一、Exception
常见的异常:
1.算术异常类:ArithmeticExecption; 2.空指针异常:NullPointerException;
3.类型强制转换异常:ClassCastException; 4.数组负下标异常:NegativeArrayException;
5.数组下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException; 6.字符串转换为数字异常:NumberFormatException;
7.操作数据库异常:SQLException; 8.输入输出异常:IOException: 9.方法未找到异常:NoSuchMethodException;
关键字:try catch
案例一:
public class Index_Laugh {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 20;
int y = 0;
try {
System.out.println(x/y);
}catch (Exception c ){
System.out.println("分母不能为零");
}
};
}
输出结果:
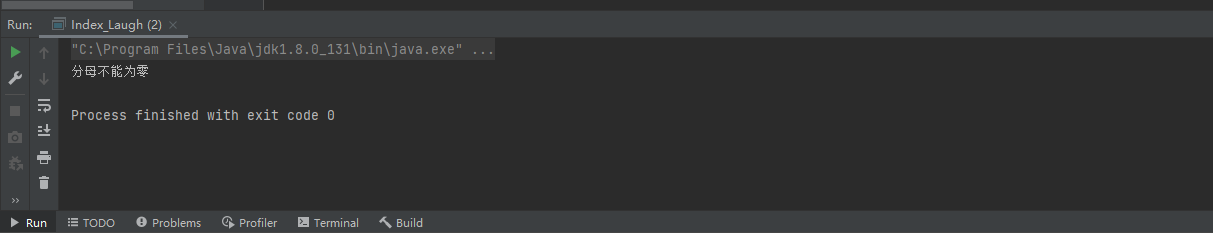
案例二:
public class Index_Laugh {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 20;
int y = 0;
try {
new Index_Laugh().a();
}catch (ArithmeticException c ){
System.out.println("ArithmeticException");
} catch (Exception e ){
System.out.println("Exception");
} catch (Throwable t ){
System.out.println("Throwable");
}finally {
System.out.println("我是不管什么情况下都会执行的!无所畏惧");
}
};
public void a(){
b();
}
public void b(){
a();
}
}
输出结果:
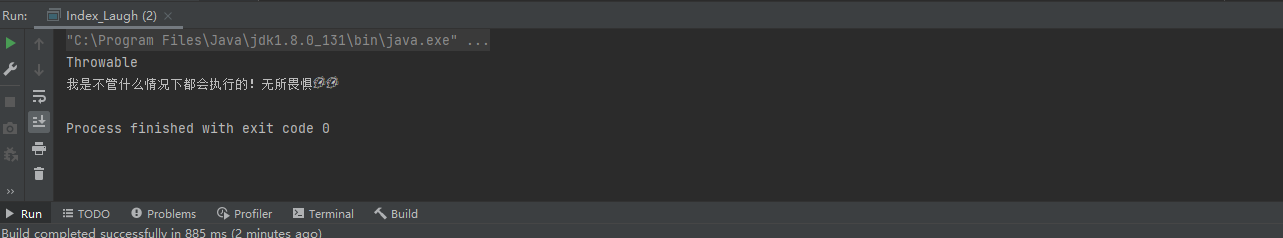
解释:异常可以多设置的,但是切记 异常的大小是递增的,不能把最大的异常放第一个catch里面,要不然下面的异常不走了;
关键字:finally
一般情况下可以try catch后直接不写finally;但是牵扯到IO流的话必须有,因为通过finally一定执行的原理,关闭其流操作;
程序正确:
public class Index_Laugh {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 20;
int y = 10;
try {
System.out.println(x/y);
}catch (Exception c ){
System.out.println("分母不能为零");
}finally {
System.out.println("我是不管什么情况下都会执行的!无所畏惧");
}
};
}
输出结果:
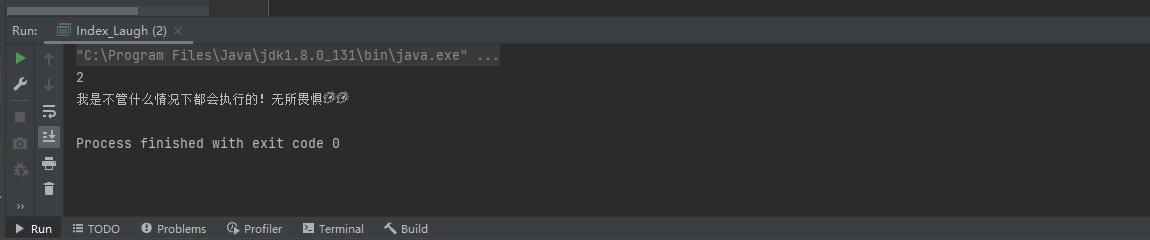
程序抛异常:
public class Index_Laugh {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 20;
int y = 0;
try {
System.out.println(x/y);
}catch (Exception c ){
System.out.println("分母不能为零");
}finally {
System.out.println("我是不管什么情况下都会执行的!无所畏惧");
}
};
}
输出结果:
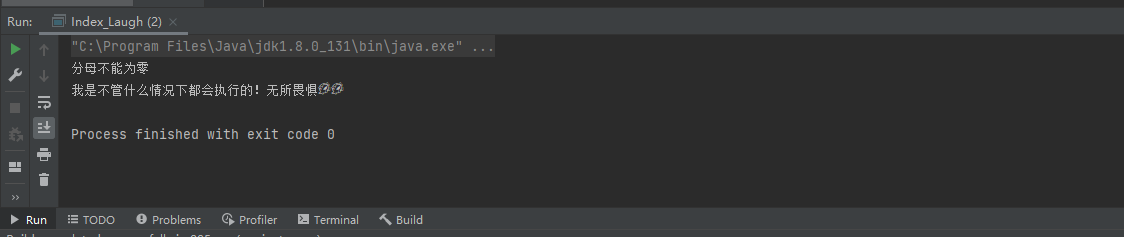
关键字:throw
解释:一般用与方法中,主动在方法里面抛出的;
关键字:throws
解释:抛给上级处理,自己处理不了,把异常抛给上级去处理;



