1.使用多线程,模拟龟兔赛跑的场景。
按照以往的故事经验,正确的故事逻辑顺序当然是因为兔子不把乌龟放在眼里,松懈了最终输了比赛。我的设定也是如此,假定乌龟每秒跑五米(是有点快但为了线程的运行速度来看还是写快点)兔子的速度为每秒十米。但是兔子在跑到一半休息了一点五秒。
代码如下:
package com.company; public class ThreadTest1 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ try { for(int i = 1;i<=100;i= i+5){ System.out.println("乌龟跑了"+i+"米"); Thread.sleep(1000); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; public class ThreadTest2 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ try { for(int j = 1;j<=100;j=j+10){ System.out.println("兔子跑了"+j+"米"); Thread.sleep(1000); if(j==51){ Thread.sleep(15000); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; import javax.naming.Name; public class ThreadMain { static int a = 200; public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest1 threadTest1 = new ThreadTest1(); ThreadTest2 threadTest2 = new ThreadTest2(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(threadTest1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadTest2); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }
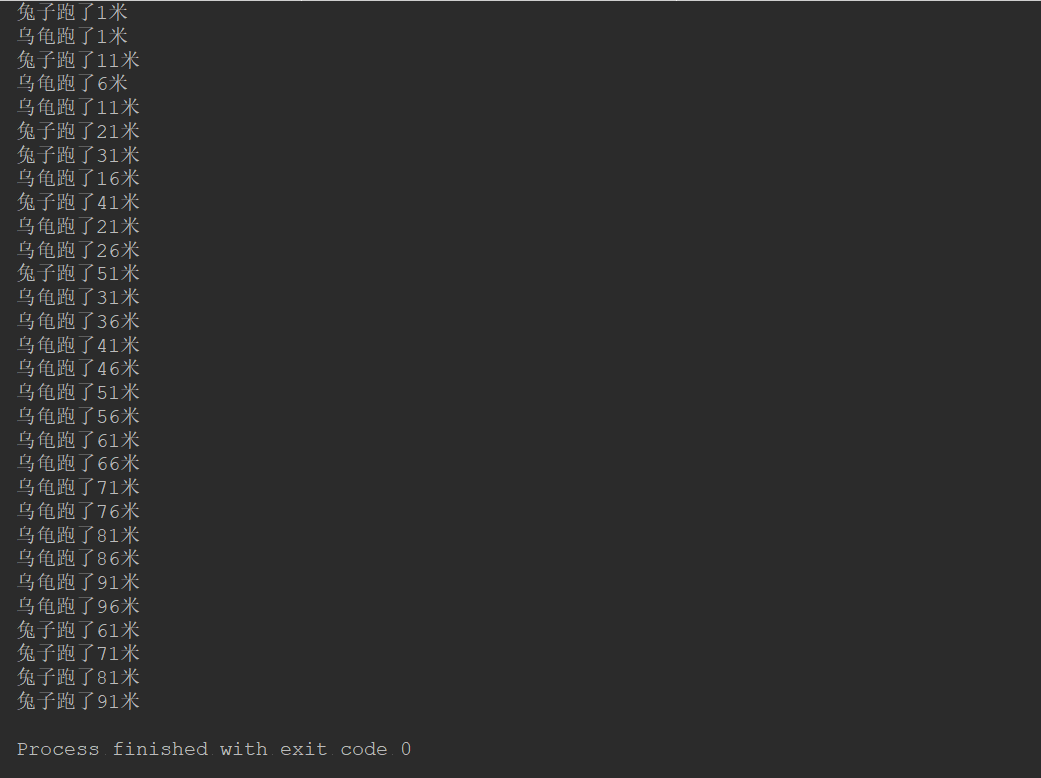
运行结果如下:
2、编写一个有两个线程的程序,第一个线程用来计算2~100000之间的素数的个数,第二个线程用来计算100000~200000之间的素数的个数,最后输出结果。
思路:确定一个数为素数,他只能将本身和1整除,即声明一个变量,写两个循坏嵌套,外面的循坏写数的范围,里面的循坏写除数,每当数能将它的除数整除,变量加1,如果最后变量的值为2即确定此数为素数
package com.company; public class ThreadTest1 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int i=2;i<=100000;i++){ int a = 0; for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ if(i%j==0){ a++; } } if(a==2)//素数只能整除1和它本身,所以a=2时说明该数为素数 System.out.println("线程1========"+i); } } }
package com.company; public class ThreadTest2 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int k=100000;k<=200000;k++){ int b = 0; for(int l=1;l<=k;l++){ if(k%l==0){ b++; } } if(b==2)//素数只能整除1和它本身,所以a=2时说明该数为素数 System.out.println("线程2======"+k); } } }
package com.company; import javax.naming.Name; public class ThreadMain { static int a = 200; public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest1 threadTest1 = new ThreadTest1(); ThreadTest2 threadTest2 = new ThreadTest2(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(threadTest1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadTest2); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }
结果片段:

3、使用多线程实现多个文件同步复制功能,并在控制台显示复制的进度,进度以百分比表示。例如:把文件A复制到E盘某文件夹下,在控制台上显示“XXX文件已复制10%”,“XXX文件已复制20%”……“XXX文件已复制100%”,“XXX复制完成!”
代码如下,设置每次截取代码长度除以文件总长度得到文件复制百分比,使用“DecimalFormat”类中的format方法将得到的数字乘以100并显示为百分数。
1 package com.company; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.text.DecimalFormat; 5 6 public class CopyFile extends Thread { 7 8 public File oldFile; 9 public File newFile; 10 11 public CopyFile(String oldFile,String newFile) { 12 this.oldFile = new File(oldFile); 13 this.newFile = new File(newFile); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void run() { 18 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; 19 FileInputStream fileInputStream =null; 20 try { 21 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFile); 22 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(oldFile); 23 byte[] b = new byte[1024]; 24 int length = 0;//返回每次读取的数据长度 25 long l = oldFile.length();//文件的长度 26 double temp = 0;// 27 DecimalFormat decimalFormat = new DecimalFormat("%"); 28 while ((length = fileInputStream.read(b))!=-1){ 29 fileOutputStream.write(b,0,length); 30 temp += length;//将每次读到的数据进行累加 31 double d = temp/l; 32 int dd = (int) d; 33 if(dd%10==0){ 34 System.out.println("文件已经复制"+decimalFormat.format(d)); 35 } 36 } 37 System.out.println(oldFile.getName()+"复制完成"); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 }finally { 41 try { 42 fileInputStream.close(); 43 fileOutputStream.close(); 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 } 50 }
package com.company; public class CopyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { CopyFile cf1 = new CopyFile("E:\a.txt", "D:\a.txt"); CopyFile cf2 = new CopyFile("E:\b.txt", "D:\b.txt"); CopyFile cf3 = new CopyFile("E:\c.txt", "D:\c.txt"); cf1.start(); cf2.start(); cf3.start(); } }
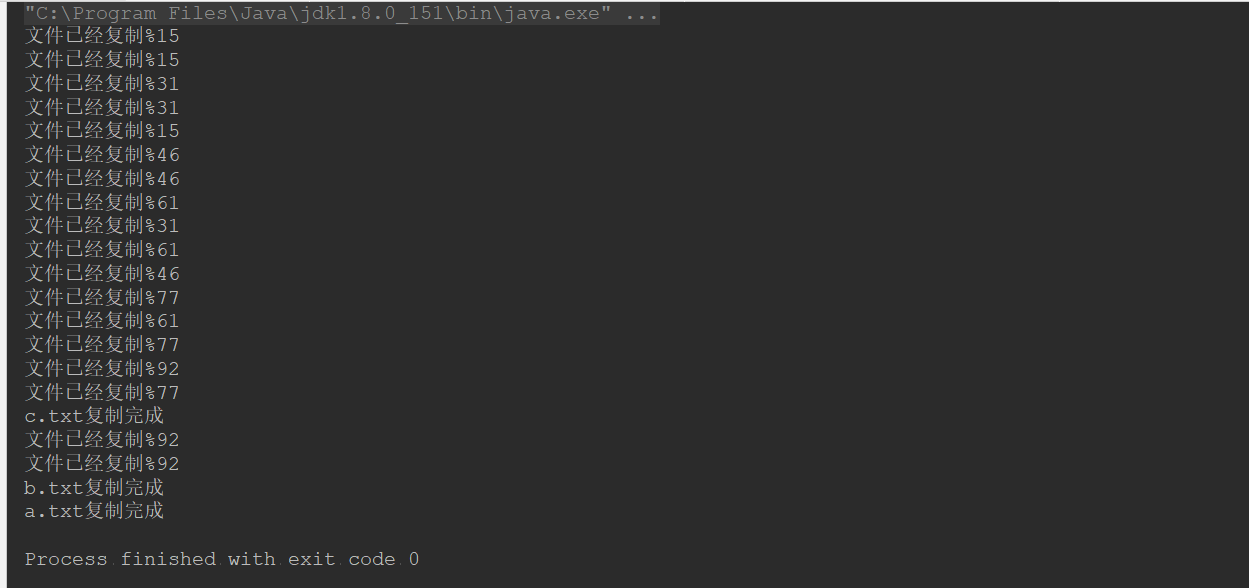
结果:
4、设计4个线程,其中两个线程每次对j增加1,另外两个线程对j每次减少1。考虑到线程的安全性写出程序。
分别书写四个线程对静态变量j进行更改,在每个线程中都加入synchronized (ThreadTest.class)保证线程安全,在更改未做完其他线程无法运行
代码如下
package com.company; public class ThreadTest1 implements Runnable { public void run() { try { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { synchronized (ThreadTest.class) { ThreadTest2.j++; System.out.println("线程1====="+ThreadTest2.j); Thread.sleep(100); }} } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; public class ThreadTest2 implements Runnable{ public static int j=500; public static int k; public void run(){ try { for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){ synchronized (ThreadTest.class){ j++; System.out.println("线程2====="+j); Thread.sleep(100); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; public class ThreadTest3 implements Runnable { public void run() { try { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { synchronized (ThreadTest.class) { ThreadTest2.j--; System.out.println("线程3=====" + ThreadTest2.j); Thread.sleep(100); }} } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; public class ThreadTest4 implements Runnable { public void run() { try { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { synchronized (ThreadTest.class) { ThreadTest2.j--; System.out.println("线程4=====" + ThreadTest2.j); Thread.sleep(100); }} } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.company; import javax.naming.Name; public class ThreadMain { static int a = 200; public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest1 threadTest1 = new ThreadTest1(); ThreadTest2 threadTest2 = new ThreadTest2(); ThreadTest3 threadTest3 = new ThreadTest3(); ThreadTest4 threadTest4 = new ThreadTest4(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(threadTest1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadTest2); Thread thread3 = new Thread(threadTest3); Thread thread4 = new Thread(threadTest4); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); thread4.start(); } }
截取部分结果如下:
