
一道较简单的题目,但借此机会要好好熟悉一下Hashset和Hashmap的基本操作。
class Solution { public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) { HashSet<Integer> set=new HashSet<>(); for(int num :nums) { if(!set.add(num)) { return true; } } return false; } }

这里扯一点集合框架的东西
最初大家都是用的数组:
int[] num1=new int[10];//带大小 int[] num2={0,1,2,3,4};//直接
int[][] num3=new int[5][5];
int[][] num4={{0,1},{1,2}};
sout(num1.length); sout(num1[0]); for(int num:num1) { sout(num); }
但是数组存在一些问题:
- 是定长的,无法动态调整大小
- 不好删除某个元素(实际上还是定长的问题)
所以有了集合框架,主要就是List,Set,Map三种,继承关系如下:
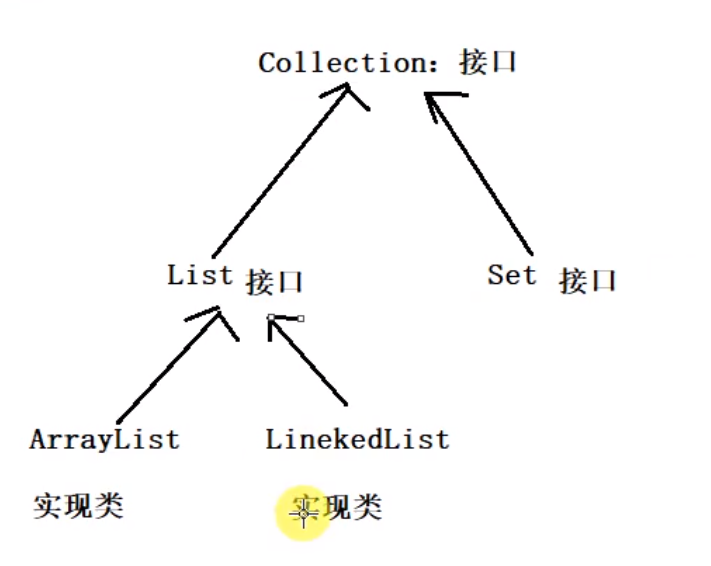
最基本的一个ArrayList的创建:这里的ArrayList中每个元素的类型实际上是Object类
ArrayList arrayList=new ArrayList();
当我们使用多态时,会变成这样:
List arrayList=new ArrayList();
当我们需要规范集合中元素类型时,使用泛型(先写new再ctrl+alt+v补全声明):
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();