前阵子听说一个面试题:你实现一个logistic Regression需要多少分钟?搞数据挖掘的人都会觉得实现这个简单的分类器分分钟就搞定了吧?
因为我做数据挖掘的时候,从来都是顺手用用工具的,尤其是微软内部的TLC相当强大,各种机器学习的算法都有,于是自从离开学校后就没有自己实现过这些基础的算法。当有一天心血来潮自己实现一个logistic regression的时候,我会说用了3个小时么?。。。羞羞
---------------------------------------------------前言结束----------------------------------------------
当然logistic regression的渊源还是有点深的,想复习理论知识的话可以去http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logistic_regression , 我这里就直接讲实现啦。
首先要了解一个logistic function
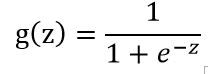
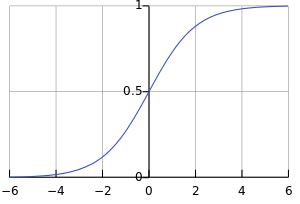
这个函数的图像是这个样子的:
而我们要实现的logistic regression model,就是要去学习出一组权值w:
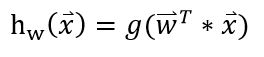
x 指feature构成的向量。 这个向量w就可以将每个instance映射到一个实数了。
假如我们要出里的是2分类问题,那么问题就被描述为学习出一组w,使得h(正样本)趋近于1, h(负样本)趋近于0.
现在就变成了一个最优化问题,我们要让误差最小化。 现在问题来了,怎么定义误差函数呢?
首先想到的是L2型损失函数啦,于是啪啪啪写上了
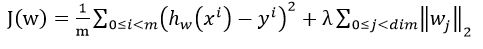 。
。
很久没有复习logistic regression的人最容易犯错的就是在这了。正确的写法是:
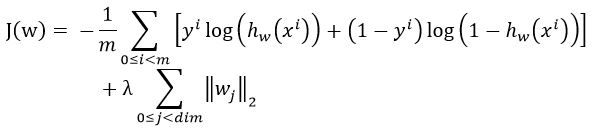 ,
,
然后对它求偏导数得到梯度下降法的迭代更新方程:
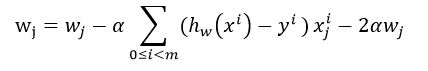 。
。
于是你会发现这个迭代方程是和线性回归的是一样的!
理清了过程时候,代码就变得异常简单了:
1 public class LogisticRegression 2 { 3 private int _maxIteration = 1000; 4 private double _stepSize = 0.000005; 5 //private double _stepSize = 0.1; 6 private double _lambda = 0.1; 7 private double decay = 0.95; 8 9 public int dim; 10 public double[] theta; 11 12 public LogisticRegression(int dim) 13 { 14 this.dim = dim; 15 } 16 17 public LogisticRegression(int dim, double stepSize) 18 : this(dim) 19 { 20 this._stepSize = stepSize; 21 } 22 23 public void Train(Instance[] instances) 24 { 25 Initialize(); 26 27 int instCnt = instances.Length; 28 double[] dev =new double[this.dim]; 29 for (int t = 0; t < this._maxIteration; t++) 30 { 31 double cost = 0; 32 for (int i = 0; i < instCnt; i++) 33 { 34 double h_x = MathLib.Logistic(MathLib.VectorInnerProd(instances[i].featureValues, this.theta)); 35 // calculate cost function 36 cost += instances[i].label * Math.Log(h_x) + (1 - instances[i].label) * Math.Log(1 - h_x); 37 } 38 cost *= -1.0 / instCnt; 39 Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", t, cost); 40 41 42 for (int i = 0; i < instCnt; i++) 43 { 44 ResetArray(dev); 45 double h_x = MathLib.Logistic(MathLib.VectorInnerProd(instances[i].featureValues, this.theta)); 46 double error = h_x- instances[i].label ; 47 for (int j = 0; j < this.dim; j++) 48 { 49 dev[j] += error*instances[i].featureValues[j] + 2*dev[j]*this._lambda; 50 this.theta[j] -= this._stepSize * dev[j] ; 51 //BoundaryLimiting(ref this.theta[j], 0, 1); 52 } 53 } 54 //this._stepSize *= decay; 55 //if (this._stepSize > 0.000001) 56 //{ 57 // this._stepSize = 0.000001; 58 //} 59 } 60 } 61 62 private void BoundaryLimiting(ref double alpha, double lowerbound, double upperbound) 63 { 64 if (alpha < lowerbound) 65 { 66 alpha = lowerbound; 67 } 68 else if (alpha > upperbound) 69 { 70 alpha = upperbound; 71 } 72 } 73 74 public double[] Predict(Instance[] instances) 75 { 76 double[] results = new double[instances.Length]; 77 for (int i = 0; i < results.Length; i++) 78 { 79 results[i] = MathLib.Logistic(MathLib.VectorInnerProd(instances[i].featureValues, this.theta)); 80 } 81 return results; 82 } 83 84 private void ResetArray(double[] dev) 85 { 86 for (int i = 0; i < dev.Length; i++) 87 { 88 dev[i] = 0; 89 } 90 } 91 92 private void Initialize() 93 { 94 Random ran = new Random(DateTime.Now.Second); 95 96 this.theta = new double[this.dim]; 97 for (int i = 0; i < this.dim; i++) 98 { 99 this.theta[i] = ran.NextDouble() * 0 ; // initialize theta with a small value 100 } 101 } 102 103 104 public static void Test() 105 { 106 LogisticRegression lr = new LogisticRegression(3); 107 108 List<Instance> instances = new List<Instance>(); 109 using (StreamReader rd = new StreamReader(@"D:\local exp\data.csv")) 110 { 111 string content = rd.ReadLine(); 112 while ((content = rd.ReadLine()) != null) 113 { 114 instances.Add(Instance.ParseInstance(content,',')); 115 } 116 } 117 118 // MinMaxNormalize(instances); 119 120 lr.Train(instances.ToArray()); 121 122 } 123 124 private static void MinMaxNormalize(List<Instance> instances) 125 { 126 int dim = instances[0].dim; 127 double[] min = new double[dim]; 128 double[] max = new double[dim]; 129 130 int instCnt = instances.Count; 131 for (int i = 0; i < instCnt; i++) 132 { 133 for (int j = 0; j < dim; j++) 134 { 135 if (i == 0 || instances[i].featureValues[j] < min[j]) 136 { 137 min[j] = instances[i].featureValues[j]; 138 } 139 if (i == 0 || instances[i].featureValues[j] > max[j]) 140 { 141 max[j] = instances[i].featureValues[j]; 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 146 147 for (int j = 0; j < dim; j++) 148 { 149 double gap = max[j] - min[j]; 150 if (gap <= 0) 151 { 152 continue; 153 } 154 for (int i = 0; i < instCnt; i++) 155 { 156 instances[i].featureValues[j] = (instances[i].featureValues[j] - min[j]) / gap; 157 } 158 } 159 160 } 161 }
前面提到说我花了3个小时,其中很大一部分原因是在debug算法为啥没有收敛。这里有个很重要的步骤是把feature规范化到[0,1] 。 如果不normalize的话,参数调起来比较麻烦,loss function也经常蹦到NaN去了。
以下是对比normalize和不加normalization的收敛曲线图:
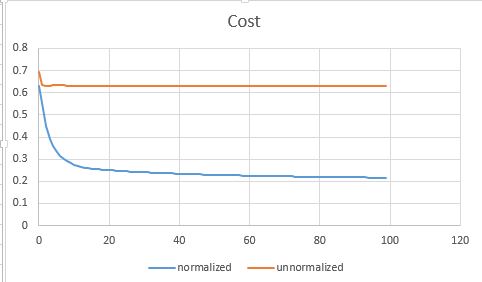
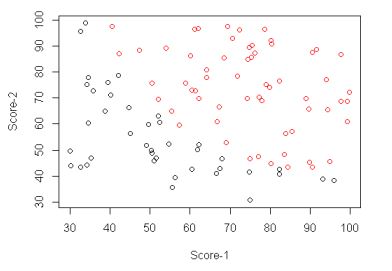
我用的实现数据可以在 http://pingax.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/data.csv 下载到。 它是一个2维的数据, 分布如下: