的注入点(InjectedElement),并把这些注入点添加到mbd的属性externallyManagedConfigMembers中
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
对bd进行操作 BeanDefinition的后置处理 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
Bean对象实例化出来之后,接下来就应该给对象的属性赋值了。在真正给属性赋值之前,Spring又提供了一个扩展点MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(),可以对此时的BeanDefinition进行加工,比如:
@Component
public class LubanMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
if (beanName.equals("userService")) {
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(User.class); // 没用,已经初始化过了 不能用
beanDefinition.setInitMethodName("initLuBan");
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("name","xxx");
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("userService")){
System.out.println("初始化前");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("userService")){
System.out.println("初始化后");
}
return bean;
}
}
@component
public class UserService{
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
public void initLuBan(){
System.out.println("UserService's initLuBan method by MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor");
}
}
public Class Test(){
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
}
}
// 打印结果:
//初始化前
//UserService's initLuBan method by MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
//初始化后
//在beanDefinition的后置处理器进行赋值
解析:
前置知识:我们需要知道它的调用位置在哪里
1.执行BeanDefinition的后置处理
2.Object exposedObject = bean; 没有进行依赖注入的bean;
3.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //填充属性 @Autowired
4.exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
initializeBean(){
4.1、执行Aware : invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
4.2、初始化前 : wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
4.3、初始化: invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
4.3.1 执行initLuBan 方法
4.4、初始化后 AOP wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
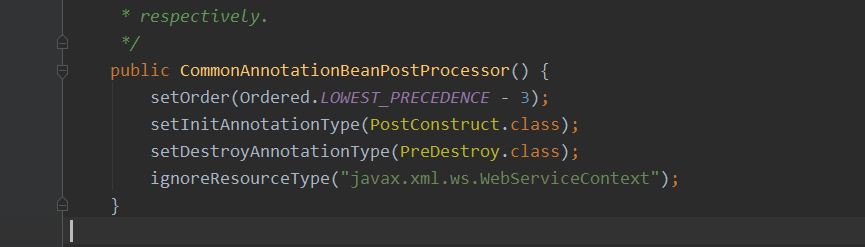
说明初始化前后会执行initLuBan 方法( 其实可以叫做是初始化方法)
initLuBan 的执行呢, 我们看一下 是在invokeInitMethods 初始化 方法中执行的
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
//============================================================================省略
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); // init-method=""
}
}
}
RootBeanDefinition#isExternallyManagedInitMethod()
public boolean isExternallyManagedInitMethod(String initMethod) {
synchronized (this.postProcessingLock) {
return (this.externallyManagedInitMethods != null &&
this.externallyManagedInitMethods.contains(initMethod));
}
}
查看this.externallyManagedInitMethods 的add方法在RootBeanDefinition#registerExternallyManagedInitMethod执行
public void registerExternallyManagedInitMethod(String initMethod) {
synchronized (this.postProcessingLock) {
if (this.externallyManagedInitMethods == null) {
this.externallyManagedInitMethods = new HashSet<>(1);
}
this.externallyManagedInitMethods.add(initMethod);//=======================
}
}
而registerExternallyManagedInitMethod 方法在InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#checkConfigMembers方法中
public void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Set<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.initMethods.size());
for (LifecycleElement element : this.initMethods) { //====================================
String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier)) {
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier);//=================
checkedInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered init method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
Set<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.destroyMethods.size());
for (LifecycleElement element : this.destroyMethods) {
String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier)) {
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier);
checkedDestroyMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered destroy method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
this.checkedInitMethods = checkedInitMethods;
this.checkedDestroyMethods = checkedDestroyMethods;
}
然后查看this.initMethods的赋值地方InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildLifecycleMetadata
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) {
return this.emptyLifecycleMetadata;
}
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>(); // ====================================
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
});
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);//=======================================
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata :
new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
}
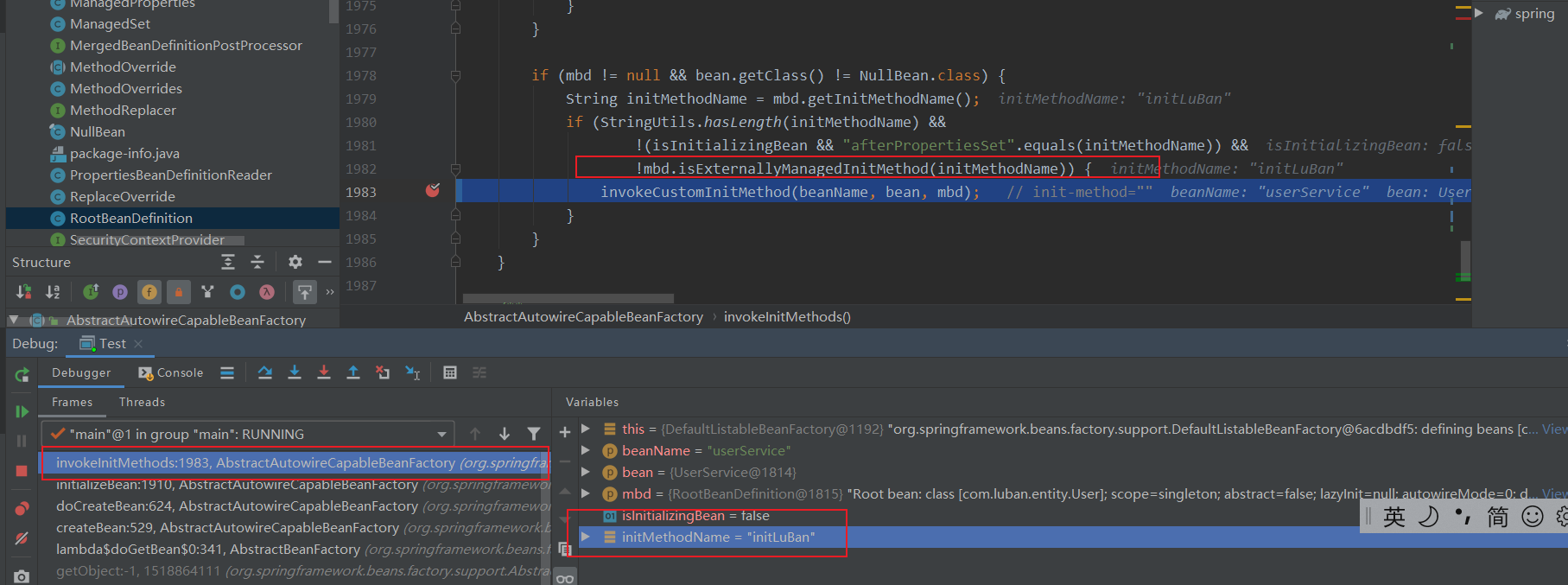
最后把这句代码挑出来就是:currInitMethods
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)
得出结论:
public boolean isExternallyManagedInitMethod(String initMethod) {
synchronized (this.postProcessingLock) {
return (this.externallyManagedInitMethods != null &&
this.externallyManagedInitMethods.contains(initMethod));
}
}
上面的isExternallyManagedInitMethod方法是为了确保:
- isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)表示
- 如果userService实现了InitializingBean,我们在userService中定义的方法initLuBan 不是afterPropertiesSet()方法。
- initLuBan 方法上面没有@PostConstruct注解
最后调用反射调用initLuBan 方法 >
重要的点:在Spring源码中,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor就是一个MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor,它的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()中会去查找注入点,并缓存在AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor对象的一个Map中(injectionMetadataCache)。
作用:给对象属性赋值,给对象添加初始化方法
7.实例化后:
前置知识:我们需要知道它的调用位置在哪里?
1.执行BeanDefinition的后置处理
2.Object exposedObject = bean; 没有进行依赖注入的bean;
3.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
3.1 实例化后 --》 bpp InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 只有他有 postProcessAfterInstantiation
作用就是填充属性然后返回Bean,使得Bean不经历下面的填充属性方法
3.2填充属性 --》 使用spring自带的方法 autowireByType 、autoWireByName填充属性
3.3 填充属性后 --》 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 中的 postProcessPropertyValues 、
postProcessProperties 进行依赖注入 @AutoWire 和@Resource
4.exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
initializeBean(){
4.1、执行Aware : invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
4.2、初始化前 : wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
4.3、初始化: invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
4.3.1 执行initLuBan 方法
4.4、初始化后 AOP wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
//=====================================实列化后操作开始========================================
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 可以提供InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,控制对象的属性注入
// 我们可以自己写一个InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,然后重写postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,那么则不会进行属性填充了
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}//================================实列化后操作结束========================
// 是否在BeanDefinition中设置了属性值
// PropertyValues 是一个(Map) key:属性的名字 value:属性值
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// autowire属性 可以理解为xml的自动注入 ,不使用xml,autoWire的属性是默认关闭的
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode(); // BeanDefinition AutowireMode
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
// by_name是根据根据属性名字找bean
// by_type是根据属性所对应的set方法的参数类型找bean
// 找到bean之后都要调用set方法进行注入
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
// 总结一下
// 其实就是Spring自动的根据某个类中的set方法来找bean,byName就是根据某个set方法所对应的属性名去找bean
// byType,就是根据某个set方法的参数类型去找bean
// 注意,执行完这里的代码之后,这是把属性以及找到的值存在了pvs里面,并没有完成反射赋值
}
// 执行完了Spring的自动注入之后,就开始解析@Autowired,这里叫做实例化回调
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
// @AUtowired注解的 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// @Resource注解的 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 调用BeanPostProcessor分别解析@Autowired、@Resource、@Value,得到属性值
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// pvs存的就是属性已经对应的值
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
作用: 程序员可以自己写一个InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,然后重写postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false
那么3.2 填充属性 --》 使用spring自带的方法 autowireByType 、autoWireByName填充属性
、 3.3 填充属性后 --》 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 中的 postProcessPropertyValues
都不会执行
3.2 代码demo
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanpostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("userService")){
UserService userService = (UserService) bean;
userService.setName("通过MyInstantationAwareBeanPostProcess 设置的name属性值");
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
@Component
public class UserService{
private String name;
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("测试4.1 执行实例化后的方法返回false 之后 orderService:" + orderService);
}
public void initLuBan(){
System.out.println("UserService's initLuBan method by MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor");
}
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
System.out.println("name " + userService.getName());
userService.test();
}
// 打印
// name 通过MyInstantationAwareBeanPostProcess 设置的name属性值
// 测试4.1 执行实例化后的方法返回false 之后 orderService:null
修改MyInstantiationAwareBeanpostProcessor 此时
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanpostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("userService")){
UserService userService = (UserService) bean;
