一、理论知识学习
(一)、线性回归
1、简单概念
(1)线性回归是对n维输入的加权和,外加偏差
![]()
(2)可使用平方损失来衡量预测值和真实值的差异

(3)线性回归有显示解
(4)线性回归可以看做是单层神经网络
2、基础优化算法
梯度下降:Wt=Wt-1-学习率*损失函数在Wt-1的梯度,学习率是步长的超参数

小批量梯度下降:随机采样b个样本来近似损失,b是批量大小
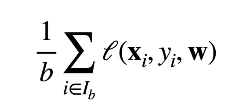
梯度下降通过不断沿着反梯度方向更新参数求解
(二)softmax回归:多类分类模型
1、从回归到多类分类
(1)均方损失
首先是独热编码,保证1位有效:
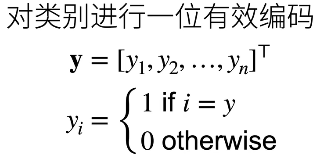
最大值作为预测
(2)无校验比例:需要更置信的识别正确类
![]()
(3)校验比例

(4)交叉熵损失:衡量两个概率的区别
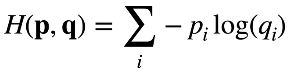
(5)梯度:

2、损失函数
(1)均方损失L2 Loss:
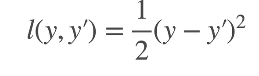
(2)绝对值损失L1 Loss:

