1. 前期准备:
① 编辑器:Eclipse
② 构建工具:Maven
③ 第三方java开发工具:FastJSON, Guava
2. 全部示例代码展示:
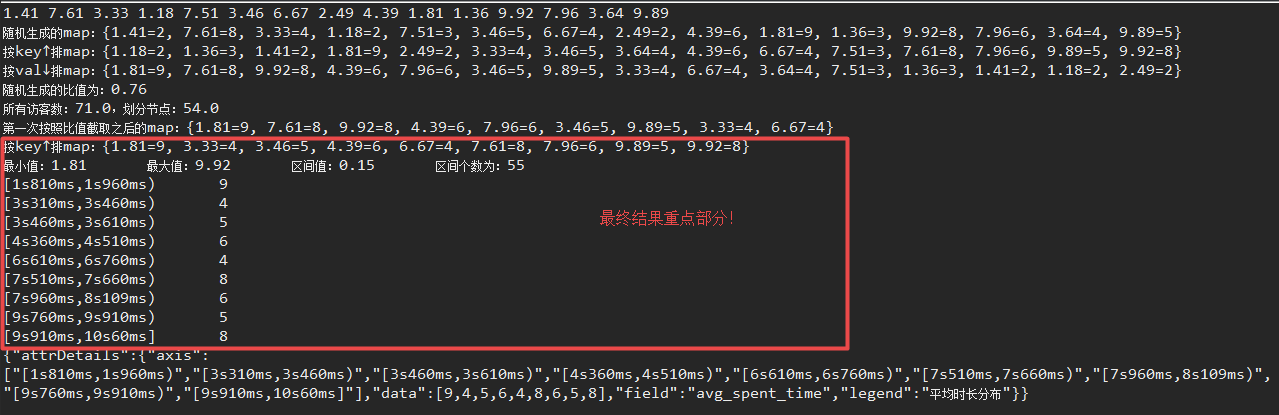
1 package com.drew.test; 2 3 import java.math.BigDecimal; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 import java.util.Collections; 6 import java.util.List; 7 import java.util.Map; 8 9 import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; 10 import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap; 11 import com.google.common.collect.Lists; 12 import com.google.common.collect.Maps; 13 14 /** 15 * @author zero 2019/04/08 16 */ 17 public class Java8future { 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 // System.out.println(genRandomRatio(0.75, 0.8, 2)); 21 // System.out.println(genRandomDoubleList(0.75, 0.8, 2, 2)); 22 // System.out.println(genRandomRatio(1, 8, 2)); 23 // System.out.println(genRandomDoubleList(1, 8, 2, 10)); 24 // System.out.println(genRandomInteger(1, 10)); 25 // System.out.println(testGenRandomIntegerList()); 26 // System.out.println(distributeInteger(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,6), 4)); 27 // testGeneratorDouble(); 28 // shuffleList(); 29 // testListSizeIsEqual(); 30 testRandomDistributeMap(); // MAIN-Test 31 // System.out.println(doubleSecToTime(0.0)); 32 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * (double)秒转时分秒毫秒(HH:mm:ss:SSS) 37 * 38 * @param seconds 秒(双精度类型的数据) 39 * @return string类型的时分秒毫秒(HH:mm:ss:SSS) 40 * @author zero 2019/04/11 41 */ 42 public static String doubleSecToTime(double seconds) { 43 if (seconds == 0.0) { 44 return "0.0"; 45 } 46 // 注意:BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP:四舍五入、BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING:向上取整 47 double d = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(seconds)).setScale(3, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 48 int msec = (int)(d * 1000) % 1000; 49 // System.out.println(msec); 50 int sec = (int)(d * 1000) / 1000; 51 // System.out.println(sec); 52 int hour = sec / 3600; 53 int minute = (sec - hour * 3600) / 60; 54 int second = (sec - hour * 3600 - minute * 60); 55 56 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 57 if (hour > 0) { 58 sb.append(hour + "h"); 59 } 60 if (minute > 0) { 61 sb.append(minute + "m"); 62 } 63 if (second > 0) { 64 sb.append(second + "s"); 65 } 66 if (msec != 0) { 67 sb.append(msec + "ms"); 68 } 69 return sb.toString(); 70 } 71 72 public static List<Integer> testGenRandomIntegerList() { 73 List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(); 74 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 75 list.add(genRandomInteger(5, 10)); 76 } 77 return list; 78 } 79 80 // ========================↓↓↓ 测试map根据key分区 ↓↓↓========================== 81 public static void testRandomDistributeMap() { 82 Map<Double, Integer> map = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(); 83 // 1. 为了测试,随机生成map数据 84 int mapKeyCount = 20; 85 // int range = 10; // 每个值的范围区间 86 for (int i = 0; i < mapKeyCount; i++) { 87 // double key = new BigDecimal(Math.random() * range).setScale(0, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 88 // Integer value = new BigDecimal(Math.random() * range).setScale(0, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).intValue(); 89 double key = genRandomRatio(1, 10, 2);// 每个double类型数据值范围区间:[1,10],精确度为2. 90 Integer value = (int)genRandomRatio(1, 10, 0);// 每个double类型数据值范围区间:[1,10],精确度为0.(是int类型) 91 map.put(key, value); 92 System.out.print(key + " "); 93 } 94 System.out.println(" 随机生成的map:" + map); 95 // 2. 对map进行排序: 96 Map<Double, Integer> sortedMapByKey = sortByKey(map, false); 97 System.out.println("按key↑排map:" + sortedMapByKey); 98 Map<Double, Integer> sortedMapByValue = sortByValue(map, true); 99 System.out.println("按val↓排map:" + sortedMapByValue); 100 // 3. 调用划分区间的方法this.randomDistribute(map,ratio)方法 101 double ratio = genRandomRatio(0.75, 0.8, 2); 102 System.out.println("随机生成的比值为:" + ratio); 103 Map<String, Integer> result = randomDistribute(sortedMapByValue, ratio); 104 // 4. 输出result数据 105 for (String timeNode : result.keySet()) { 106 System.out.println(timeNode + " " + result.get(timeNode)); 107 } 108 // 5. 组装前端所需的数据格式:树状图(同chart数据格式) 109 Map<String, Object> needResultFormatterMap = Maps.newHashMap(); 110 needResultFormatterMap.put("attrDetails", ImmutableMap.of("axis", result.keySet(), "data", result.values(), 111 "field", "avg_spent_time", "legend", "平均时长分布")); 112 System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(needResultFormatterMap)); 113 } 114 115 /** 116 * 将map数据按照key分隔区间 117 * 118 * @param map key:时刻,value:访客数(time-visits) 119 * @param ratio 比值(重点查看多少比例的数据) 120 * @return Map<String, Integer>中,key:时间区间,value:访问数 121 * @author zero 2019/04/10 122 */ 123 public static Map<String, Integer> randomDistribute(Map<Double, Integer> map, double ratio) { 124 if (map.isEmpty()) { 125 return ImmutableMap.of("No data!", 0); 126 } 127 Map<String, Integer> result = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(); 128 double sum = map.values().stream().reduce((a, b) -> a + b).get();// map的value累加求和。 129 double dirtributeNode = Math.round(sum * ratio); 130 System.out.println("所有访客数:" + sum + ",划分节点:" + dirtributeNode); 131 // 第一次划分区间:(8--2) 132 Map<Double, Integer> tMap = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(); 133 long tmpSum = 0; 134 for (Double key : map.keySet()) { 135 tmpSum += map.get(key); 136 if (tmpSum <= dirtributeNode) { 137 tMap.put(key, map.get(key)); 138 } else { 139 tMap.put(key, map.get(key)); 140 break; 141 } 142 } 143 System.out.println("第一次按照比值截取之后的map:" + tMap); 144 Map<Double, Integer> afterRatioMap = sortByKey(tMap, false); 145 System.out.println("按key↑排map:" + afterRatioMap); 146 List<Double> keys = Lists.newArrayList(afterRatioMap.keySet()); 147 // 对keys集合分区间: 148 List<List<Double>> indexList = distributeDouble(keys, genRandomInteger(30, 60), 2); 149 // System.out.println("固定划分好的区间段:" + distributeDouble(keys, 60, 2)); 150 151 for (List<Double> list : indexList) { 152 // start为一小段的闭区间,end:为一小段的开区间。如:list为[1,5]表示的值范围为[1,5)即 1<=x<5,但是indexList中如果list为最后一个,最为双闭区间 153 // 注意:如果划分之后的区间,list无元素存在;则不显示此区间的个数为0.(根据需求更改:无元素在此区间,也得显示区间的元素为0.) 154 Integer tmp = 0; 155 double start = list.get(0), end = list.get(1); 156 for (Double timeKey : afterRatioMap.keySet()) { 157 if (indexList.indexOf(list) == indexList.size() - 1) { 158 if (start <= timeKey && timeKey <= end) { 159 tmp = result.get("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + "]") == null ? 0 160 : result.get("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + "]"); 161 result.put("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + "]", 162 tmp + afterRatioMap.get(timeKey)); 163 } 164 } else { 165 if (start <= timeKey && timeKey < end) { 166 tmp = result.get("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + ")") == null ? 0 167 : result.get("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + ")"); 168 result.put("[" + doubleSecToTime(start) + "," + doubleSecToTime(end) + ")", 169 tmp + afterRatioMap.get(timeKey)); 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 } 174 return result; 175 } 176 177 /** 178 * 随机生成一个[low,high]双闭区间中随机的一个double类型数据 179 * 180 * @param low 最小值(包含) 181 * @param high 最大值(包含) 182 * @param effective_number double类型的精度(如果effective_number=3,则保留三位有效数字) 183 * @return [low,high]双闭区间中随机的一个double类型数据,例如:0.77 184 * @author zero 2019/04/10 185 */ 186 public static double genRandomRatio(double low, double high, int effective_number) { 187 double d = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(Math.random() * (high - low) + low)) 188 .setScale(effective_number, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 189 return d; 190 } 191 192 public static int genRandomInteger(int low, int high) { 193 return new BigDecimal(Math.random() * (high - low + 1) + low).intValue(); 194 } 195 196 /** 197 * 随机生成一个[low,high]双闭区间中随机count个数的double类型数据的list集合 198 * 199 * @param low 最小值(包含) 200 * @param high 最大值(包含) 201 * @param effective_number double类型的精度(如果effective_number=3,则保留三位有效数字) 202 * @param count list大小(即生成多少个随机数字) 203 * @return 204 * @author zero 2019/04/10 205 */ 206 public static List<Double> genRandomDoubleList(double low, double high, int effective_number, int count) { 207 List<Double> randomDouble = Lists.newArrayList(); 208 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 209 double d = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(Math.random() * (high - low) + low)) 210 .setScale(effective_number, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 211 randomDouble.add(d); 212 } 213 return randomDouble; 214 } 215 216 /** 217 * 将integer类型的集合按照区间个数划分固定区间范围的多个子集合(左开右闭) TODO 可以借鉴distributeDouble()方法的分区间原理 218 * 219 * @param list 待划分的区间 220 * @param count 区间个数 221 * @return 222 * @author zero 2019/04/10 223 */ 224 public static List<List<Integer>> distributeInteger(List<Integer> list, int count) { 225 Collections.sort(list); 226 int min = list.get(0); 227 int max = list.get(list.size() - 1); 228 // TODO 特殊情况:当list为:1,2,3,4时,区间格式为4,则结果为[[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [4, 5]]。即最后一个区间[4,5]是没有数据的 229 int range = (max - min) / count == 0 ? 1 : (max - min) / count; 230 System.out.println("最大值:" + max + " 最小值:" + min + " 区间范围:" + range); 231 List<List<Integer>> resultList = Lists.newArrayList(); 232 int tmpStart = min, b1, b2; 233 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 234 b1 = tmpStart; 235 b2 = range; 236 resultList.add(Arrays.asList(b1, b1 + b2)); 237 tmpStart = b1 + b2; 238 } 239 if (tmpStart < max) { 240 resultList.add(Arrays.asList(tmpStart, max)); 241 } 242 return resultList; 243 } 244 245 /** 246 * 分散有序的list集合(打乱有序集合) 247 * 248 * @author zero 2019/04/10 249 */ 250 public static void shuffleList() { 251 List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); 252 Collections.shuffle(list);// 打乱初始的list集合。 253 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 254 } 255 256 // ========================↓↓↓ double集合分区 ↓↓↓========================== 257 public static void testGeneratorDouble() { 258 int effective_number = 3;// 生成double值的精确度 259 int length = 15;// 生成list集合数量 260 int range = 100;// 每个数字的范围 261 int space = 5; // 划分十个区间 262 // 随机生成 263 List<Double> list = generatorDouble(effective_number, length, range); 264 System.out.println(list); 265 // 不定区间-碰撞算法 266 267 // 固定区间-划分 268 List<List<Double>> distributeList = distributeDouble(list, space, effective_number); 269 System.out.println(distributeList); 270 } 271 272 /** 273 * 生成双精度类型的list集合数据 274 * 275 * @param effective_number 生成double值的精确度 276 * @param length 生成list集合数量 277 * @param range 每个值所在区间[0,100] 278 * @return 279 * @author zero 2019/04/09 280 */ 281 public static List<Double> generatorDouble(int effective_number, int length, int range) { 282 List<Double> randomList = Lists.newArrayList(); 283 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { 284 // 如:取0-100随机数,则range=100 285 BigDecimal temp = new BigDecimal(Math.random() * range); 286 // 如:取effective_number=3位有效位 287 double add_data = temp.setScale(effective_number, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 288 randomList.add(add_data); 289 } 290 return randomList; 291 } 292 293 /** 294 * 将list集合划分固定范围区间(每小段区间范围是固定的) 295 * 296 * @param list double集合 297 * @param space 需要划分的具体区间数字,例如:10为划分十个区间 298 * @param effective_number 每个值的精确度 299 * @author zero 2019/04/09 300 */ 301 public static List<List<Double>> distributeDouble(List<Double> list, int space, int effective_number) { 302 // 针对double划分区间 303 Collections.sort(list); 304 double min = list.get(0); 305 double max = list.get(list.size() - 1); 306 double range = (max - min) / space; 307 BigDecimal temp = new BigDecimal(range); 308 range = temp.setScale(effective_number, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); 309 // ↑↑划分区间的核心代码 ↑↑ 310 311 // 显示每个划分好的固定区间的范围 312 List<List<Double>> distributeList = Lists.newArrayList(); 313 double tmpStart = min; 314 BigDecimal b1, b2; 315 for (int i = 0; i < space; i++) { 316 b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(tmpStart)); 317 b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(range)); 318 // System.out.println("[" + b1.doubleValue() + "," + b1.add(b2).doubleValue() + ")");// 左闭右开 319 distributeList.add(Arrays.asList(b1.doubleValue(), b1.add(b2).doubleValue())); 320 tmpStart = b1.add(b2).doubleValue(); 321 } 322 if (tmpStart < max) { 323 distributeList.add(Arrays.asList(tmpStart, max)); 324 } 325 System.out.println("最小值:" + min + " 最大值:" + max + " 区间值:" + range + " 区间个数为:" + distributeList.size()); 326 return distributeList; 327 } 328 329 // ========================↓↓↓ 对map进行排序 ↓↓↓========================== 330 public static void testSortMap() { 331 Map<String, Integer> map = ImmutableMap.of("0", 3, "1", 8, "0.29", 7, "1.67", 3); 332 System.out.println("原始的map:" + map); 333 System.out.println("根据map的key降序:" + sortByKey(map, true)); 334 System.out.println("根据map的key升序:" + sortByKey(map, false)); 335 System.out.println("根据map的value降序:" + sortByValue(map, true)); 336 System.out.println("根据map的value升序:" + sortByValue(map, false)); 337 } 338 339 /** 340 * 根据map的key排序(如果map中的key为Integer类型的字符串,请将map中的key设置为Integer) 341 * 342 * @param map 待排序的map 343 * @param isDesc 是否降序,true:降序,false:升序 344 * @return 排序好的map 345 * @author zero 2019/04/08 346 */ 347 public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Map<K, V> sortByKey(Map<K, V> map, boolean isDesc) { 348 Map<K, V> result = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(); 349 if (isDesc) { 350 map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<K, V>comparingByKey().reversed()) 351 .forEachOrdered(e -> result.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); 352 } else { 353 map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<K, V>comparingByKey()) 354 .forEachOrdered(e -> result.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); 355 } 356 return result; 357 } 358 359 /** 360 * 根据map的value排序 361 * 362 * @param map 待排序的map 363 * @param isDesc 是否降序,true:降序,false:升序 364 * @return 排序好的map 365 * @author zero 2019/04/08 366 */ 367 public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Map<K, V> sortByValue(Map<K, V> map, boolean isDesc) { 368 Map<K, V> result = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(); 369 if (isDesc) { 370 map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<K, V>comparingByValue().reversed()) 371 .forEach(e -> result.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); 372 } else { 373 map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<K, V>comparingByValue()) 374 .forEachOrdered(e -> result.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue())); 375 } 376 return result; 377 } 378 379 }
3. 示例结果展示: