合成拷贝控制与继承
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Base 5 { 6 public: 7 Base() { cout << "Base contruction" << endl; } 8 virtual ~Base() { cout << "Base deconstruction" << endl; } 9 10 }; 11 12 class Derived : public Base 13 { 14 public: 15 Derived(int i) 16 { 17 num = i; 18 cout << "Derived contruction " << num << endl; 19 } 20 virtual ~Derived() 21 { 22 cout << "Derived deconstruction" << num << endl; 23 } 24 private: 25 int num; 26 }; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 Derived derived(1); 31 32 Base* basePtr; 33 basePtr = new Derived(2); 34 delete basePtr; 35 }
输出结果:
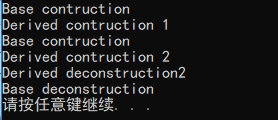
2. 测试代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Base 5 { 6 private: 7 Base() { cout << "Base contruction" << endl; } 8 virtual ~Base() { cout << "Base deconstruction" << endl; } 9 10 }; 11 12 class Derived : public Base 13 { 14 public: 15 Derived(int i) 16 { 17 num = i; 18 cout << "Derived contruction " << num << endl; 19 } 20 virtual ~Derived() 21 { 22 cout << "Derived deconstruction" << num << endl; 23 } 24 private: 25 int num; 26 }; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 Derived derived(1); 31 32 Base* basePtr; 33 basePtr = new Derived(2); 34 delete basePtr; 35 }
报告结果:
错误 E0330 "Base::~Base()" (已声明 所在行数:8) 不可访问 错误 C2248 “Base::Base”: 无法访问 private 成员(在“Base”类中声明) 错误 C2248 “Base::~Base”: 无法访问 private 成员(在“Base”类中声明) 错误 C2248 “Base::~Base”: 无法访问 private 成员(在“Base”类中声明)
虚析构函数
直接的讲,C++中基类采用virtual虚析构函数是为了防止内存泄漏。具体地说,如果派生类中申请了内存空间,并在其析构函数中对这些内存空间进行释放。假设基类中采用的是非虚析构函数,当删除基类指针指向的派生类对象时就不会触发动态绑定,因而只会调用基类的析构函数,而不会调用派生类的析构函数。那么在这种情况下,派生类中申请的空间就得不到释放从而产生内存泄漏。所以,为了防止这种情况的发生,基类的析构函数应采用virtual虚析构函数。
1.删除一个指向派生类对象的基类指针,而基类析构函数又是非虚的话, 那么就会先调用基类的析构函数(上面第2种情况),派生类的析构函数得不到调用。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Base { 5 public: 6 Base() { cout << "Base Constructor" << endl; } 7 ~Base() { cout << "Base Destructor" << endl; } 8 }; 9 class Derived : public Base { 10 public: 11 Derived() { cout << "Derived Constructor" << endl; } 12 ~Derived() { cout << "Derived Destructor" << endl; } 13 }; 14 int main() { 15 Base *p = new Derived(); 16 delete p; 17 return 0; 18 }
输出结果:
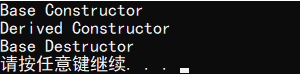
2.如果删除一个指向派生类的基类指针时,应该把析构函数声明为虚函数。 事实上,《Effective C++》中的观点是,只要一个类有可能会被其它类所继承, 就应该声明虚析构函数。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Base { 5 public: 6 Base() { cout << "Base Constructor" << endl; } 7 virtual ~Base() { cout << "Base Destructor" << endl; } 8 }; 9 class Derived : public Base { 10 public: 11 Derived() { cout << "Derived Constructor" << endl; } 12 ~Derived() { cout << "Derived Destructor" << endl; } 13 }; 14 int main() { 15 Base *p = new Derived(); 16 delete p; 17 return 0; 18 }
输出结果:
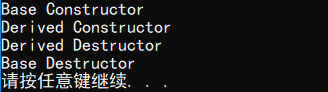
定义派生类的拷贝或移动构造函数
对派生类进行拷贝构造时,如果想让基类的成员也同时拷贝,就一定要在派生类拷贝构造函数初始化列表中显示调用基类拷贝构造函数(当然在函数体内将基类部分的值拷贝也是可以的,只不过它是先用默认构造函数初始化后再修改的基类成员变量的值,效率比较低),否则它会调用基类的默认构造函数,而不会对基类的成员变量拷贝值,这样生成的对象,它的派生类部分和被拷贝的对象派生类部分一样,而基类部分则是默认构造函数的初始化结果。
1. 测试代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class A { 5 public: 6 A() { cout << "A default constructor" << endl; } 7 A(A&) { cout << "A copy constructor" << endl; } 8 }; 9 class B : public A { 10 public: 11 B() { cout << "B default constructor" << endl; } 12 B(B &b) { cout << "B copy constructor" << endl; } 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 B b; 18 B c = b; 19 return 0; 20 }