(3)Huber's Robust Loss

3、具体实现(复杂版)
1 import torch 2 from IPython import display 3 #pip install d2l 4 from d2l import torch as d2l 5 6 batch_size = 256 7 train_iter,test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) 8 9 num_inputs = 784#展平图像为28*28=784 10 num_outputs = 10#10个类别,输出维度为10 11 12 W = torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(num_inputs,num_outputs),requires_grad=True) 13 b = torch.zeros(num_outputs,requires_grad=True) 14 15 #定义softmax 16 X = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0,3.0],[4.0,5.0,6.0]]) 17 X.sum(0,keepdim=True),X.sum(1,keepdim=True) 18 #(tensor([[5., 7., 9.]]), tensor([[ 6.],[15.]])) 19 20 def softmax(X): 21 X_exp = torch.exp(X) 22 partition = X_exp.sum(1,keepdim = True)#对每一行进行求和 23 return X_exp / partition#广播机制,对第i行除以partition的第i个元素 24 25 X = torch.normal(0, 1, (2,5)) 26 X_prob = softmax(X) 27 X_prob,X_prob.sum(1) 28 #(tensor([[0.1276, 0.1159, 0.4678, 0.0687, 0.2200], 29 # [0.0985, 0.2689, 0.1220, 0.2625, 0.2481]]), tensor([1.0000, 1.0000])) 30 31 def net(X): 32 return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1,W.shape[0])),W)+b)#W.shape[0]=784,batch_size=256,所以X的size为256*784 33 #reshape括号里的括号值得是一个元组,是单个变量 34 35 #创建数据 36 y = torch.tensor([0,2])#两个真实的标号 37 y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1,0.3,0.6],[0.3,0.2,0.5]])#预测值 38 y_hat[[0,1],y]#[0,1]是取axis,即外面的行;[0,2]是取axis1的下标 39 #[0,1],y 对于第0样本,把对应标号的预测值y0;对于第1样本,拿出y1下标对应的输出。y_hat的[0,0][1,2] 40 41 #定义交叉熵损失函数 42 def cross_entropy(y_hat,y): 43 return -torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)),y])#range(len(y_hat))=y_hat.shape[0],提取矩阵行数 44 cross_entropy(y_hat,y)#y_hat 2*3 y 2 45 #tensor([2.3026, 0.6931])分别是样本0和样本1的损失 46 47 def accuracy(y_hat,y): #计算预测正确的个数 48 if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:#shape大于1且列数大于1 49 y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)#最大数的下标存到y_hat里 50 cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y#将y_hat的数据类型转成y的数据类型,cmp是true/false 51 return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())#cmp转换成0/1 52 accuracy(y_hat,y) / len(y)#预测正确个数除以y的个数是预测正确的概率 0.5 53 54 55 #评估准确率 56 def evaluate_accuracy(net,data_iter): 57 if isinstance(net,torch.nn.Module):#判断是否是torch.nn的模型类别,是的话将模型设置为评估模式 58 net.eval()#评估模式 59 metric = Accumulator(2)#正确预测数、预测总数 60 for X,y in data_iter: 61 metric.add(accuracy(net(X),y),y.numel())#y.numel()样本总数 62 return metric[0] / metric[1]#分类正确样本数/总样本数 63 64 #在n个变量上累加,创建了两个变量 65 class Accumulator: 66 def __init__(self, n): 67 self.data = [0.0] * n 68 69 def add(self, *args): 70 self.data = [a + float(b) for a, b in zip(self.data, args)] 71 72 def reset(self): 73 self.data = [0.0] * len(self.data) 74 75 def __getitem__(self, idx): 76 return self.data[idx] 77 evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)#0.118 这个数是随机的 78 79 def train_epoch_ch3(net,train_iter,loss,updater): 80 if isinstance(net,torch.nn.Module): 81 net.train() 82 metric = Accumulator(3)#长度为3的迭代器 83 for X,y in train_iter: 84 y_hat = net(X) 85 l = loss(y_hat, y) 86 if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer): 87 updater.zero_grad() 88 l.backward() 89 updater.step() 90 metric.add(float(l)*len(y),accuracy(y_hat,y),y.size().numel())#记录分类的正确的个数 91 else: 92 l.sum().backward()#如果是自定义,算出来的是向量,需要求和 93 updater(X.shape[0])#根据批量大小update 94 metric.add(float(l.sum()),accuracy(y_hat,y),y.numel()) 95 return metric[0] / metric[2],metric[1] / metric[2]#loss的累加除以总样本数、分类正确数除以总样本数 96 97 class Animator: 98 """在动画中绘制数据。""" 99 def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None, 100 ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear', 101 fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1, 102 figsize=(3.5, 2.5)): 103 if legend is None: 104 legend = [] 105 d2l.use_svg_display() 106 self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize) 107 if nrows * ncols == 1: 108 self.axes = [self.axes,] 109 self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(self.axes[ 110 0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend) 111 self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts 112 113 def add(self, x, y): 114 if not hasattr(y, "__len__"): 115 y = [y] 116 n = len(y) 117 if not hasattr(x, "__len__"): 118 x = [x] * n 119 if not self.X: 120 self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)] 121 if not self.Y: 122 self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)] 123 for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)): 124 if a is not None and b is not None: 125 self.X[i].append(a) 126 self.Y[i].append(b) 127 self.axes[0].cla() 128 for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts): 129 self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt) 130 self.config_axes() 131 display.display(self.fig) 132 display.clear_output(wait=True) 133 134 def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): 135 """训练模型(定义见第3章)。""" 136 animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9], 137 legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc']) 138 for epoch in range(num_epochs): 139 train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater) 140 test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter) 141 animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,)) 142 train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics 143 assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss 144 assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc 145 assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc 146 147 lr = 0.1 148 149 def updater(batch_size): 150 return d2l.sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size)#实现sgd 151 152 num_epochs = 10 153 train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
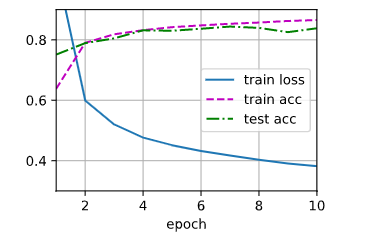
损失函数和精度的图片如下所示:
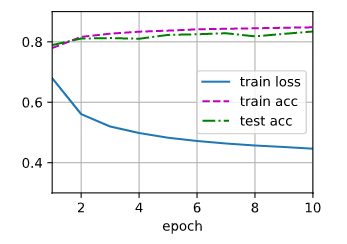
1 def predict_ch3(net, test_iter, n=6): 2 """预测标签(定义见第3章)。""" 3 for X, y in test_iter: 4 break 5 trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y) 6 preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1)) 7 titles = [true + ' ' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)] 8 d2l.show_images(X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n]) 9 10 predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
对图像进行分类预测:

4、具体实现(简单版)
1 #简洁实现 2 import torch 3 from torch import nn 4 from d2l import torch as d2l 5 6 batch_size = 256 7 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) 8 9 net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 10))#flatten表示任何维度的tensor保持第0维度,其他展成向量 10 11 def init_weights(m):#m是当前layer 12 if type(m) == nn.Linear: 13 nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)#默认为0,方差为0.01 14 15 net.apply(init_weights);#将这个函数apply到net里 16 #交叉熵损失函数中传递未归一化的预测,并同时计算softmax及其对数 17 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 18 #使用学习率为0.1的小批量随机梯度下降作为优化算法 19 trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1) 20 21 num_epochs = 10 22 d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
损失函数和正确率结果图如下:

(三)感知机
1、感知机概念
给定输入x,权重w,偏移b,感知机输出:
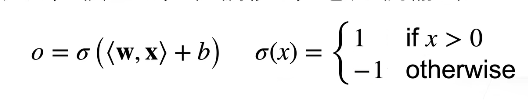
感知机是个二分类问题,1或0,1或-1,如果两者异号预测错误。
损失函数:分类错误则后面一项为正,损失函数不为0,要进入梯度下降更新
![]()
感知机不能拟合XOR函数(异或),只能产生线性分割面
2、多层感知机
以XOR函数为例,用两个感知机组合实现多层感知机。超参数为隐藏层数和各个隐藏层大小。
常用的激活函数:
(1)Sigmoid激活函数

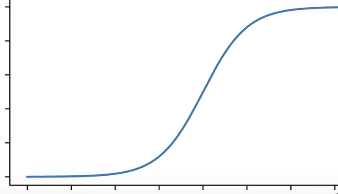
(2)Tanh激活函数
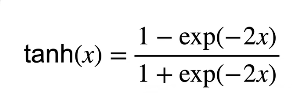
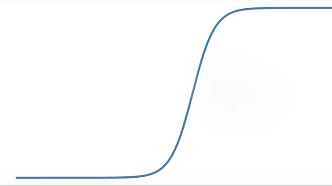
(3)ReLU激活函数
![]()
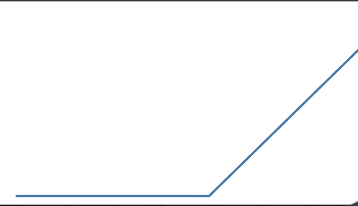
3、代码实现
1 #多层感知机 2 import torch 3 from torch import nn 4 from d2l import torch as d2l 5 6 batch_size = 256 7 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) 8 9 num_inputs,num_outputs,num_hiddens = 784,10,256#包含了256个隐藏单元 10 #单隐藏层的多层感知机 11 W1 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(num_inputs, num_hiddens, requires_grad=True) * 0.01) 12 b1 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens, requires_grad=True))#偏差为0 13 W2 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(num_hiddens, num_outputs, requires_grad=True) * 0.01) 14 b2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)) 15 16 params = [W1, b1, W2, b2]#第一层和第二层 17 18 #ReLU激活函数 19 def relu(X): 20 a = torch.zeros_like(X)#数据类型和形状一样 元素值为0 21 return torch.max(X, a) 22 #定义网络 23 def net(X): 24 X = X.reshape((-1, num_inputs))#28*28拉成784 25 H = relu(X @ W1 + b1)#@是矩阵乘法 26 return (H @ W2 + b2) 27 #交叉熵损失函数 28 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 29 #训练过程 30 num_epochs, lr = 10, 0.1 31 updater = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=lr) 32 d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater)
结果图如下所示:
1 #简洁实现 2 import torch 3 from torch import nn 4 from d2l import torch as d2l 5 6 net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10))#加了relu激活函数 7 8 def init_weights(m): 9 if type(m) == nn.Linear: 10 nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01) 11 12 net.apply(init_weights); 13 14 batch_size, lr, num_epochs = 256, 0.1, 10 15 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 16 trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) 17 18 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) 19 d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
结果图如下所示:

