1、《Selective Kernel Networks》
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
开源参考地址:github: https://github.com/implus/SKNet
SKNet核心思想是用多尺度的特征获得通道级别的权重,使用5×5的Kernel提升精度,采用普遍的Attention操作。为降低参数量,使用Group Convolution做trade off
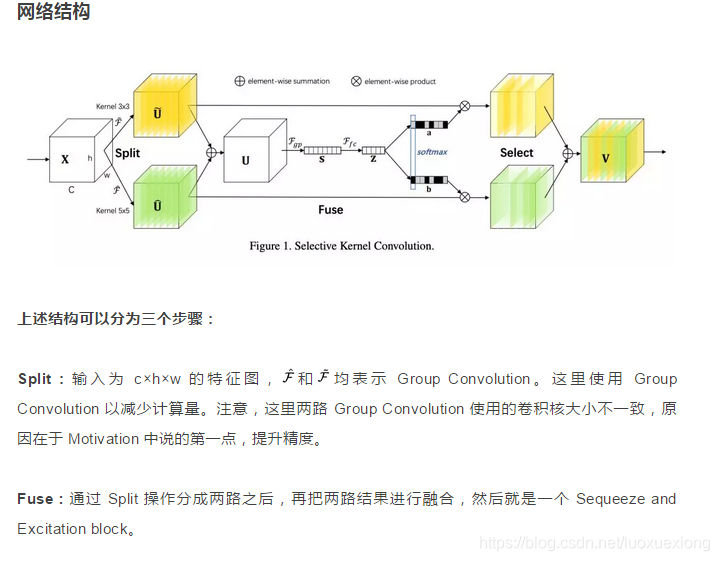

简单来说,SKNet将原始的feature map经过不同大小的kernel得到多个特征图,特征图相加得到U,用全局平均池化沿着H*W维度进行平均,获得关于channel的C×1×1的一维向量,通过线性变换将C维映射到Z维,再使用线性变换(个数与kernel的个数一致)从Z维映射到C维,获得channel维度的信息提取,再使用softmax进行归一化,代表channel的重要程度(相当于mask)。这三个mask与多个特征图相乘得到三个模块,相加后得到最终模块A。(先分支-再合并)
代码:
1 import torch.nn as nn 2 import torch 3 class SKConv(nn.Module): 4 def __init__(self, features, WH, M, G, r, stride=1, L=32): 5 super(SKConv, self).__init__() 6 d = max(int(features / r), L) 7 self.M = M 8 self.features = features 9 self.convs = nn.ModuleList([]) 10 for i in range(M): 11 # 使用不同kernel size的卷积 12 self.convs.append( 13 nn.Sequential( 14 nn.Conv2d(features, 15 features, 16 kernel_size=3 + i * 2, 17 stride=stride, 18 padding=1 + i, 19 groups=G), nn.BatchNorm2d(features), 20 nn.ReLU(inplace=False))) 21 22 self.fc = nn.Linear(features, d) 23 self.fcs = nn.ModuleList([]) 24 for i in range(M): 25 self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(d, features)) 26 self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) 27 def forward(self, x): 28 for i, conv in enumerate(self.convs): 29 fea = conv(x).unsqueeze_(dim=1) 30 if i == 0: 31 feas = fea 32 else: 33 feas = torch.cat([feas, fea], dim=1) 34 fea_U = torch.sum(feas, dim=1) 35 fea_s = fea_U.mean(-1).mean(-1) 36 fea_z = self.fc(fea_s) 37 for i, fc in enumerate(self.fcs): 38 print(i, fea_z.shape) 39 vector = fc(fea_z).unsqueeze_(dim=1) 40 print(i, vector.shape) 41 if i == 0: 42 attention_vectors = vector 43 else: 44 attention_vectors = torch.cat([attention_vectors, vector], 45 dim=1) 46 attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors) 47 attention_vectors = attention_vectors.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) 48 fea_v = (feas * attention_vectors).sum(dim=1) 49 return fea_v 50 if __name__ == "__main__": 51 t = torch.ones((32, 256, 24,24)) 52 sk = SKConv(256,WH=1,M=2,G=1,r=2) 53 out = sk(t) 54 print(out.shape)
2、《Strip Pooling: Rethinking Spatial Pooling for Scene Parsing》
代码地址:https://github.com/Andrew-Qibin/SPNet
作者提出长条性的Kernel应用于特定场景,使用了两个模块:SPM(在横向与纵向backbone的feature map上进行global pooling操作,增大网络感受野,用于优化特征图)、MPM(对backbone部分和backbone上模块进行优化)
(1)Strip Pooling Module
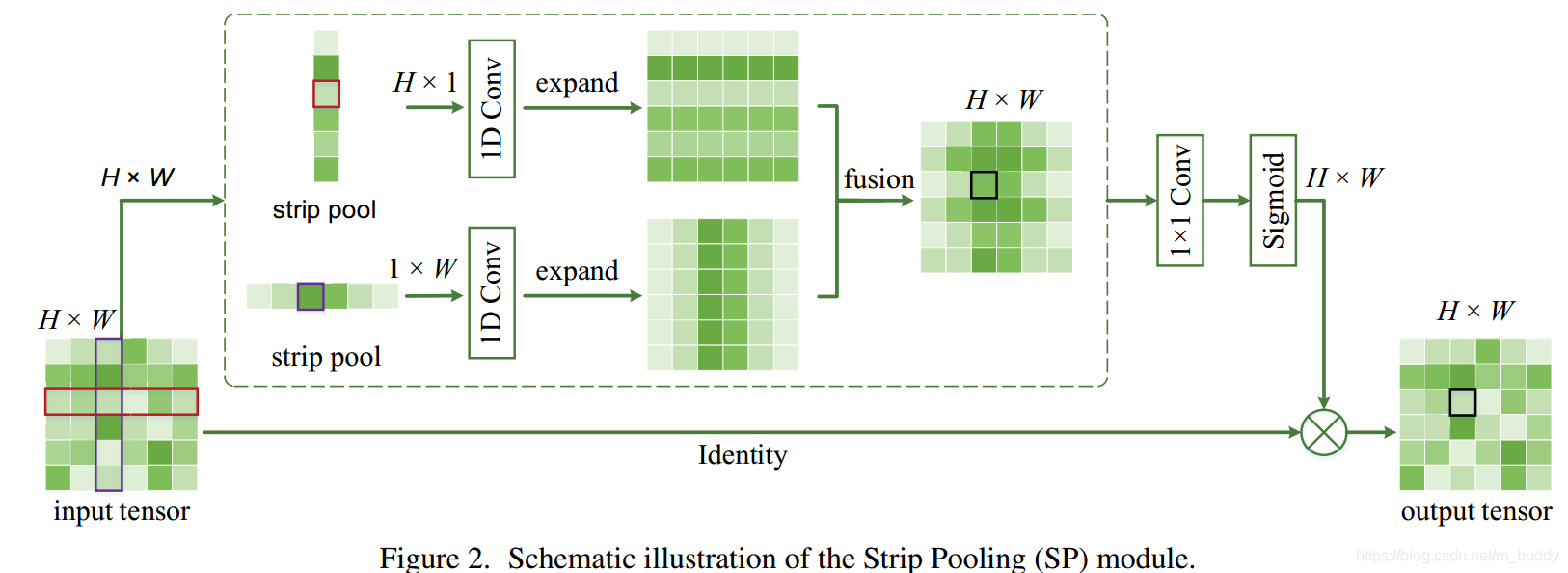
分别在垂直方向和水平方向做池化操作,再应用卷积核为3的一维卷积进行调和,再expand到原先的特征图大小,再将两个特征图进行融合,添加了1×1的卷积用于改变channel个数。经过sigmoid激活函数后获得权重矩阵再与原特征图进行点乘得到最后的结果,这就类似于attention机制。
(2)Mixed Pooling Module金字塔模型
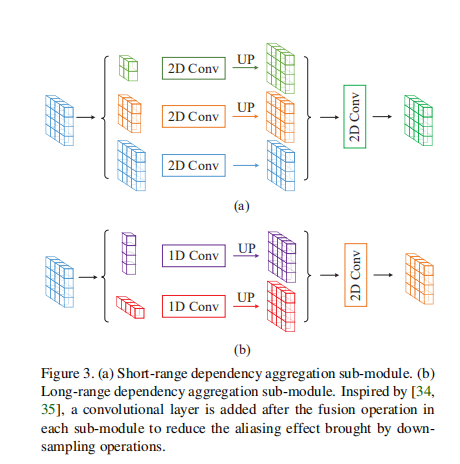
MPM由两个子模块(长依赖和短依赖)构成。上图(a)是针对短依赖,类似金字塔模型,使用轻量化的PPM模块进行设计,解决局部依赖问题。上图(b)是针对长依赖,使用strip pooling操作替换原有的全局平均池化操作。
1 ### 通过AdaptiveAvgPool2d实现strip pooling 2 self.pool1 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(pool_size[0]) 3 self.pool2 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(pool_size[1]) 4 self.pool3 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None)) 5 self.pool4 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1)) 6 7 ## SPM模块 8 def forward(self, x): 9 _, _, h, w = x.size() 10 x1 = self.conv1_1(x) 11 x2 = self.conv1_2(x) 12 x2_1 = self.conv2_0(x1) 13 x2_2 = F.interpolate(self.conv2_1(self.pool1(x1)), (h, w), **self._up_kwargs) 14 x2_3 = F.interpolate(self.conv2_2(self.pool2(x1)), (h, w), **self._up_kwargs) 15 x2_4 = F.interpolate(self.conv2_3(self.pool3(x2)), (h, w), **self._up_kwargs) 16 x2_5 = F.interpolate(self.conv2_4(self.pool4(x2)), (h, w), **self._up_kwargs) 17 x1 = self.conv2_5(F.relu_(x2_1 + x2_2 + x2_3)) 18 x2 = self.conv2_6(F.relu_(x2_5 + x2_4)) 19 out = self.conv3(torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)) 20 return F.relu_(x + out)
3、《HRNet:Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation》
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09212.pdf
github:https://github.com/leoxiaobin/deep-high-resolution-net.pytorch
动机:
- 分类网络并不适合区域层次和像素层次的问题,因为学到的表征本质上具有低分辨率的特点,在分辨率上的巨大损失使得其在对空间精度敏感的任务上很难取得准确的预测结果;
- 作者认为不应该局限于从分类卷积神经网络生成的低分辨率表征来恢复高分辨率表征这一路线,而应该为高分辨率表征学习建立新的网络结构。
方法:
由传统的串行连接高低分辨率卷积,改成并行连接高低分辨率卷积,始终保持高分辨率特征,并且多次进行高低分辨率的信息交换,学习到较为丰富的特征表示。
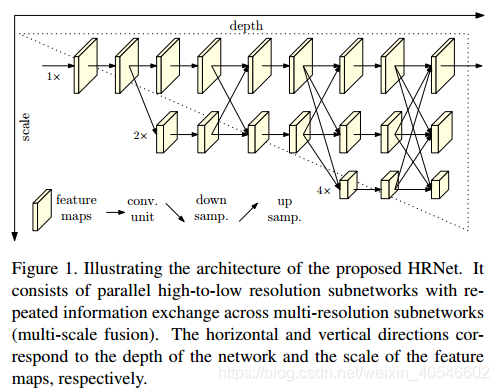
横向为depth变化,纵向为scale变化。第一行为主干网络,特征图保持高分辨率水平,作为第一阶段。后面逐渐并行加入分辨率子网络建立更多的阶段。各个并行网络之间相互交换信息,实现多尺度的特征融合和特征提取。最终预测图所估计的关键点是在高分辨率主干网络进行输出。但是训练量大,不是轻量级的网络结构。