userService.setName("通过MyInstantationAwareBeanPostProcess 设置的name属性值");
}
return true;
}
}
结果如下:orderService属性注入成功
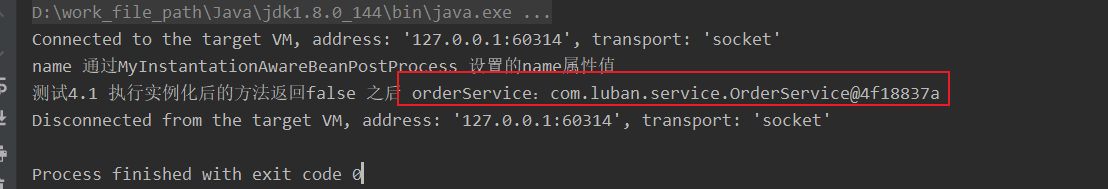
8. 自动注入
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
//=====================================实列化后操作开始========================================
// 省略
//================================实列化后操作结束========================
// 是否在BeanDefinition中设置了属性值
// PropertyValues 是一个(Map) key:属性的名字 value:属性值
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// autowire属性 可以理解为xml的自动注入 ,不使用xml,autoWire的属性是默认关闭的
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode(); // BeanDefinition AutowireMode
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
// by_name是根据根据属性名字找bean
// by_type是根据属性所对应的set方法的参数类型找bean
// 找到bean之后都要调用set方法进行注入
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
// 总结一下
// 其实就是Spring自动的根据某个类中的set方法来找bean,byName就是根据某个set方法所对应的属性名去找bean
// byType,就是根据某个set方法的参数类型去找bean
// 注意,执行完这里的代码之后,这是把属性以及找到的值存在了pvs里面,并没有完成反射赋值
}
// 执行完了Spring的自动注入之后,就开始解析@Autowired,这里叫做实例化回调
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
// @AUtowired注解的 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// @Resource注解的 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 调用BeanPostProcessor分别解析@Autowired、@Resource、@Value,得到属性值
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// pvs存的就是属性已经对应的值
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
- int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
- BeanDefinition AutowireMode属性是自动关闭的,不使用xml的自动注入 ,autoWire的属性是默认关闭的
spring自动注入方式:byTye 、ByName
1.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 方式的使用
1、 本人的笔记错误代码展示
@Component
public class UserService{
private OrderService orderService;
public OrderService getOrderService() {
return orderService;
}
@Bean(autowire = Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public void setOrderService(OrderService orderService) {
this.orderService = orderService;
}
}
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
}
显示报错:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'setOrderService' defined in class path resource [com/luban/service/UserService.class]: Unsatisfied dependency expressed through method 'setOrderService' parameter 0: Ambiguous argument values for parameter of type [com.luban.service.OrderService] - did you specify the correct bean references as arguments?
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver.createArgumentArray(ConstructorResolver.java:857)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver.instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(ConstructorResolver.java:600)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1409)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBeanInstance(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1232)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:574)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:529)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:341)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:243)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:339)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:204)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:917)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:921)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:574)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.<init>(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.java:107)
at com.luban.Test.main(Test.java:28)
2.使用spring注入,注入方式为byType
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
public class UserService{
private OrderService orderService;
public OrderService getOrderService() {
return orderService;
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(autowire= Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public UserService userService(){
