// 1.长字符串
// 1.1
let longString1 = "This is a very long string which needs " +
"to wrap across multiple lines because " +
"otherwise my code is unreadable.";
// 1.2 反斜杠
let longString2 = "This is a very long string which needs
to wrap across multiple lines because
otherwise my code is unreadable.";
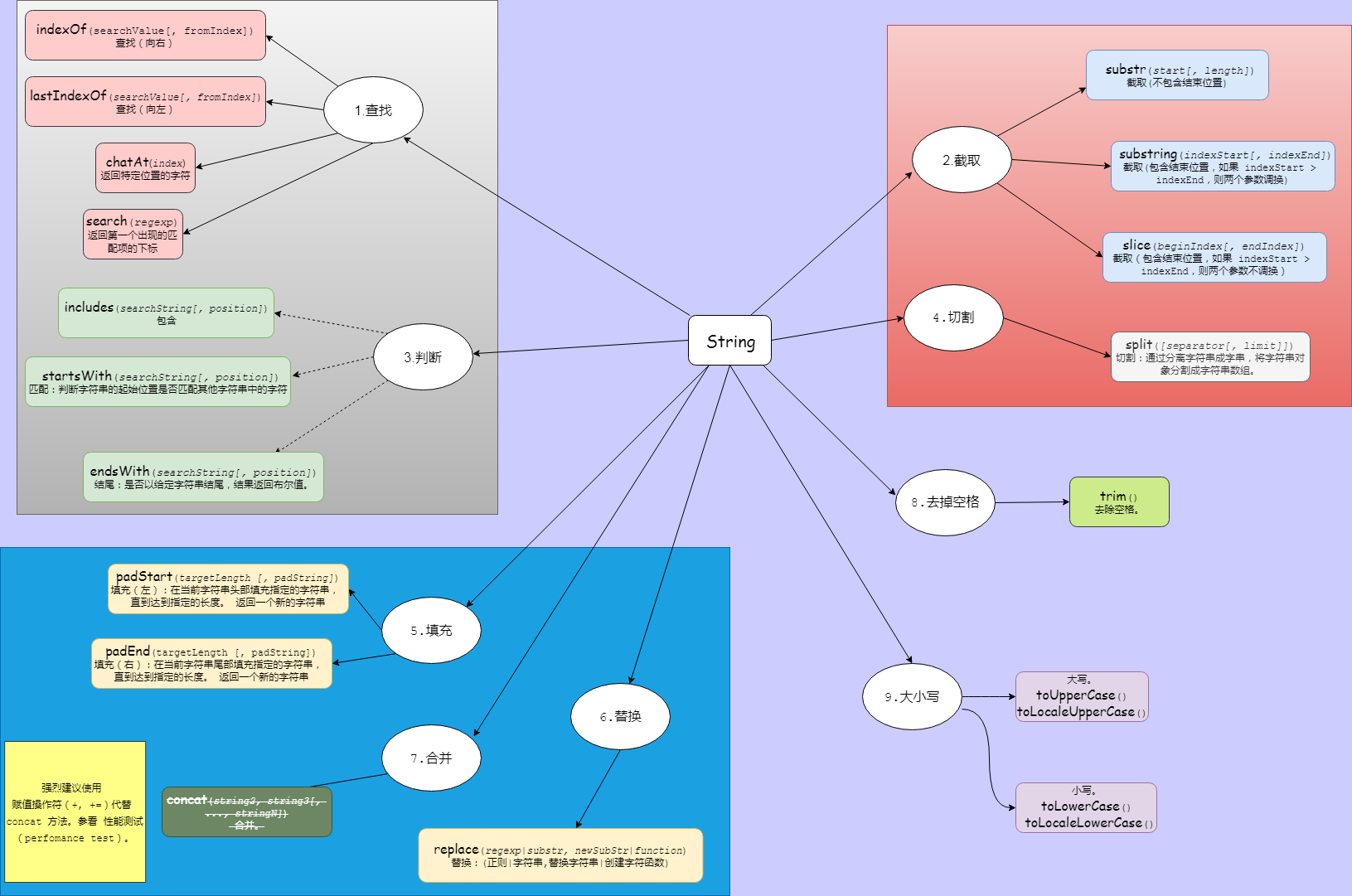
// 2.常用方法
// 2.1 查找
{
// 2.1.1 indexOf(searchValue[, fromIndex])
// 查找(向右):从字符串对象中返回首个被发现的给定值的索引值,如果没有找到则返回-1。
"Blue Whale".indexOf("Blute"); // 返回 -1
"Blue Whale".indexOf("Whale", 0); // 返回 5
"Blue Whale".indexOf("Whale", 3); // 返回 5 fromIndex 大于 0 且小于等于 str.length 时,返回 fromIndex;
"Blue Whale".indexOf("Whale", 5); // 返回 5,这里1 - 5 都返回 5
// 2.1.2 lastIndexOf(searchValue[, fromIndex])
// 查找(向左):从字符串对象中返回最后一个被发现的给定值的索引值,如果没有找到则返回-1。
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a'); // returns 3 (没有指明fromIndex则从末尾l处开始反向检索到的第一个a出现在l的后面,即index为3的位置)
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a', 2); // returns 1(指明fromIndex为2则从n处反向向回检索到其后面就是a,即index为1的位置)
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a', 0); // returns -1(指明fromIndex为0则从c处向左回向检索a发现没有,故返回-1)
'abab'.lastIndexOf('ab', 2) // returns 2 因为fromIndex只限制待匹配字符串的开头那一个
// 2.1.3 charAt()
// 返回特定位置的字符。
var charAt = 'cat'.charAt(1); // returns "a"
console.log("charAt() 从字符串中获取单个字符:" + charAt);
// 2.1.4 search(regexp)
// 对正则表达式和指定字符串进行匹配搜索,返回第一个出现的匹配项的下标。
var str = "hey JudE";
var re = /[A-Z]/g;
var re2 = /[.]/g;
console.log(str.search(re)); // returns 4, which is the index of the first capital letter "J"
console.log(str.search(re2)); // returns -1 cannot find '.' dot punctuation
// 2.1.5 match()
// 方法检索返回一个字符串匹配正则表达式的的结果。
// 参考正则表达式:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Regular_Expressions
