缓冲流
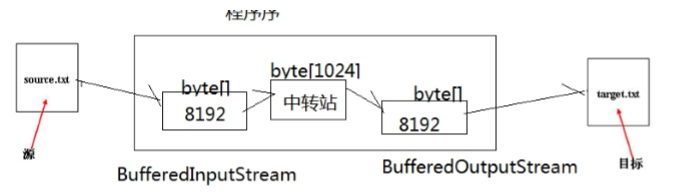
1.读文件和写文件都使用了缓冲区,减少了读写次数,从而提高了效率
2.当创建这两个缓冲流的对象时,会创建内部缓冲数组,缺省使用32字节大小的缓冲区
3.当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区
4.当写入数据时,首先写入缓冲区,当缓冲区满时,其中的数据写入所连接的输出流。使用方法flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流。
5.关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反。只要关闭高层流即可,关闭高层流其实关闭了底层节点流。
6.Flush的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「彭浩95」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33193871/article/details/88196322
字节缓冲流
import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class TestBufferedCopy { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedInputStream bis=null; BufferedOutputStream bos=null; try { bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("F://test.txt")); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F://copy2.txt")); byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; int len=0; while((len=bis.read(buf))!=-1) { bos.write(buf, 0, len); bos.flush(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(bos!=null) { try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis!=null) { try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader
readLine()
每次读取一行数据
BufferedWriter
newLine()
写入一个换行符
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class TestBuffered { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader br=null; BufferedWriter bw=null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F://test.txt")); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("F://copy3.txt")); String str=null; while((str=br.readLine())!=null) { bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(bw!=null) { try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(br!=null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }