上一篇我们讲解了线程安全的问题,那么要解决线程安全的问题,我们就必须用到线程同步,保证线程之间不互相影响而产生脏数据,下面我们来讲讲具体的实现吧。
首先我们看下例子,我们有个Outputter类,用于输出
/***
*
* 输出类
* @author yangqingshan
*
*/
public class Outputter {
public void output(String name) throws InterruptedException {
// 逐个输出名称
for(int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
然后我们还需要一个线程类,用于调用线程
/***
*
* 线程同步示例
* @author yangqingshan
*
*/
public class SynchronizedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个输出类
final Outputter output = new Outputter();
// new一个线程, 打印名称:yangqingshan
new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
output.output("yangqingshan");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
}.start();
// new一个线程, 打印名称:mayongcheng
new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
output.output("mayongcheng");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
}.start();
}
}
打印出来的结果
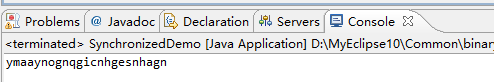
那么我们可以在代码块或者方法加上线程同步,首先看下代码块的。
/***
*
* 输出类
* @author yangqingshan
*
*/
public class Outputter {
public void output(String name) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
// 逐个输出名称
for(int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
}
方法加上线程同步
/***
*
* 输出类
* @author yangqingshan
*
*/
public class Outputter {
public synchronized void output(String name) throws InterruptedException {
// 逐个输出名称
for(int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
通过以上的线程同步可以初步解决线程安全的问题

本站文章为 宝宝巴士 SD.Team 原创,转载务必在明显处注明:(作者官方网站: 宝宝巴士 )
转载自【宝宝巴士SuperDo团队】 原文链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/superdo/p/4872142.html