一、序列化与反序列化
1.序列化能保存的元素
a) 只能保存对象的非静态成员变量(因为被static修饰的变量,即静态变量,是属于类的,不是属于对象的)
b) 不能保存任何成员方法和静态的成员变量(序列化是对属性的序列化,而不是对方法的序列化)
c) 不保存 transient 成员变量(对象中不希望被序列化的变量可以加上 transient 关键字)
d) 如果一个对象的成员变量是一个对象,这个对象的成员变量也会保存
e) 串行化保存的只是变量的值,对于变量的任何修饰符,都不能保存
2.使用对象流把一个对象写到文件时不仅保证该对象是序列化的,而且该对象的成员对象也必须是可序列化的。
3.如果一个可序列化的对象包含对某个不可序列化的对象的引用,那么整个序列化操作将会失败,并且会抛出一个NotSerializableException。我们可以将这个引用标记为transient,那么对象仍然可以序列化。
二、对象序列化注意事项
1 import java.io.Serializable; 2 3 public class Student implements Serializable{ 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 public static String schoolName; 7 public transient String pwd; 8 public String getName() { 9 return name; 10 } 11 public void setName(String name) { 12 this.name = name; 13 } 14 public int getAge() { 15 return age; 16 } 17 public void setAge(int age) { 18 this.age = age; 19 } 20 public String getPwd() { 21 return pwd; 22 } 23 public void setPwd(String pwd) { 24 this.pwd = pwd; 25 } 26 public Student(String name, int age, String pwd) { 27 super(); 28 this.name = name; 29 this.age = age; 30 this.pwd = pwd; 31 } 32 public Student() { 33 super(); 34 } 35 @Override 36 public String toString() { 37 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + "]" + "schoolname=" + schoolName; 38 } 39 40 }
TestStudent类
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 6 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 7 8 public class TestStudent { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // read(); 11 write(); 12 } 13 14 public static void read() { 15 ObjectOutputStream oos=null; 16 try { 17 oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F://student.txt")); 18 Student stu=new Student("nexfia", 20, "lvr123**"); 19 Student.schoolName="圣芙蕾雅学园"; 20 System.out.println(Student.schoolName); 21 oos.writeObject(stu); 22 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 }finally { 29 if(oos!=null) { 30 try { 31 oos.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 public static void write() { 42 ObjectInputStream ois=null; 43 try { 44 ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("F://student.txt")); 45 Student stu=(Student) ois.readObject(); 46 System.out.println(stu); 47 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 48 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 51 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } catch (IOException e) { 54 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 }finally { 57 if(ois!