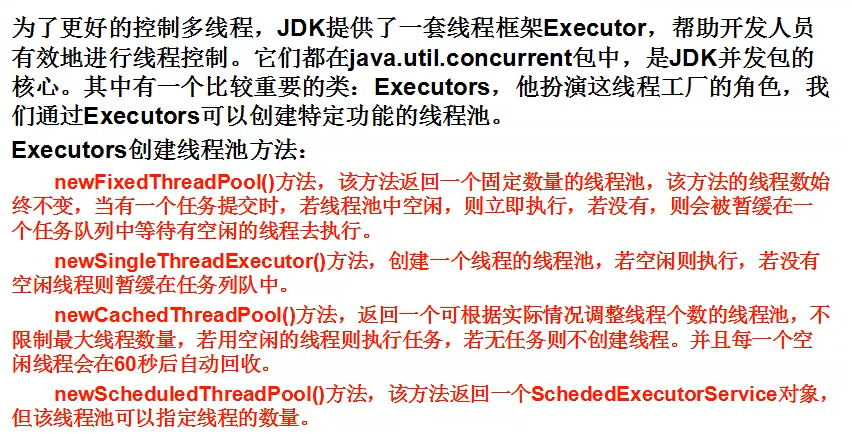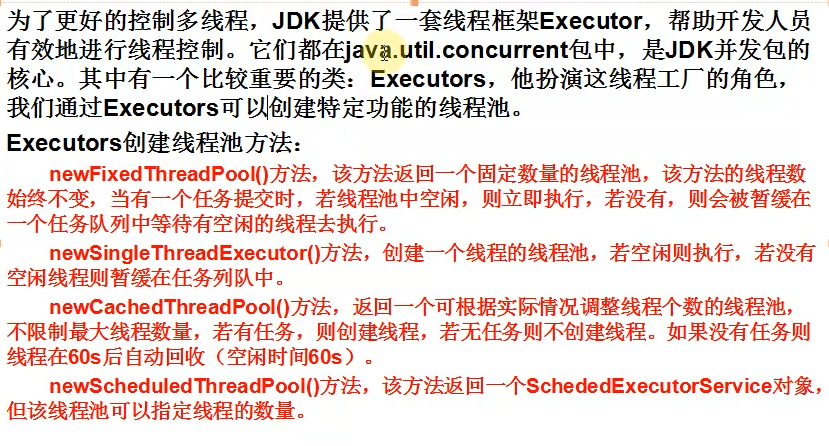

class Temp extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("run");
}
}
public class UseExecutors {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//ThreadPoolExecutor
Temp command = new Temp();
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleTask = scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(command, 5, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
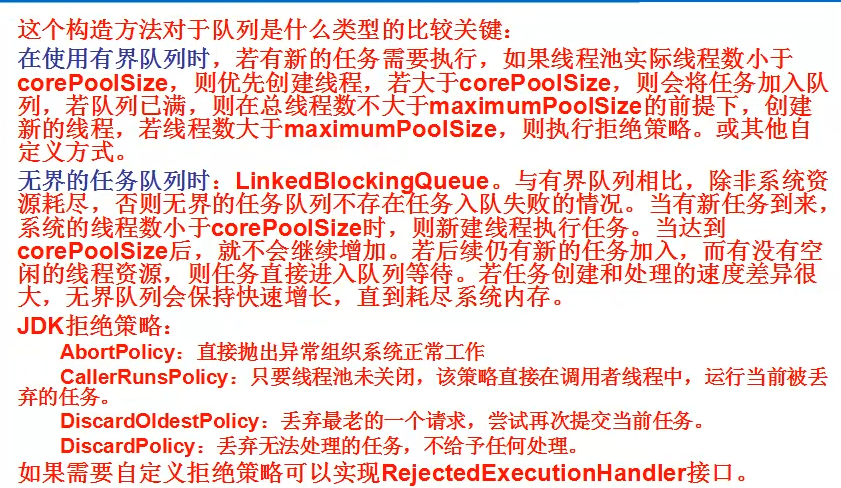
* 在使用有界队列时,若有新的任务需要执行,如果线程池实际线程数小于corePoolSize,则优先创建线程,
* 若大于corePoolSize,则会将任务加入队列,
* 若队列已满,则在总线程数不大于maximumPoolSize的前提下,创建新的线程,
* 若线程数大于maximumPoolSize,则执行拒绝策略。或其他自定义方式。
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, //coreSize
2, //MaxSize
60, //60
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3) //指定一种队列 (有界队列)
//new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
, new MyRejected()
//, new DiscardOldestPolicy()
);
MyTask mt1 = new MyTask(1, "任务1");
MyTask mt2 = new MyTask(2, "任务2");
MyTask mt3 = new MyTask(3, "任务3");
MyTask mt4 = new MyTask(4, "任务4");
MyTask mt5 = new MyTask(5, "任务5");
MyTask mt6 = new MyTask(6, "任务6");
pool.execute(mt1);
pool.execute(mt2);
pool.execute(mt3);
pool.execute(mt4);
pool.execute(mt5);
pool.execute(mt6);
pool.shutdown();
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
public class MyRejected implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public MyRejected(){
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println("自定义处理..");
System.out.println("当前被拒绝任务为:" + r.toString());
}
}
public class MyTask implements Runnable{
private int taskId;
private String taskName;
public MyTask(int taskId, String taskName){
this.taskId = taskId;
this.taskName = taskName;
}
public int getTaskId() {
return taskId;
}
public void setTaskId(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
public String getTaskName() {
return taskName;
}
public void setTaskName(String taskName) {
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run taskId =" + this.taskId);
Thread.sleep(5*1000);
//System.out.println("end taskId =" + this.taskId);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String toString(){
return Integer.toString(this.taskId);
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class UseThreadPoolExecutor2 implements Runnable{
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int temp = count.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("任务" + temp);
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue =
//new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10);
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5, //core
10, //max
120L, //2fenzhong
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 20; i++){
executor.execute(new UseThreadPoolExecutor2());
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("queue size:" + queue.size()); //10
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
Executor框架: