1、示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Promise和setTimeout执行顺序 面试题</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(1)
}, 0);
new Promise(function(a, b) {
console.log(2);
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
i == 9 && a();
}
console.log(3);
}).then(function() {
console.log(4)
});
console.log(5)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、解释
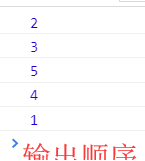
最需要 解释的是:then和settimeout执行顺序,即setTimeout(fn, 0)在下一轮“事件循环”开始时执行,Promise.then()在本轮“事件循环”结束时执行。因此then 函数先输出,settimeout后输出。先执行promise是宏任务队列,而setTimeout是微任务队列。
下面的输出结果是多少
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1);
resolve();
console.log(2);
})
promise.then(() => {
console.log(3);
})
console.log(4);
Promise 新建后立即执行,所以会先输出 1,2,而 Promise.then()内部的代码在 当次 事件循环的 结尾 立刻执行 ,所以会继续输出4,最后输出3
3、自测题:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>js 执行顺序</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/lodash.js/4.17.10/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
console.log(1)
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(2);
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
console.log(7);
resolve()
}).then(function(){
console.log(8)
});
},1000);
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(10);
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
console.log(11);
resolve()
}).then(function(){
console.log(12)
});
},0);
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
console.log(3);
resolve()
}).then(function(){
console.log(4)
}).then(function(){
console.log(9)
});
console.log(5)
</script>
</body>
</html>