=null) { 58 try { 59 ois.close(); 60 } catch (IOException e) { 61 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 62 e.printStackTrace(); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 } 68 }
TestStudent 类 Read() 方法输出结果
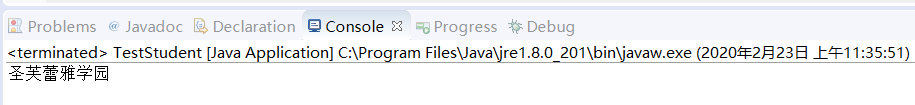
TestStudent类 Write() 方法输出结果

实验二:测试使用对象流把一个对象写到文件时不仅保证该对象是序列化的,而且该对象的成员对象也必须是可序列化的
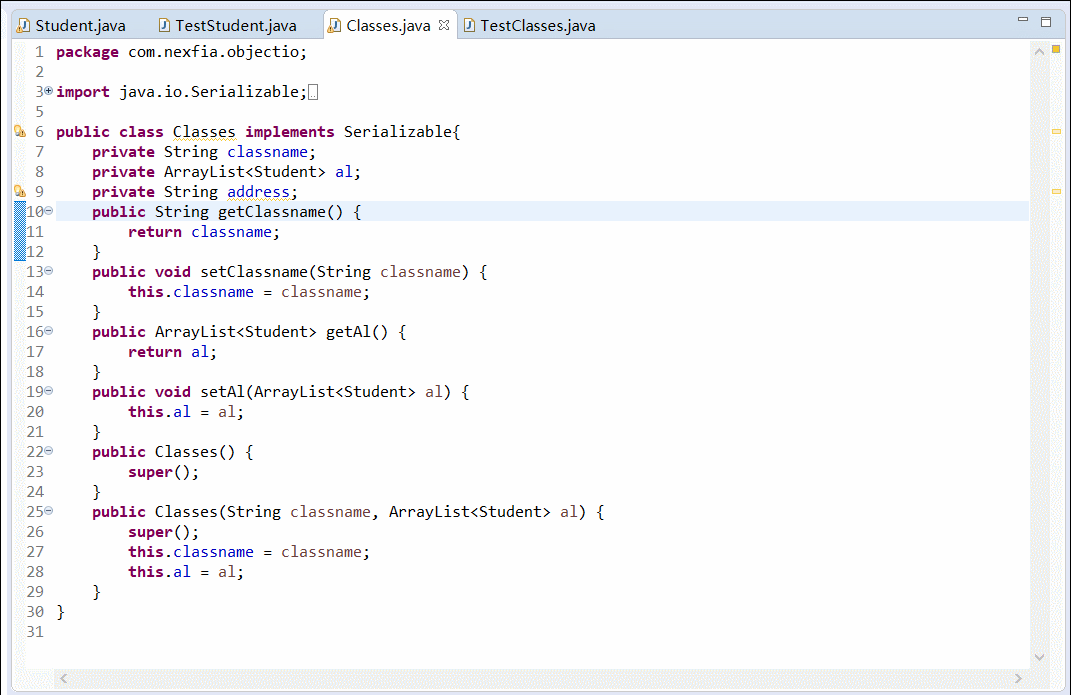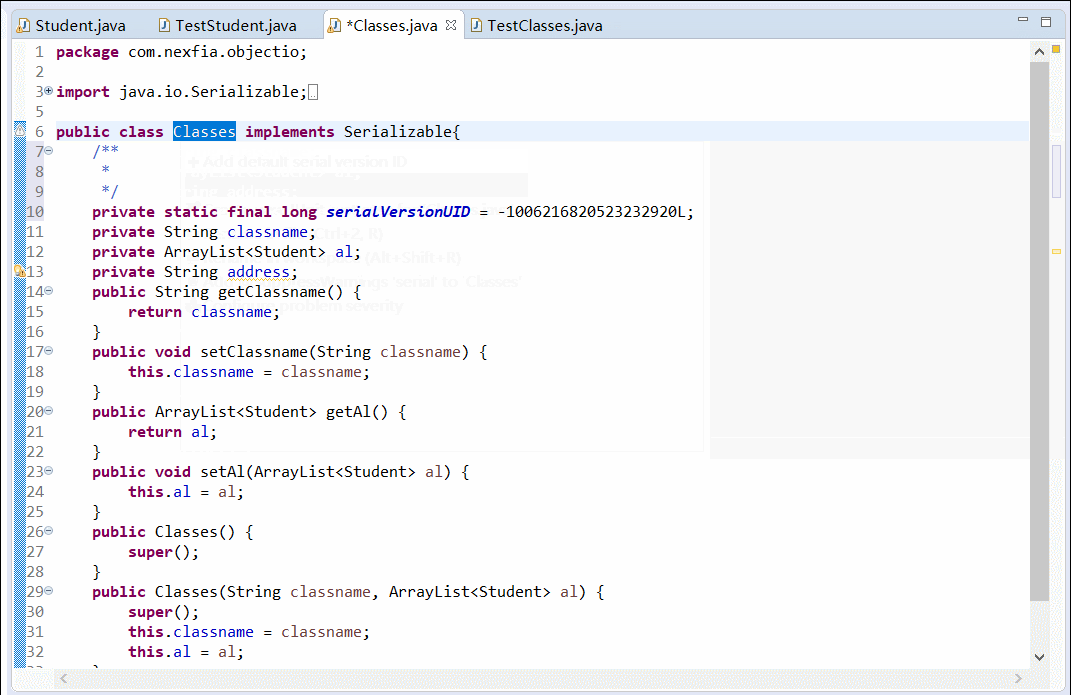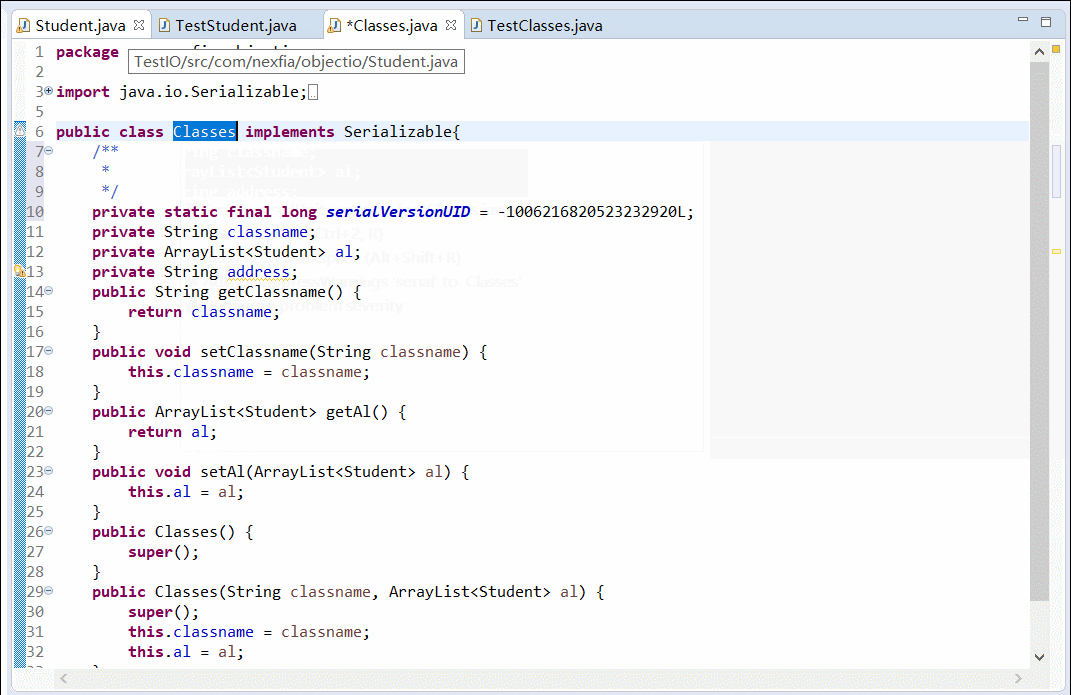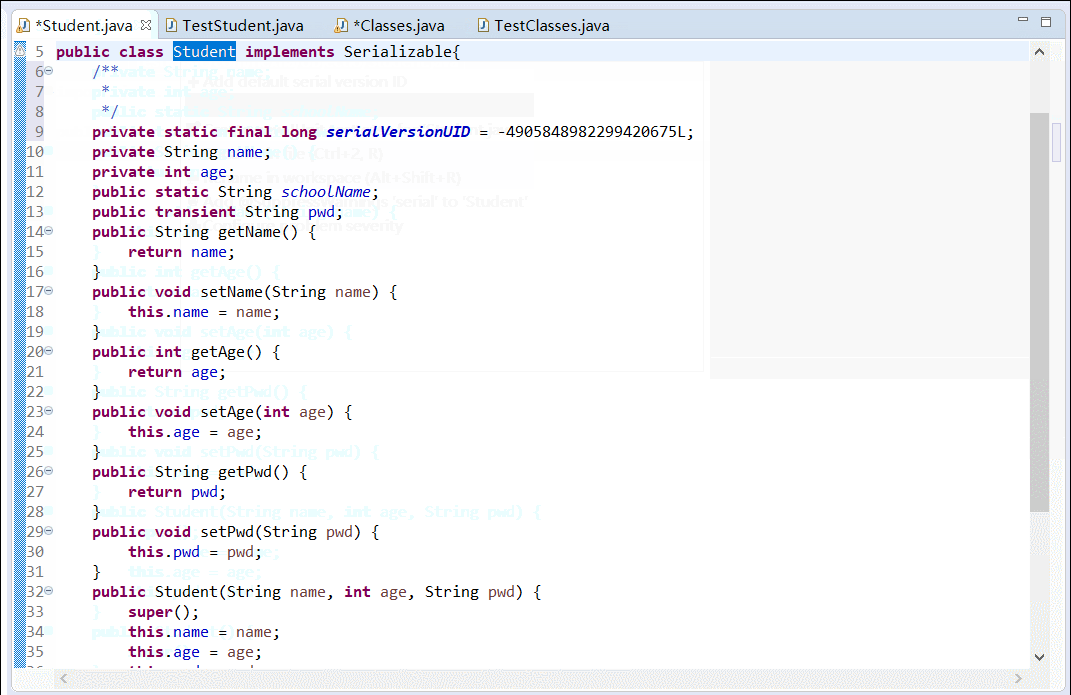
Classes 类
1 import java.io.Serializable; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 4 public class Classes implements Serializable{ 5 private String classname; 6 private ArrayList<Student> al; 7 private String address; 8 public String getClassname() { 9 return classname; 10 } 11 public void setClassname(String classname) { 12 this.classname = classname; 13 } 14 public ArrayList<Student> getAl() { 15 return al; 16 } 17 public void setAl(ArrayList<Student> al) { 18 this.al = al; 19 } 20 public Classes() { 21 super(); 22 } 23 public Classes(String classname, ArrayList<Student> al) { 24 super(); 25 this.classname = classname; 26 this.al = al; 27 } 28 }
Student类(修改后,不再继承Serializable接口)
1 public class Student{ 2 private String name; 3 private int age; 4 public static String schoolName; 5 public transient String pwd; 6 public String getName() { 7 return name; 8 } 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 public int getAge() { 13 return age; 14 } 15 public void setAge(int age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 public String getPwd() { 19 return pwd; 20 } 21 public void setPwd(String pwd) { 22 this.pwd = pwd; 23 } 24 public Student(String name, int age, String pwd) { 25 super(); 26 this.name = name; 27 this.age = age; 28 this.pwd = pwd; 29 } 30 public Student() { 31 super(); 32 } 33 @Override 34 public String toString() { 35 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + "]" + "schoolname=" + schoolName; 36 } 37 }
TestClasses类
