①基类——不变

②成员类——添加虚函数
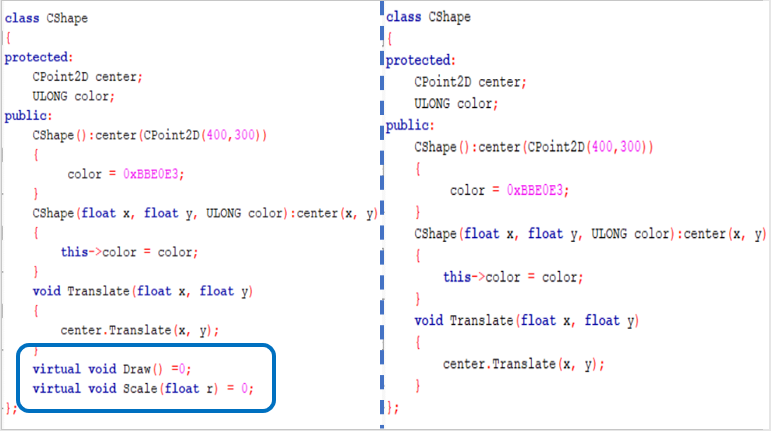
③长方形、椭圆形、三角形、甜甜圈——都不变

class CRectangle: public CShape { float len; float wid; public: CRectangle() { len = 300; wid = 200; color = 0xBBE0E3; } CRectangle(float x, float y, float len, float wid, ULONG color):CShape(x, y, color) { this->len = len; this->wid = wid; } void Draw() { CPoint2D v1(center.x-len/2, center.y+wid/2); CPoint2D v2(center.x+len/2, center.y-wid/2); setColor(color); fillRectangle(v1.x, v1.y, v2.x, v2.y); setColor(BLACK); rectangle(v1.x, v1.y, v2.x, v2.y); } void Scale(float r) { center.Scale(r); len = len*r; wid = wid*r; } }; class CEllipse: public CShape { protected: float xRadius; float yRadius; public: CEllipse() { xRadius = 150; yRadius = 100; } CEllipse(float x, float y, float rx, float ry, ULONG color):CShape(x, y, color) { this->xRadius = 0.5*rx; this->yRadius = 0.5*ry; } void Draw() { setColor(color); fillEllipse(center.x, center.y, xRadius, yRadius); setColor(BLACK); ellipse(center.x, center.y, xRadius, yRadius); } void Scale(float r) { center.Scale(r); xRadius = xRadius*r; yRadius = yRadius*r; } }; class CDonut: public CEllipse { float ratio; public: CDonut() { ratio = 0.5; } CDonut(float x, float y, float rx, float ry, float r, ULONG color):CEllipse(x, y, rx, ry, color) { this->ratio = r; } void Draw() { setColor(color); fillDonut(center.x, center.y, xRadius, yRadius, ratio); setColor(BLACK); donut(center.x, center.y, xRadius, yRadius, ratio); } }; class CTriangle:public CShape { float len; float wid; public: CTriangle() { len = 300; wid = 200; } CTriangle(float x, float y, float len, float wid, ULONG color):CShape(x, y, color) { this->len = len; this->wid = wid; } void Draw() { CPoint2D v1(center.x-len/2, center.y-wid/2); CPoint2D v2(center.x+len/2, center.y-wid/2); CPoint2D v3(center.x, center.y+wid/2); setColor(color); fillTriangle(v1.x, v1.y, v2.x, v2.y, v3.x, v3.y); setColor(BLACK); triangle(v1.x, v1.y, v2.x, v2.y, v3.x, v3.y); } void Scale(float r) { center.Scale(r); len = len*r; wid = wid*r; } };
④vector数组定义减少

⑤利用指针的方便开始了!

d=====( ̄▽ ̄*)b d=====( ̄▽ ̄*)b d=====( ̄▽ ̄*)b d=====( ̄▽ ̄*)b d=====( ̄▽ ̄*)b
1.虚函数
1.1 存在的问题
◼ 在不同形状类的成员函数调用中存在大量逻辑相似的重复代码
◼ 如果形状种类数进一步增加,将增大代码维护难度
1.2 定义
virtual 函数类型 函数表(形参表)
{
函数体;
}
1.3 注意
✓ 只有类的成员函数才能声明为虚函数
✓ 虚函数不能是静态成员函数,也不能是友元函数
✓ 若在基类中定义虚函数,在派生类中还需重新定义
✓ 构造函数不能是虚函数,析构函数可以是虚函数
1.4 纯虚函数

◼ 一般情况下,在基类中,是一个很抽象的概念,你也不会知道之后会有什么内容,所以{ }里一般不写,又简化为 = 0
函数体没有意义的时候用纯虚函数
◼ 一个类中一旦有了纯虚函数,就变成了抽象类,不能定义对象,因为定义之后系统会给对象自动分配内存空间,但是可以定义指针啊之类的,不占空间
CShape obj1; ❌ CShape *obj2; ✔
2.抽象类
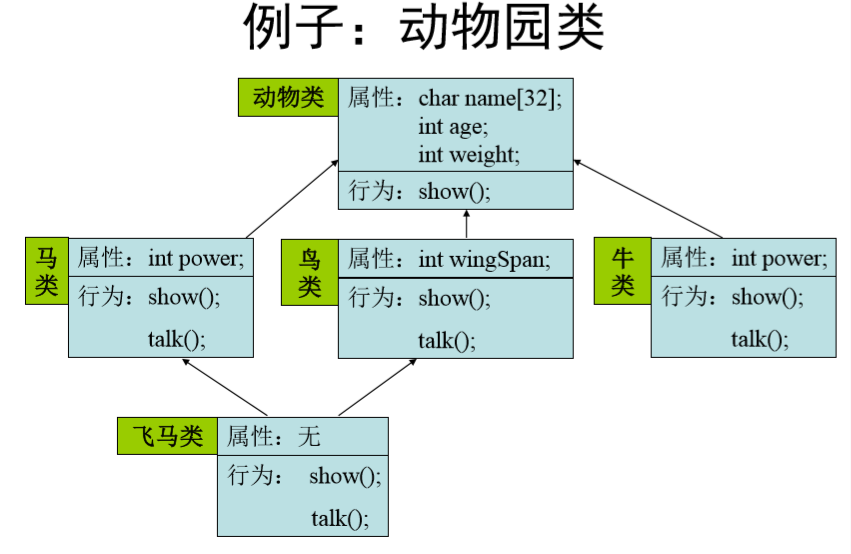
2.1 栗子~~
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <mmsystem.h> using namespace std; class CAnimal { string name; int age; int weight; public: CAnimal(string strName="", int a=0, int w=0) { name = strName; age = a; weight = w; cout << "Animal constructor " << name << endl; } virtual void Show() { cout << "[Property]" << name << " " << age << " " << weight << endl; } virtual void Talk() = 0; //使得基类可以调用派生类函数,不然后面CZoo类无法使用 ~CAnimal() { cout << "Animal destructor " << name << endl; } }; class CBird: virtual public CAnimal { protected: int wingSpan; public: CBird(string strName="", int a=0, int w=0, int ws=0):CAnimal(strName, a, w) { wingSpan = ws; cout << "Bird constructor " << endl; } void Show() { CAnimal::Show(); cout << "Wingspan:" << wingSpan << endl; } void Fly() { cout << "I can fly! I can fly!!" << endl; } void Talk() { cout << "Chirp..." << endl; PlaySound(".\sound\eagle.wav",NULL, SND_FILENAME|SND_SYNC); //WINDOWSAPI函数 } ~CBird() { cout << "Bird destructor " << endl; } }; class CHorse: virtual public CAnimal { protected: int power; //派生类要用 public: CHorse(string strName="", int a=0, int w=0, int pow=0):CAnimal(strName, a, w) { power = pow; cout << "Horse constructor " << endl; } void Show() { CAnimal::Show(); cout << "Power:" << power << endl; } void Run() { cout << "I can run! I run because I love to!!" << endl; } void Talk() { cout << "Whinny!..." << endl; PlaySound(".