(四)模型选择
1、训练误差:模型在训练数据上的误差
泛化误差:模型在新数据上的误差
验证数据集:一个用来评估模型好坏的数据集
测试数据集:只用一次的数据集
K-折交叉验证(数据不够时使用):将训练数据分割成K块,循环使用第i块作为验证数据集,其余作为训练数据集,报告K个验证集误差的平均
2、过拟合和欠拟合
模型容量:拟合各种函数的能力
低容量的模型难以拟合训练数据,高容量的模型可以记住所有的训练数据


VC维衡量训练误差和繁华误差的间隔
3、代码模拟
import math import numpy as np import torch from torch import nn #!pip install d2l from d2l import torch as d2l max_degree = 20#特征为20 n_train, n_test = 100, 100 true_w = np.zeros(max_degree) true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6])#剩下的为0,是噪音项 features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1)) np.random.shuffle(features)#打乱顺序 poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1))#计算features的max_degree次方 for i in range(max_degree): poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1)#计算函数中传递的数字的伽玛值。 labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w)#矩阵乘法、点积 labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape) true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32) for x in [true_w, features, poly_features, labels]] features[:2], poly_features[:2, :], labels[:2] def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss): """评估给定数据集上模型的损失。""" metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) for X, y in data_iter: out = net(X) y = y.reshape(out.shape) l = loss(out, y) metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel()) return metric[0] / metric[1] def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,num_epochs=400): loss = nn.MSELoss() input_shape = train_features.shape[-1] net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False)) batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0]) train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),batch_size) test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),batch_size, is_train=False) trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],legend=['train', 'test']) for epoch in range(num_epochs): d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer) if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0: animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss), evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss))) print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy()) train(poly_features[:n_train, :4], poly_features[n_train:, :4], labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:]) train(poly_features[:n_train, :2], poly_features[n_train:, :2],#欠拟合,只使用了前两列的数据 labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:]) train(poly_features[:n_train, :], poly_features[n_train:, :],#过拟合,用了所有的列,包括噪音 labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:], num_epochs=1500)
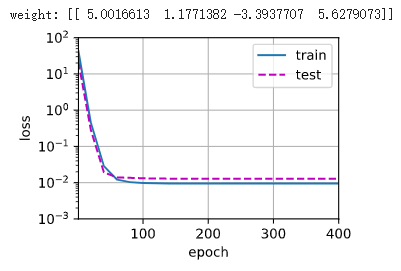
训练结果和测试结果图:
欠拟合结果图:
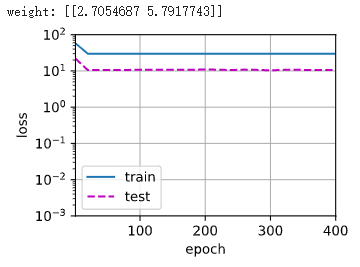
过拟合结果图:

(五)权重衰退:常用的处理过拟合的方法
1、正则化惩罚
均方范数:通过限制参数值的选择范围控制模型容量,通常不限制偏移b
![]()


权重衰退的理解:
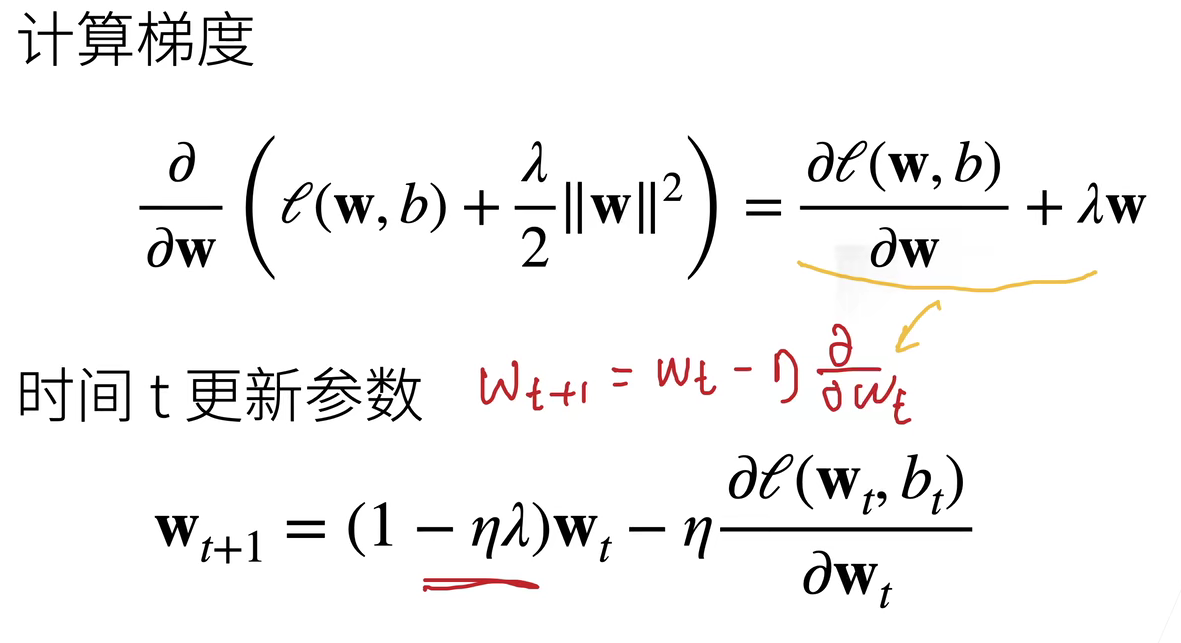
2、代码实现
1 %matplotlib inline 2 import torch 3 from torch import nn 4 from d2l import torch as d2l 5 6 n_train, n_test, num_inputs, batch_size = 20, 100, 200, 5 7 true_w, true_b = torch.ones((num_inputs, 1)) * 0.01, 0.05 8 train_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_train) 9 train_iter = d2l.load_array(train_data, batch_size) 10 test_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_test) 11 test_iter = d2l.load_array(test_data, batch_size, is_train=False) 12 #初始化模型参数 13 def init_params(): 14 w = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(num_inputs, 1), requires_grad=True) 15 b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True) 16 return [w, b] 17 #定义L2范数 18 def l2_penalty(w): 19 return torch.sum(w.pow(2)) / 2 20 21 def train(lambd): 22 w, b = init_params() 23 net, loss = lambda X: d2l.linreg(X, w, b), d2l.squared_loss#线性回归、平方损失函数 24 num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003 25 animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log', 26 xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test']) 27 for epoch in range(num_epochs):#迭代次数 28 for X, y in train_iter:#迭代器 29 #with torch.enable_grad(): 30 l = loss(net(X), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w) 31 l.sum().backward() 32 d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) 33 if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0: 34 animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss), 35 d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss))) 36 print('w的L2范数是:', torch.norm(w).item()) 37 38 train(lambd=0) 39 train(lambd=3)
当lambd为0时忽略正则化会产生过拟合:

3、Dropout丢弃法:在层之间加入噪音,随机置0,避免过拟合,通常用在隐藏全连接层的输出上,丢弃概率是控制模型复杂度的超参数

dropout是个正则项,正则项只在训练中使用。
4、代码实现
1 import torch 2 from torch import nn 3 from d2l import torch as d2l 4 5 def dropout_layer(X, dropout): 6 assert 0 <= dropout <= 1#定义dropout的范围 7 if dropout == 1: 8 return torch.zeros_like(X)#如果deopout=1,输出为0 9 if dropout == 0: 10 return X#如果deopout=0,输出为X 11 mask = (torch.randn(X.shape) > dropout).float()#mask是用于随机生成0和1,选择X中哪些数据需要丢弃的 12 return mask * X / (1.0 - dropout) 13 14 X = torch.arange(16, dtype=torch.float32).reshape((2, 8)) 15 print(X) 16 print(dropout_layer(X, 0.)) 17 print(dropout_layer(X, 0.5)) 18 print(dropout_layer(X, 1.)) 19 20 # tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.], 21 # [ 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15.]]) 22 # tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.], 23 # [ 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15.]]) 24 # tensor([[ 0., 0., 0., 6., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 25 # [16., 18., 0., 0., 24., 0., 0., 0.]]) 26 # tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 27 # [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]) 28 29 30 #定义有两个隐藏层的多层感知机,每个隐藏层包含256个单元 31 num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10, 256, 256 32 dropout1, dropout2 = 0.2, 0.5 33 class Net(nn.Module): 34 def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2,is_training=True):#训练 35 super(Net, self).__init__() 36 self.num_inputs = num_inputs 37 self.training = is_training 38 self.lin1 = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens1) 39 self.lin2 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2) 40 self.lin3 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens2, num_outputs) 41 self.relu = nn.ReLU() 42 43 def forward(self, X): 44 H1 = self.relu(self.lin1(X.reshape((-1, self.num_inputs))))#第一个隐藏层 45 if self.training == True: 46 H1 = dropout_layer(H1, dropout1)#在训练就dropout 47 H2 = self.relu(self.lin2(H1))#第二个隐藏层 48 if self.training == True: 49 H2 = dropout_layer(H2, dropout2) 50 out = self.lin3(H2)#输出层 51 return out 52 53 net = Net(num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2) 54 55 num_epochs, lr, batch_size = 10, 0.5, 256 56 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 57 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) 58 trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) 59 d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
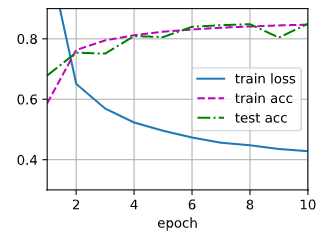
(六)数值稳定性
1、数值稳定性常见的两个问题:梯度爆炸和梯度消失
梯度爆炸的问题(ReLu易导致):值超出值域、对学习率敏感
梯度消失的问题(Sigmoid易导致):梯度值变为0、训练无进展、对底部层影响更大
2、模型初始化
为了让梯度值在合理范围内,可以将乘法变成加法(ResNet,LSTM)、归一化或合理的权重初始化和激活函数
Xavier初始:
第一个条件使得前向输出的方向是一致的,第二个条件是梯度是一致的
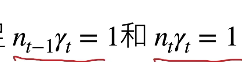
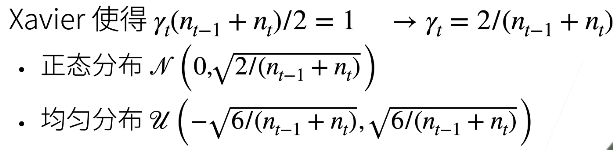
激活函数:让x趋于0时,激活函数的泰勒展开结果为0,sigmoid不符合需要调整

二、问题和收获
1、问题:复杂版和简单版的损失函数曲线在为0的初始点不同?


2、问题:应用了dropout之后loss略有增加,测试的正确率有波动


3、收获
又学习到了很多新的知识,逐渐锻炼代码实操能力,QA环节能够很好地解决我大部分疑惑。数值稳定性模块太难了,数学基础差的我看的迷迷糊糊,混混沌沌。今天真是高质量码农的一天。