return new UserService();
}
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
// 打印com.luban.service.OrderService@7f3b84b8
使用的是autoWire = byType
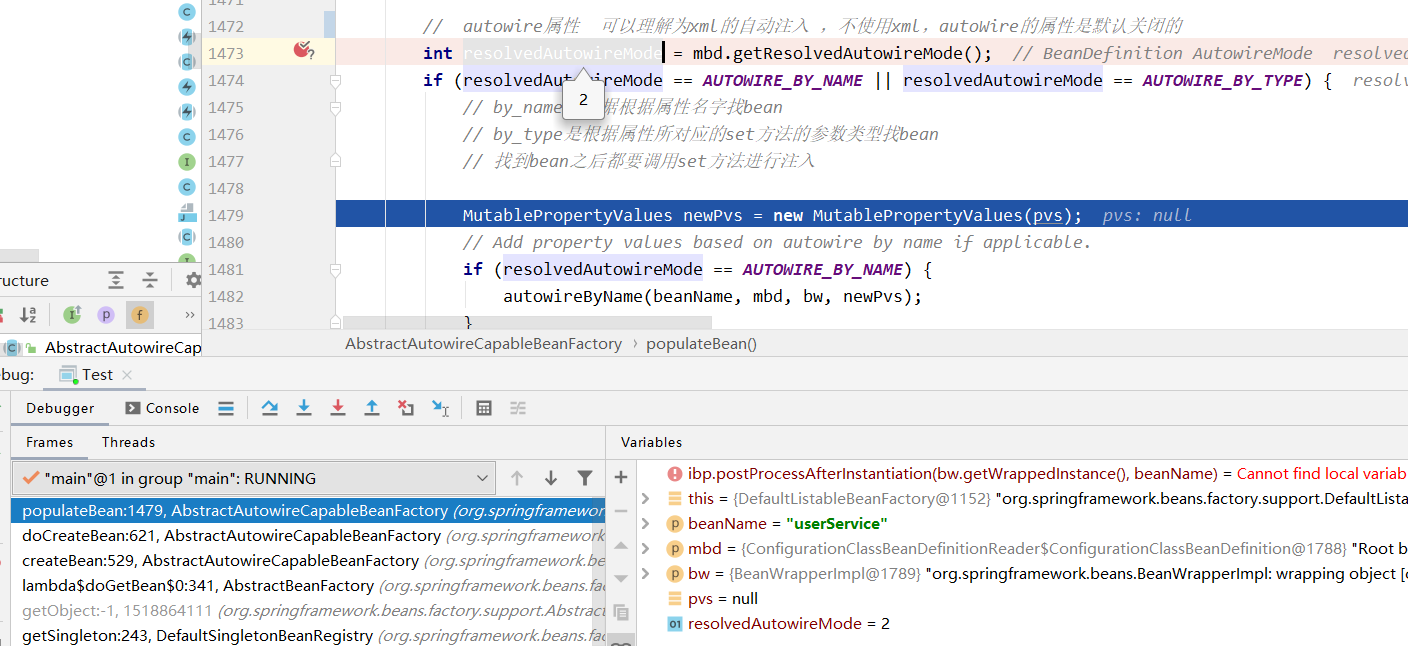
修改修改AppConfig 类,此时orderService 不注入
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
// @Bean(autowire= Autowire.BY_TYPE)
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
return new UserService();
}
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
// 打印null
2.xml方式的使用
9. 处理属性
通过 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 中的 postProcessPropertyValues 进行属性注入,
这个步骤中,就会处理@Autowired、@Resource、@Value等注解,也是通过InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties()扩展点来实现的,比如我们甚至可以实现一个自己的自动注入功能,比如:
@Component
public class ZhouyuInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userService".equals(beanName)) {
for (Field field : bean.getClass().getFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(ZhouyuInject.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(bean, "1ja23");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
return pvs;
}
}
关于@Autowired、@Resource、@Value的底层源码,会在后续的依赖注入课程中详解
10. 执行Aware
这些Aware回调函数在哪里执行呢?
1.执行BeanDefinition的后置处理
2.Object exposedObject = bean; 没有进行依赖注入的bean;
3.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
3.1 实例化后 --》 bpp InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 只有他有 postProcessAfterInstantiation
作用就是填充属性然后返回Bean,使得Bean不经历下面的填充属性方法
3.2填充属性 --》 使用spring自带的方法 autowireByType 、autoWireByName填充属性
3.3 填充属性后 --》 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 中的 postProcessPropertyValues 、
postProcessProperties 进行依赖注入 @AutoWire 和@Resource
4.exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
initializeBean(){
4.1、执行Aware : invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
4.2、初始化前 : wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
4.3、初始化: invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
4.3.1 执行initLuBan 方法
4.4、初始化后 AOP wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
完成了属性赋值之后,Spring会执行一些回调,包括:
- BeanNameAware:回传beanName给bean对象。
- BeanClassLoaderAware:回传classLoader给bean对象。
- BeanFactoryAware:回传beanFactory给对象。
代码位置:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 4.1、执行Aware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 4.2、初始化前
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 4.3、初始化
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 4.4、初始化后 AOP ()
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
demo1: 演示BeanNameAware 功能
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
public class UserService implements BeanNameAware {
private String beanName;
private OrderService orderService;
public OrderService getOrderService() {
return orderService;
}
public void setOrderService(OrderService orderService) {
this.orderService = orderService;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println(orderService);
System.out.println(beanName);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName = name;
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(autowire= Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public UserService getUserService12345(){
return new UserService();
}
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("getUserService12345");
userService.test();
}
// 打印
// com.luban.service.OrderService@57a3af25
// getUserService12345
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(autowire= Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public UserService getUserService12345(){
return new UserService();
}
}
疑惑不解的地方: 能获取到beanName的名字很正常,就是不知道为啥beanName="getUserService12345"怎样来的,应该是跟生命周期中,扫描配置项目生成beanDefinition有关。传送门1.3spring为beanDefintion设置beanName属性
这边的代码我一定要找到
等着跟着依赖注入相关代码一起研究???????????????????????
demo2:
将demo1: 演示BeanNameAware 功能的代码中UserService.java修改如下
public class UserService implements BeanFactoryAware {
private OrderService orderService;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
public void test(){
System.out.println(orderService);
System.out.println(beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
// 打印
null
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@17579e0f: defining beans [org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor,org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory,appConfig,myInstantiationAwareBeanpostProcessor,user,orderService,getUserService12345]; root of factory hierarchy
很明显这边因为this.orderService 没有提供setter方法,所以spring 没有给this.orderService 注入属性值
this.beanFactory 提供了setter()方法,所以我们使用spring的byType 就能够注入
所以spring的byType是依靠属性的setter方法
11. 初始化前
dem3 : 获取ApplicationContext
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages= "com.luban")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(autowire= Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public UserService getUserService12345(){
return new UserService();
}
}
public class UserService implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void test(){
System.out.println(applicationContext);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for ( String beanDefinitionName: applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
sb.append(beanDefinitionName);
sb.append("
");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
public class Test{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("getUserService12345");
userService.test();
}
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:59196', transport: 'socket'
org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@2aafb23c, started on Wed Sep 15 18:51:17 CST 2021
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
appConfig
myInstantiationAwareBeanpostProcessor
user
orderService
getUserService12345
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:59196', transport: 'socket'
Process finished with exit code 0
我们看代码,UserService 实现了ApplicationContextAware ,但是这个回调方法并没有在invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
中回调。它是在BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法执行的
1.在spring容器初始化过程中,会执行AbstractApplicationContext类的prepareBeanFactory方法,这里面会创建一个bean后置处理器ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,如下图红框所示:
2.在bean被初始化之前,所有的bean后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法都会被执行,如下图红框所示:
3.由以上两步可以确定:对于每个bean后置处理器来说,它的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法会在每个bean的初始化之前被调用一次;
4.来看看ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,按照前面的分析,该方法在每个bean被初始化之前都会被执行,如下图红框所示,invokeAwareInterfaces方法会被调用,这是我们要关注的重点:
5.展开invokeAwareInterfaces方法看看:
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(
new EmbeddedValueResolver(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory()));
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
在Spring源码中:
- InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor会在初始化前这个步骤中执行@PostConstruct的方法,
- ApplicationContextAwareProcessor会在初始化前这个步骤中进行其他Aware的回调:
- EnvironmentAware:回传环境变量
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware:回传占位符解析器
- ResourceLoaderAware:回传资源加载器
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware:回传事件发布器
- MessageSourceAware:回传国际化资源
- ApplicationStartupAware:回传应用其他监听对象,可忽略
- ApplicationContextAware:回传Spring容器ApplicationContext
12. 初始化
- 查看当前Bean对象是否实现了InitializingBean接口,如果实现了就调用其afterPropertiesSet()方法
- 执行BeanDefinition中指定的初始化方法 ,, 看一下 6.BeanDefinition的后置处理
13. 初始化后
这是Bean创建生命周期中的最后一个步骤,也是Spring提供的一个扩展点:BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),比如:
@Component
public class ZhouyuBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userService".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("初始化后");
}
return bean;
}
}
可以在这个步骤中,对Bean最终进行处理,Spring中的AOP就是基于初始化后实现的,初始化后返回的对象才是最终的Bean对象。
总结BeanPostProcessor
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
- 实例化
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation()
- 自动注入
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties()
- Aware对象
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()
- 初始化
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()