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 6 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 9 public class TestClasses { 10 public static void write() { 11 ArrayList<Student> al=new ArrayList<Student>(); 12 al.add(new Student("Lily", 21, "qaz123")); 13 al.add(new Student("Mary", 22, "456")); 14 al.add(new Student("Alice", 18, "222")); 15 16 Classes cl=new Classes("gzcc01", al); 17 18 ObjectOutputStream oos=null; 19 try { 20 oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F://cl.txt")); 21 oos.writeObject(cl); 22 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 }finally { 29 if(oos!=null) { 30 try { 31 oos.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 public static void read() { 41 ObjectInputStream ois=null; 42 try { 43 ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("F://cl.txt")); 44 Classes cl=(Classes)ois.readObject(); 45 System.out.println(cl.getClassname()+" "+cl.getAl()); 46 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 47 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 50 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } catch (IOException e) { 53 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 }finally { 56 if(ois!=null) { 57 try { 58 ois.close(); 59 } catch (IOException e) { 60 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 public static void main(String[] args) { 68 // read(); 69 write(); 70 } 71 }
TestClasses类Read()方法输出结果
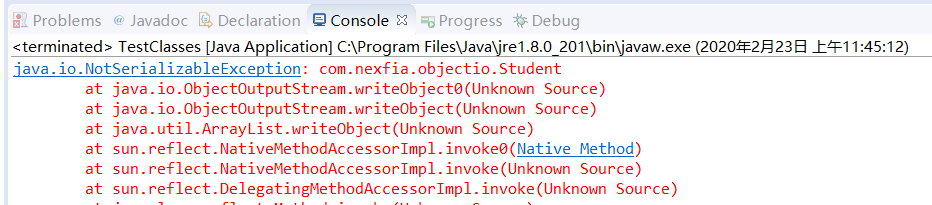
如果一个可序列化的对象包含对某个不可序列化的对象的引用,那么整个序列化操作将会失败,并且会抛出一个NotSerializableException。我们可以将这个引用标记为transient,那么对象仍然可以序列化。
实验三:测试序列化编号的使用
Classes 类
import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Classes implements Serializable{ private String classname; private ArrayList<Student> al; public String getClassname() { return classname; } public void setClassname(String classname) { this.classname = classname; } public ArrayList<Student> getAl() { return al; } public void setAl(ArrayList<Student> al) { this.al = al; } public Classes() { super(); } public Classes(String classname, ArrayList<Student> al) { super(); this.classname = classname; this.al = al; } }
Student 类
import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable{ private String name; private int age; public static String schoolName; public transient String pwd; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Student(String name, int age, String pwd) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.pwd = pwd; } public Student() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + "]" + "schoolname=" + schoolName; } }
TestClasses 类
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; public class TestClasses { public static void write() { ArrayList<Student> al=new ArrayList<Student>(); al.add(new Student("Lily", 21, "qaz123")); al.add(new Student("Mary", 22, "456")); al.add(new Student("Alice", 18, "222")); Classes cl=new Classes("01", al); ObjectOutputStream oos=null; try { oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F://cl.txt")); oos.writeObject(cl); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(oos!=null) { try { oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void read() { ObjectInputStream ois=null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("F://cl.txt")); Classes cl=(Classes)ois.readObject(); System.out.println(cl.getClassname()+" "+cl.getAl()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(ois!=null) { try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // read(); write(); } }
先运行 TestClasses 类的 write() 方法将 Classes 对象 cl 写入 F:\cl.txt 中
再运行 read() 方法读取
输出结果
01 [Student [name=Lily, age=21, pwd=null]schoolname=null, Student [name=Mary, age=22, pwd=null]schoolname=null, Student [name=Alice, age=18, pwd=null]schoolname=null]
修改 Classes 类,增加一个 String 类型的私有属性 address
Classes 类(修改后)
import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Classes implements Serializable{ private String classname; private ArrayList<Student> al; private String address; public String getClassname() { return classname; } public void setClassname(String classname) { this.classname = classname; } public ArrayList<Student> getAl() { return al; } public void setAl(ArrayList<Student> al) { this.al = al; } public Classes() { super(); } public Classes(String classname, ArrayList<Student> al) { super(); this.classname = classname; this.al = al; } }
再次运行 TestClasses 类的 read() 方法

运行 TestClasses 类的 write() 方法将 Classes 对象 cl 写入 F:\cl.txt 中,再运行 read() 方法读取
修改 Classes 类,增加一个 String 类型的私有属性 address,再次运行 TestClasses 类的 read() 方法
此次读取成功