}
// 2.2 截取
{
// 2.2.1 substr(start[, length])
// 截取(不包含结束位置)
var str = "abcdefghij";
console.log("(1,2): " + str.substr(1, 2)); // (1,2): bc
console.log("(-3,2): " + str.substr(-3, 2)); // (-3,2): hi = (-3+str.length,2)
// 2.2.2 substring(indexStart[, indexEnd])
// 截取(包含结束位置,如果 indexStart > indexEnd,则两个参数调换)
var anyString = "Mozilla";
console.log(anyString.substring(0, 3)); // 输出 "Moz"
console.log(anyString.substring(3, 0)); // 输出 "Moz",indexStart > indexEnd,两个参数调换
console.log(anyString.substring(4, 7)); // 输出 "lla"
// 2.2.3 slice(beginIndex[, endIndex])
// 截取(包含结束位置,如果 indexStart > indexEnd,则两个参数不调换)
var strSlice = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.';
var s = strSlice.slice(31); // the lazy dog.
strSlice.slice(31, 43); // "the lazy do"
}
//2.3 判断
{
//2.3.1 includes(searchString[, position])
// 包含。
'Blue Whale'.includes('blue'); // false
// 2.3.2 startsWith(searchString[, position])
// 匹配:判断字符串的起始位置是否匹配其他字符串中的字符。
var str = "To be, or not to be, that is the question.";
str.startsWith("To be"); // true
str.startsWith("not to be"); // false
str.startsWith("not to be", 10); // true
//2.3.3 endsWith()
// 结尾:是否以给定字符串结尾,结果返回布尔值。
var str = "To be, or not to be, that is the question.";
str.endsWith("question."); // true
str.endsWith("to be"); // false
str.endsWith("to be", 19); // true
}
// 2.4 切割
{
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String/split
// split([separator[, limit]])
// @separator 可以是一个字符串或正则表达式
// @limit 限定返回的分割片段数量
// 切割:通过分离字符串成字串,将字符串对象分割成字符串数组。
var str = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.';
var words1 = str.split();
console.log(words1);
// ["The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."]
var words2 = str.split('');
console.log(words2);
//(44) ["T", "h", "e", " ", "q", "u", "i", "c",......"d", "o", "g", "."]
var words3 = str.split(' ');
console.log(words3);
//(9) ["The", "quick", "brown", "fox", "jumps", "over", "the", "lazy", "dog."]
var words4 = str.split(' ', 3);
console.log(words4);
//(3) ["The", "quick", "brown"]
}
//2.5 填充
{
// 2.5.1 padStart(targetLength [, padString])
// @targetLength 当前字符串需要填充到的【目标长度】。如果这个数值小于当前字符串的长度,则返回当前字符串本身。
// @padString 填充字符串。如果字符串太长,超过了目标长度,则只保留最左侧的部分,其他部分会被截断。
// 填充(左):在当前字符串头部填充指定的字符串, 直到达到指定的长度。 返回一个新的字符串。
'abc'.padStart(10); // " abc" -- 总共长度为10
'abc'.padStart(10, "foo"); // "foofoofabc"
'abc'.padStart(6, "123465"); // "123abc"
'abc'.padStart(8, "0"); // "00000abc"
'abc'.padStart(1); // "abc"
// 2.5.2 padEnd(targetLength [, padString])
// @targetLength 当前字符串需要填充到的【目标长度】。如果这个数值小于当前字符串的长度,则返回当前字符串本身。
// @padString 填充字符串。如果字符串太长,超过了目标长度,则只保留最左侧的部分,其他部分会被截断。
// 填充(右):在当前字符串尾部填充指定的字符串, 直到达到指定的长度。 返回一个新的字符串。
'abc'.padEnd(10); // "abc "
'abc'.padEnd(10, "foo"); // "abcfoofoof"
'abc'.padEnd(6, "123456"); // "abc123"
'abc'.padEnd(1); // "abc" 如果这个数值小于当前字符串的长度,则返回当前字符串本身。
}
// 2.6 替换
{
// replace(regexp|substr, newSubStr|function)
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String/replace
// @regexp (pattern) 一个RegExp 对象或者其字面量。
// @substr(pattern) 一个将被 newSubStr 替换的 字符串。(仅第一个匹配项会被替换。)
// @newSubStr(replacement) 用于替换掉第一个参数在原字符串中的匹配部分的字符串。该字符串中可以内插一些特殊的变量名。
// 替换字符串:$$,$&,$`,$',$n
// @function (replacement) 一个用来创建新子字符串的函数,该函数的返回值将替换掉第一个参数匹配到的结果。
// 参数:@match, p1, p2, p3, offset, string
var p = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy [dog]. If the [dog] reacted, was it really lazy?';
var regex = /dog/gi; //全局替换(g)和忽略大小写(i)
console.log(p.replace(regex, 'ferret'));
// expected output: "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy [ferret]. If the [ferret] reacted, was it really lazy?"
console.log(p.replace('dog', 'monkey'));
// expected output: "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy [monkey]. If the [dog] reacted, was it really lazy?"
// 第2个括号的dog未被替换
}
//2.7 合并
{
// 强烈建议使用 赋值操作符(+, +=)代替 concat 方法。参看 性能测试(perfomance test)。
// concat(string2, string3[, ..., stringN])
// 合并。
var hello = "Hello, ";
console.log(hello.concat("Kevin", " have a nice day.")); /* Hello, Kevin have a nice day. */
}
//2.8 去掉空格
{
// trim()
// 去除空格。
}
//2.9 大小写
{
// 小写。
// 2.9.1 toLowerCase()
// 2.9.2 toLocaleLowerCase()
// 大写。
// 2.9.3 toUpperCase()
// 2.9.4 toLocaleUpperCase()
}