输出结果:
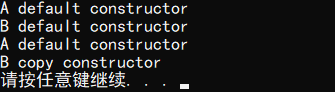
2. 测试代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class A { 5 public: 6 A() { cout << "A 默认构造函数" << endl; } 7 A(A&) { cout << "A 拷贝构造函数" << endl; } 8 A& operator= (const A& a) 9 { 10 cout << "A 拷贝赋值运算符" << endl; 11 return *this; 12 } 13 }; 14 class B : public A { 15 public: 16 B() { cout << "B 默认构造函数" << endl; } 17 B(B &b) : A(b) { cout << "B 拷贝构造函数" << endl; } 18 B& operator= (const B& b) 19 { 20 A::operator=(b); 21 cout << "B 拷贝赋值运算符" << endl; 22 return *this; 23 } 24 }; 25 26 int main() 27 { 28 B b; 29 B c = b; 30 c = b; 31 return 0; 32 } 33 34 /* 35 A 默认构造函数 36 B 默认构造函数 37 A 拷贝构造函数 38 B 拷贝构造函数 39 A 拷贝赋值运算符 40 B 拷贝赋值运算符 41 请按任意键继续. 42 */
输出结果:

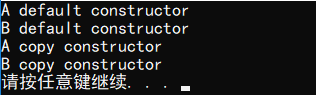
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class A { 5 public: 6 A() { cout << "A default constructor" << endl; } 7 A(A&) { cout << "A copy constructor" << endl; } 8 }; 9 class B : public A { 10 public: 11 B() { cout << "B default constructor" << endl; } 12 B(B &b): A(b) { cout << "B copy constructor" << endl; } 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 B b; 18 B c = b; 19 return 0; 20 }
输出结果:
继承的构造函数
继承中不能继承的三个部分: ①构造函数 ②析构函数 ③赋值运算符重载
子类为完成基类初始化,在C++11之前,需要在初始化列表调用基类的构造函数,从而完成构造函数的传递。如果基类拥有多个构造函数,那么子类也需要实现多个与基类构造函数对应的构造函数。
1 class Base 2 { 3 public: 4 Base(int va) : m_value(va), m_c(‘0’) {} 5 Base(char c) : m_c(c), m_value(0) {} 6 private: 7 int m_value; 8 char m_c; 9 }; 10 11 class Derived : public Base 12 { 13 public: 14 //初始化基类需要透传基类的各个构造函数,那么这是很麻烦的 15 Derived(int va) : Base(va) {} 16 Derived(char c) : Base(c) {} 17 18 //假设派生类只是添加了一个普通的函数 19 void display() 20 { 21 //dosomething 22 } 23 };
书写多个派生类构造函数只为传递参数完成基类的初始化,这种方式无疑给开发人员带来麻烦,降低了编码效率。从C++11开始,推出了继承构造函数(Inheriting Constructor),使用using来声明继承基类的构造函数,我们可以这样书写。
1 class Base { 2 public: 3 Base(int va) : m_value(va), m_c('0') {} 4 Base(char c) : m_c(c), m_value(0) {} 5 private: 6 int m_value; 7 char m_c; 8 }; 9 10 class Derived : public Base { 11 public: 12 //使用继承构造函数 13 using Base::Base; 14 15 //假设派生类只是添加了一个普通的函数 16 void display() { /* dosomething */ } 17 };
上面代码中,我们通过using Base::Base把基类构造函数继承到派生类中,不再需要书写多个派生类构造函数来完成基类的初始化。更为巧妙的是,C++11标准规定,继承构造函数与类的一些默认函数(默认构造、析构、拷贝构造函数等)一样,是隐式声明,如果一个继承构造函数不被相关代码使用,编译器不会为其产生真正的函数代码。这样比通过派生类构造函数“透传构造函数参数”来完成基类初始化的方案,总是需要定义派生类的各种构造函数更加节省目标代码空间。
注意事项
(2)构造函数拥有默认值会产生多个构造函数版本,且继承构造函数无法继承基类构造函数的默认参数,所以我们在使用有默认参数构造函数的基类时就必须要小心。
class A { public: A(int a = 3, double b = 4) : m_a(a), m_b(b) {} void display() { cout << m_a << " " << m_b << endl; } } private: int m_a; double m_b; }; class B : public A { public: using A::A; };
那么A中的构造函数会有下面几个版本:
A() A(int) A(int,double) A(constA&)
那么B中对应的继承构造函数将会包含如下几个版本:
B() B(int) B(int,double) B(constB&)
可以看出,参数默认值会导致多个构造函数版本的产生,因此在使用时需格外小心。
(3)多继承的情况下,继承构造函数会出现“冲突”的情况,因为多个基类中的部分构造函数可能导致派生类中的继承构造函数的函数名、参数(即函数签名)相同。考察如下代码:
class A { public: A(int i) {} }; class B { public: B(int i) {} }; class C : public A, public B { public: using A::A; using B::B; //编译出错,重复定义C(int) //显示定义继承构造函数C(int) C(int i) :A(i), B(i) {} };
为避免继承构造函数冲突,可以通过显示定义继承类冲突的构造函数,组织隐式生成相应的继承构造函数。
此外,使用继承构造函数时,还需要注意以下几点:
- 如果基类构造函数被申明为私有成员函数,或者派生类是从基类中虚继承的 ,那么就不能在派生类中申明继承构造函数;
- 一旦使用继承构造函数,编译器就不会再为派生类生成默认构造函数了。
