该计算器使用Python tkinter模块开发
效果如下图
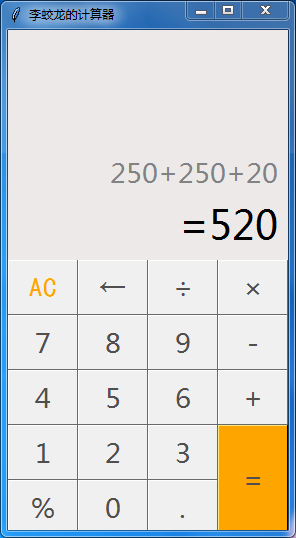
1 import tkinter #导入tkinter模块 2 3 root = tkinter.Tk() 4 root.minsize(280,500) 5 root.title('李蛟龙的计算器') 6 7 8 #1.界面布局 9 #显示面板 10 result = tkinter.StringVar() 11 result.set(0) #显示面板显示结果1,用于显示默认数字0 12 result2 = tkinter.StringVar() #显示面板显示结果2,用于显示计算过程 13 result2.set('') 14 #显示版 15 label = tkinter.Label(root,font = ('微软雅黑',20),bg = '#EEE9E9',bd ='9',fg = '#828282',anchor = 'se',textvariable = result2) 16 label.place(width = 280,height = 170) 17 label2 = tkinter.Label(root,font = ('微软雅黑',30),bg = '#EEE9E9',bd ='9',fg = 'black',anchor = 'se',textvariable = result) 18 label2.place(y = 170,width = 280,height = 60) 19 20 21 22 23 #数字键按钮 24 25 btn7 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '7',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('7')) 26 btn7.place(x = 0,y = 285,width = 70,height = 55) 27 btn8 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '8',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('8')) 28 btn8.place(x = 70,y = 285,width = 70,height = 55) 29 btn9 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '9',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('9')) 30 btn9.place(x = 140,y = 285,width = 70,height = 55) 31 32 btn4 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '4',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('4')) 33 btn4.place(x = 0,y = 340,width = 70,height = 55) 34 btn5 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '5',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('5')) 35 btn5.place(x = 70,y = 340,width = 70,height = 55) 36 btn6 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '6',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('6')) 37 btn6.place(x = 140,y = 340,width = 70,height = 55) 38 39 btn1 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '1',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('1')) 40 btn1.place(x = 0,y = 395,width = 70,height = 55) 41 btn2 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '2',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('2')) 42 btn2.place(x = 70,y = 395,width = 70,height = 55) 43 btn3 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '3',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('3')) 44 btn3.place(x = 140,y = 395,width = 70,height = 55) 45 btn0 = tkinter.Button(root,text = '0',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda : pressNum('0')) 46 btn0.place(x = 70,y = 450,width = 70,height = 55) 47 48 49 #运算符号按钮 50 btnac = tkinter.Button(root,text = 'AC',bd = 0.5,font = ('黑体',20),fg = 'orange',command = lambda :pressCompute('AC')) 51 btnac.place(x = 0,y = 230,width = 70,height = 55) 52 btnback = tkinter.Button(root,text = '←',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = '#4F4F4F',bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('b')) 53 btnback.place(x = 70,y = 230,width = 70,height = 55) 54 btndivi = tkinter.Button(root,text = '÷',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = '#4F4F4F',bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('/')) 55 btndivi.place(x = 140,y = 230,width = 70,height = 55) 56 btnmul = tkinter.Button(root,text ='×',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = "#4F4F4F",bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('*')) 57 btnmul.place(x = 210,y = 230,width = 70,height = 55) 58 btnsub = tkinter.Button(root,text = '-',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('-')) 59 btnsub.place(x = 210,y = 285,width = 70,height = 55) 60 btnadd = tkinter.Button(root,text = '+',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('+')) 61 btnadd.place(x = 210,y = 340,width = 70,height = 55) 62 btnequ = tkinter.Button(root,text = '=',bg = 'orange',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda :pressEqual()) 63 btnequ.place(x = 210,y = 395,width = 70,height = 110) 64 btnper = tkinter.Button(root,text = '%',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('%')) 65 btnper.place(x = 0,y = 450,width = 70,height = 55) 66 btnpoint = tkinter.Button(root,text = '.',font = ('微软雅黑',20),fg = ('#4F4F4F'),bd = 0.5,command = lambda:pressCompute('.')) 67 btnpoint.place(x = 140,y = 450,width = 70,height = 55) 68 69 70 71 72 #操作函数 73 lists = [] #设置一个变量 保存运算数字和符号的列表 74 isPressSign = False #添加一个判断是否按下运算符号的标志,假设默认没有按下按钮 75 isPressNum = False 76 #数字函数 77 def pressNum(num): #设置一个数字函数 判断是否按下数字 并获取数字将数字写在显示版上 78 global lists #全局化lists和按钮状态isPressSign 79 global isPressSign 80 if isPressSign == False: 81 pass 82 else: #重新将运算符号状态设置为否 83 result.set(0) 84 isPressSign = False 85 86 #判断界面的数字是否为0 87 oldnum = result.get() #第一步 88 if oldnum =='0': #如过界面上数字为0 则获取按下的数字 89 result.set(num) 90 else: #如果界面上的而数字不是0 则链接上新按下的数字 91 newnum = oldnum + num 92 result.set(newnum) #将按下的数字写到面板中 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 #运算函数 102 def pressCompute(sign): 103 global lists 104 global isPressSign 105 num = result.get() #获取界面数字 106 lists.append(num) #保存界面获取的数字到列表中 107 108 lists.append(sign) #讲按下的运算符号保存到列表中 109 isPressSign = True 110 111 if sign =='AC': #如果按下的是'AC'按键,则清空列表内容,讲屏幕上的数字键设置为默认数字0 112 lists.clear() 113 result.set(0) 114 if sign =='b': #如果按下的是退格‘’,则选取当前数字第一位到倒数第二位 115 a = num[0:-1] 116 lists.clear() 117 result.set(a) 118 119 120 121 #获取运算结果函数 122 def pressEqual(): 123 global lists 124 global isPressSign 125 126 127 curnum = result.get() #设置当前数字变量,并获取添加到列表 128 lists.append(curnum) 129 130 computrStr = ''.join(lists) #讲列表内容用join命令将字符串链接起来 131 endNum = eval(computrStr) #用eval命令运算字符串中的内容 132 # a = str(endNum) 133 # b = '='+a #给运算结果前添加一个 ‘=’ 显示 不过这样写会有BUG 不能连续运算,这里注释,不要 = 134 # c = b[0:10] #所有的运算结果取9位数 135 result.set(endNum) #讲运算结果显示到屏幕1 136 result2.set(computrStr) #将运算过程显示到屏幕2 137 lists.clear() #清空列表内容 138 139 140 141 142 root.mainloop()

欢迎大家评论指导,如果你也对Python有兴趣,想和博主聊聊技术,爱情,理想,私生活,可以关注我微信账号,有100G的学习资料等着你哦!
因为字数不够,此处省略一万字,用#号代替
###############################################
################################################################
##################################################################################