-
使用pureRender,setState和Immutable.js来操作state
Immutable 中文意思不可变。
不能直接修改state的值,要用setState 和Immutable
react 官方要求不要直接修改state,比如this.state.name = "suyuan"是错误的写法,应该用this.setState({name, "suyuan"});
原因1.其实state并不是不可变的,官方是希望你把他当做不变来用,因为只有setState的时候才会发生消息给react 来re-render,this.state.name="bianhua" 不会引起re-rener;
原因2.本来不管你数据有没有变化, setState就一定会重新渲染,为了提高性能一般会引去pureRender技术(本文其他章节有描述),该技术是进行浅比较(根节点的地址),p1,p2,p3
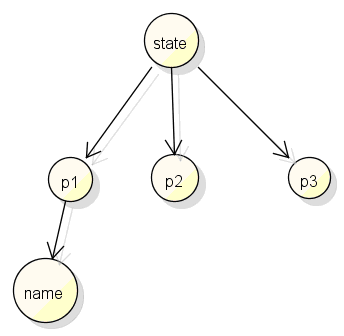
假如你这样错误的写:
let p1=state.p1; p1.name = "bianhua"; this.setState({p1:p1});
用了pureRender技术后,react 发现p1没有变化(p1的地址没变,不是新对象),也不会re-render
所以你应该这样写
let p1=JsFrom(state.p1); p1.name = "bianhua"; this.setState({p1:p1});
这篇文章描述了immutable
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20295971?columnSlug=purerender
使用PureRenders
Example Mixin 混入类s:
var PureRenderMixin = require('react-addons-pure-render-mixin'); React.createClass({ mixins:[PureRenderMixin], render: function() { return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>; } });
Example using ES6 class syntax:
import PureRenderMixin from 'react-addons-pure-render-mixin'; class FooComponent extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.shouldComponentUpdate=PureRenderMixin.shouldComponentUpdate.bind(this); } render() { return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>; } }
或者用pure-render-decorator 装饰器
import {Component} from 'react';
import pureRender from 'pure-render-decorator';
@pureRender
export default class Test extends Component {
render() {
return <div />;
}
}
a. 优化了性能
PureRenderMixin 重写了shouldComponentUpdate,只有在props或者state真正改变的时候才会重新render,这个在react性能上是一个优化,从此以后你可以大胆的setState,而不需要写这样的代码
if (this.state.someVal !== computedVal) { // 判断是否需要setState,因为每次setState都会引起render,不管你的数据是不是真的变化了 this.setState({someVal: computedVal}) }
b.有一点要注意,继承PureRenderMixin要求render 必须是纯函数,当然本来react官文就说render should 纯函数,这里跟需要时纯函数,为什么?
b.1.单纯react来讲,页面和state直接反应,如果render不是纯函数,就会导致页面展示和state对不上号,还有去查询其他关联数据;
b.2.从继承混入类来说,如果你写了下面这种不纯的代码
render: function () { //… if (this._previousFoo !== this.props.foo) { // <-- IMPURE return renderSomethingDifferent(); } }
依赖了一个其他变量this._previousFoo,就会引入bug;
>本来不用混入类,你setState后就算state不改变,也会render,然后再render过程中this._previousFoo的数据变化可能导致页面发生变化;
>现在引入混入类,完蛋了,setState后,state数据不变也就不会render了,页面不变了,和你希望的不一样了。
所以render要纯正,除非上面this._previousFoo 你保证永远不变,是个const
c 还有个重要的事情要说,我觉得太重要了,PureRenderMixin混入类 只会进行浅比较,就是C++里面的指针(地址比较),如果你修改了一个数组的某个item,你其实是希望render的,但是PureRenderMixin 认为数组的地址没变,数组也就没变,也就没render;怎么办?
c.1.组件创建新对象--切片 array.silce()
c.2.object创建新对象-- var copy = Object.assign({}, obj);
c.3.react 自带的操作数据的方式 https://facebook.github.io/react/docs/update.html
c.4..第三方库Immutable.js 和 mori
这里有个坑,用了purRender有时候无效,比如组件下面包含了子组件的时候,this.props.children 就算数据不变,对象也不是原来的对象的,为了优化某个组件的性能我还特意重写了shouldComponentUpdate,把props.children 排除了,这个可能是purRender的原则,看了下源代码完全没搞明白,所以假如render不纯的话(比如使用了this.name)我估计还是会重写渲染,有兴趣会试验一下
这里插入一句,redux中的mapToState() 做为reducer和Component的桥梁,reducer 在返回newState后虽然肯定会执行mapToState,但是mapToState中return出去的数据{xkey:xvalue},如果xvalue的地址没有改变,mapToState关联的Component也不会render;
适当的使用context,方便给子组件传变量
父组件给子组件上下文定义个变量,子组件声明这个变量,就可以使用;
方便数据传递,不需要通过props一层层塞进去
// ------Component A class A extends React.Component { // add the following property static childContextTypes = { user: React.PropTypes.object.isRequired } // add the following method getChildContext() { return { user: this.props.user //children 组件可以使用this.context.user } } render() { <div>{this.props.children}</div> } } // -----Component D class D extends React.Component { // add the following property static contextTypes = { user: React.PropTypes.object.isRequired } render() { <div>{this.context.user.name}</div> } }
或者
function D(props, context) { return ( <div>{this.context.user.name}</div> ); } D.contextTypes = { user: React.PropTypes.object.isRequired }
使用propTypes 和defaultProps
class Greeting extends React.Component { static propTypes = { name: React.PropTypes.string } static defaultProps = {
name: "suyuans"
} render() { return ( <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1> ); } }
React 可以帮你检测传入的props是否有误,自己在使用组件时候也会更清晰需要传入什么props
不过要记得在编译线上版本的时候设置环境变量NODE_ENV="production",避免影响线上的性能
减少操作state
所有的编程语言在写代码的过程中,都希望是无状态的,纯函数的方式;
React 提供了setState 接口,但是我们还要是减少他的使用;
如果state使用不好可能导致组件复杂混乱,re-render 失控;
比如在 componentDidMount() or componentDidUpdate()生命周期中使用setState,1是控制不好可能发生死循环,2是加入子组件也类似的使用,子子组件等刷新的次数会成2的幂次方增加;
不过使用state是必不可少的,但是一定要封装好state,确保只有本组件可见;
假如父组件需要知道一些关于子组件的state,这就破坏了组件的结构,意味着组件的抽象失败,可以需要对该组件重构
集中管理state
在工作中,父组件需要知道子组件的state或者信息是必不可少的,一般我们把state完全集中在一个地方(一般最顶层)控制,
父组件通过props向子组件传递信息,
这就是Flux 架构模型:用集合仓库来管理state,用action事件来驱动state的更新,这时候state的存储和操作都是原子性的,任何state的变化都会去重新渲染组件,以达到单向数据流的目的;
意思就是所有组件都依赖props渲染数据,数据源全部来自数据中心state,组件通过 事件、管道、回调、方法、stream来和数据中心通信。
这个看起来有点低效,但是react所倡导的就是 js的速度很快和虚拟dom diff的思想;
纯props的组件库会更好的发挥purRender相关的优势;
缺点是 会使得原来一些简单的通过setSate的事情变的麻烦了,但是优点是单向数据流更直观的反应了我们的应用。
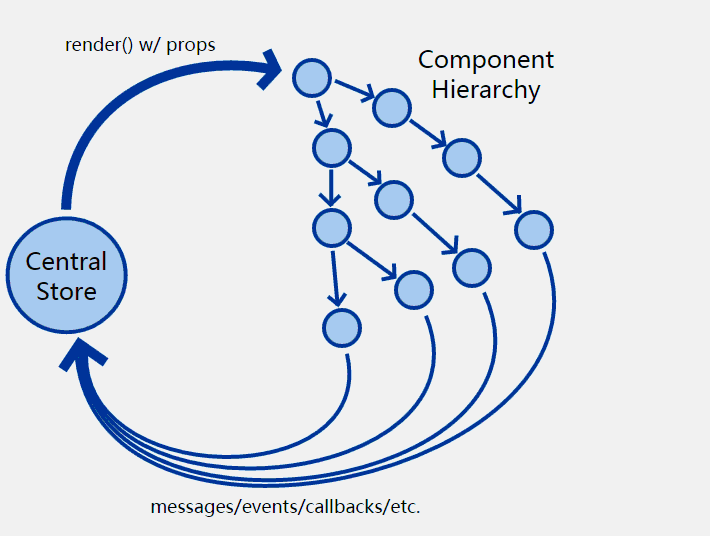
这种思想就像flux架构,见下图
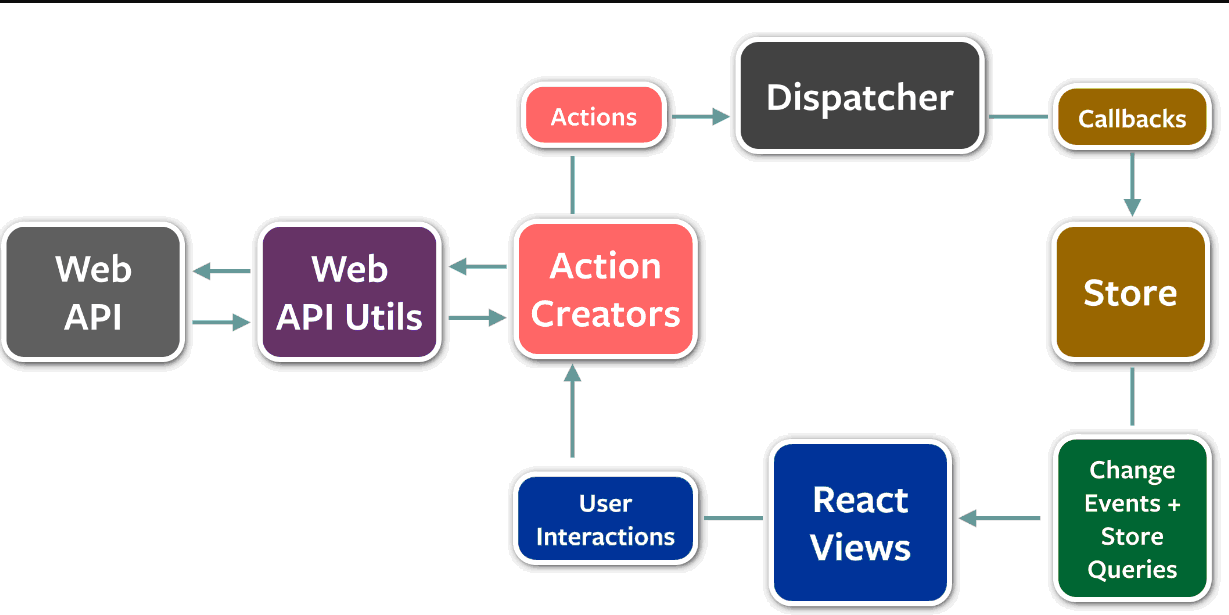
一旦数据中心store 数据变更了,他就render组件,组件会向子组件传递变更的数据
说白了,组件就是处理props 到 页面的纯函数,这样的组件也更容易使用和测试, 组件正常的展示,正常触发事件,触发事件后store数据更新正常 就表明组件一切ok。
如果组件之间通过回调函数来操作,组件之间的耦合性就太高,需要知道对方的一些数据、接口、函数,这样抽象就失败了,应该通过action的方式相互通讯。
尽量把代码写在render中
尽量把componentWillReceiveProps or componentWillMount 下面的代码写到render中,
把一些处理props,或者计算setState的处理函数写到render
永远不要担心js的速度,这样写的好处很多,减少bug并容易发现bug,减少重复代码等
// bad componentWillMount: function () { this.setState({ computedFoo: compute(this.props.foo) }); }, componentWillReceiveProps: function (nextProps) { this.setState({ computedFoo: compute(nextProps.foo) }); }, render: function () { return React.DOM.div({className: this.state.computedFoo}); } // better render: function () { var computedFoo = compute(this.props.foo); return React.DOM.div({className: computedFoo}); }
也可以在render 中计算获取其他的组件,在render 做更多的事情,当然也不要把render搞的太长太大
MIXIN 或者extend 非常好用
可以用他们来创建复用的功能块
PureRenderMixin 就是覆盖了shouldComponentUpdate() 方法
你可能有疑问了,生命周期componentWillMount之类的继承下来不就遭了,有的我不需要是不是要重写个空的?放心,mixin特意把生命周期排除出去啊,哈哈 机智啊
比如我们可以把处理state的逻辑放到mixin中,就算只有一个组件只用也ok,这样可以保证组件内部的无状态性,通过mixin 来构建有状态的组件,以后你可以通过修改mixin来更换功能,复用这个组件,mixin这时候有点control层的角色扮演,不过小心的是mixin要被抛弃了,用extend把
使用类实例的属性
尽管组件应该是以props为参数的纯函数,但是有时候使用实例属性也是明智的。
有时候this.foo比this.props.foo要更合适;要注意的是PureRender 的时候render下不要这样使用,原因看之前的内容。
如果这个数据不影响页面的呈现,这样用是非常方便的
componentWillReceiveProps: function () { this._timer = Date.now(); }, onLoadHandler: function () { this.trigger("load:time", Date.now() - this._timer); }, render: function () { return React.DOM.img({ src: this.props.src, onLoad: this.onLoadHandler }); }
上面用一个实例属性来存放开始时候,以计算load时间,这个时间变化后我也不需要页面展示渲染,所以可以放在实例属性中。
一句话,数据变化了,页面不需要刷新变化的,可以作为实例属性
数据变化,页面变化的那就是state了
组件通信
父到子 1.props, 2.ref
子到父 1.回调函数this.props.callback()
兄弟 1.通过父绕一圈,2.采用第三方消息系统如js-signals: https://github.com/millermedeiros/js-signals
一切通信,如果用了flux或者redux就解决了
下面是一些js使用建议
1.遵循es6严格模式
2.声明变量的优先级 const、let
3.箭头函数代替繁杂的bind
4.可以引用typescript减少bug,当然用了严格模式也足够了
推荐个组件库 antd
推荐使用redux(control、modal层) 管理react(view层s)
本文参考了
React建议:http://aeflash.com/2015-02/react-tips-and-best-practices.html
immutable使用:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20295971?columnSlug=purerender