\sound\horse.wav",NULL, SND_FILENAME|SND_SYNC); } ~CHorse() { cout << "Horse destructor " << endl; } }; class CPegasus: public CHorse, public CBird { public: CPegasus(string strName="", int a=0, int w=0, int ws=0, int pow=0) : CAnimal(strName, a, w), CHorse(strName, a, w, pow), CBird(strName, a, w, ws) //调用三个构造函数 { cout << "Pegasus constructor" << endl; } void Talk() { CHorse::Talk(); } void Show() { CAnimal::Show(); cout << "Power:" << CHorse::power << endl; cout << "Wingspan:" << CBird::wingSpan << endl; } ~CPegasus() { cout << "Pegasus destructor" << endl; } }; class CBull: public CAnimal { int power; public: CBull(string strName="", int a=0, int w=0, int pow=0):CAnimal(strName, a, w) { power = pow; cout << "Bull constructor " << endl; } ~CBull() { cout << "Bull destructor" << endl; } void Show() { CAnimal::Show(); cout << "Power:" << power << endl; } void Talk() { cout << "Moo..." << endl; PlaySound(".\sound\bull.wav",NULL, SND_FILENAME|SND_SYNC); } }; const int MAX_ANIM_NUM = 100; //存储动物的数量最多100个 class CZoo //设计一个动物园类,管理不同种类的动物 { int size; CAnimal *m_animal[MAX_ANIM_NUM]; public: CZoo() { size = 0;} void Add(CAnimal *anim) //类型兼容 { if(size<MAX_ANIM_NUM) { m_animal[size] = anim; size++; } }; void Show(); void Talk(); }; void CZoo::Show() { for (int i=0; i<size; i++) m_animal[i]->Show(); } void CZoo::Talk() { for (int i=0; i<size; i++) m_animal[i]->Talk(); } int main() { CBird birdObj("Eagle", 5, 50, 2); CHorse horObj("Mogolia horse", 5, 1000, 10000); CBull bullObj1("Africa ox", 3, 2000, 20000); CBull bullObj2("China ox", 5, 3000, 40000); CPegasus pegObj("Pegasus", 5, 5000, 4, 100000); CZoo zoo; zoo.Add(&birdObj); zoo.Add(&horObj); zoo.Add(&bullObj1); zoo.Add(&bullObj2); zoo.Add(&pegObj); zoo.Show(); zoo.Talk(); return 0; }
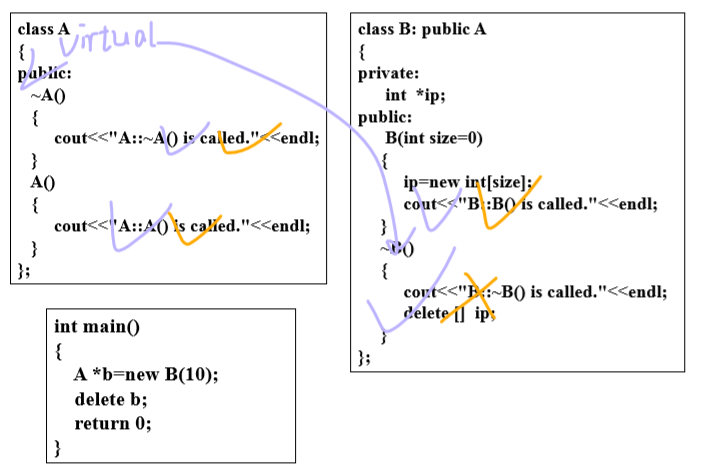
2.2 虚析构函数
2.2.1 定义
virtual ~ 类名( )
{
函数体;
}
◼ 定义基类的析构函数是虚析构函数,当程序运行结束时,通过基类指针删除派生类对象时,先调用派生类析构函数,然后调用基类析构函数
2.2.2 优点
3.静态联编与动态联编
3.1 RTTI
◼ 运行时刻类型识别(RunTime Type Identification):允许使用基类指针或引用操纵对象的程序获得这些指针或引用实际所指对象的类型。
◼ dynamic_cast运算符

◼ typeid运算符

3.2 静态联编
◼ 在编译时确定同名函数的具体操作对象
• 重载函数
• 函数模板
• 运算符重载
◼ 特点:执行效率高,但灵活性差
3.3 动态联编
◼ 在程序运行时(run time)确定对象所调用的函数
• 虚函数
• 纯虚函数
◼ 特点:灵活性强,但效率可能会降低
