本次内容列表:
1.使用线程的经验:设置名称、响应中断、使用ThreadLocal
2.Executor:ExecutorService和Future
3.阻塞队列:put和take、offer和poll、drainTo
4.线程间的协调手段:lock、condition、wait、notify、notifyAll
5.Lock-free:atomic、concurrentMap.putlfAbsent、CopyOnWriteArrayList
6.关于锁使用的经验介绍
7.并发流程控制手段:CountDownlatch、Barrier
8.定时器:ScheduledExecutorService、大规模定时器TimeWheel
9.并发三大定律:Amdahl、Gustafson、Sun-Ni
1.线程的经验:无论何种方式,启动一个线程,就要给它一个名字。这对排错诊断系统监控有帮助。否则诊断问题时,无法直观知道某个线程的用途
设置名称:以下为常用的几种命名方式:
1 //命名方式一: 2 Thread thread = new Thread("thread name one") { 3 public void run() { 4 //do xxx 5 } 6 };
1 //命名方式二: 2 Thread thread = new Thread() { 3 public void run() { 4 //do xxx 5 } 6 }; 7 thread.setName("thread name two"); 8 thread.start();
1 //命名方式三: 2 public class MyThread extends Thread{ 4 public MyThread() { 5 super("thread name three"); 6 } 7 public void run() { 8 //do xxx 9 } 10 } 11 MyThread thread = new MyThread(); 12 thread.start();
1 //命名方式四: 2 Thread thread = new Thread(task, "thread name four"); 3 thread.start();
响应线程中断:thread.interrupt(); 程序应该对线程中断作出恰当的响应
1 //中断响应方式一: 2 Thread thread = new Thread("interrupt test") { 3 public void run() { 4 for(;;) { 5 try { 6 doXXX(); 7 } catch(InterruptedException e) { 8 break; 9 } catch(Exception e) { 10 //handle Exception 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 }; 15 thread.start();
1 //中断响应方式二: 2 Thread thread = new Thread("interrupt test") { 3 public void run() { 4 for(;;) { 5 if(Thread.interrupted()) { 6 break; 7 } 8 } 9 } 10 }; 11 thread.start();
1 //中断响应方式三: 2 public void foo() throws InterruptedException{ 3 if(Thread.interrupted()) { 4 throw new InterruptedException(); 5 } 6 }
ThreadLocal(局部线程变量):它的功能非常简单,就是为每一个使用该变量的线程都提供一个变量值的副本,是每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会和其他线程的副本冲突。从线程的角度看,就好像每一个线程都完全拥有该变量。使用ThreadLocal,一般都是声明在静态变量中,如果不断的创建ThreadLocal而且没有调用其remove方法,将会导致内存泄漏。如果是static的ThreadLocal,一般不需要调用remove。
2.Executor
为了方便并发执行任务,使用Executor用来专门执行任务的实现,任务的提交者不需要在创建管理线程,使用更方便,也减少了开销。
java.util.concurrent.Executors是Executor的工厂类,通过Executors可以创建你所需要的Executor。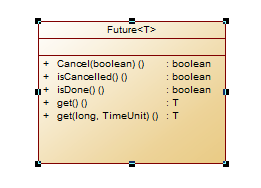
任务的提交者和执行者之间的通讯手段
1 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); 2 Callable<Object> task = new Callable<Object>() { 3 @Override 4 public Object call() throws Exception { 5 Object result = ""; 6 return result; 7 } 8 }; 9 public void subTask() { 10 Future<Object> future = executor.submit(task); 11 try { 12 future.get(); //等待至完成 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 }
Task Submitter
1 Future<Object> future = executor.submit(task); 2 //等待到任务被执行完毕返回结果 3 //如果任务执行出错,这里会抛ExecutionException 4 future.get(); 5 //等待3秒,超时后会抛TimeoutException 6 future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Task Executor
1 Callable<Object> task = new Callable<Object>() { 2 @Override 3 public Object call() throws Exception { 4 Object result = ...; 5 return result; 6 } 7 };
Task Submitter 把任务提交给Executor执行,他们之间需要一种通讯手段,这种手段的具体实现,通常叫做Future。Future通常包括get(阻塞至任务完成),cancel, get(timeout)(等待一段时间)等等。Future也用于异步变同步的场景。
3.阻塞队列:阻塞队列,是一种常用的并发数据结构,常用域生产者-消费者模式。
有多种阻塞队列:
ArrayBlockingQueue(最常用)
LinkedBolckingQueue(不会满的)
SynchronousQueue(size为0)
PriorityBlockingQueue
阻塞中常用的方法有:
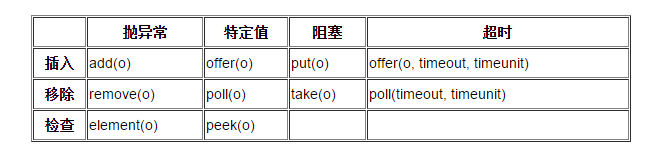
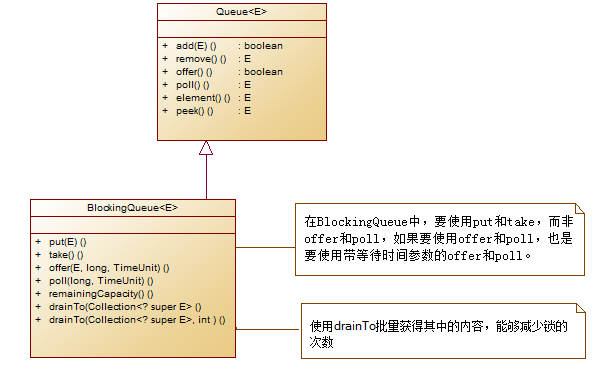
注:在使用BlockingQueue的时候,尽量不要使用从Queue继承下来的方法,否则就失去了Blocking的特性了。
例1:
1 final BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQ = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Object>(10); 2 Thread thread = new Thread("consumer thread") { 3 public void run() { 4 for(;;) { 5 try { 6 Object object = blockingQ.take(); //等到有数据才继续 7 handle(object); //处理 8 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 9 break; 10 } catch(Exception e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 };
例2:
1 final BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQ = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Object>(10); 2 Thread thread = new Thread("consumer thread two") { 3 public void run() { 4 for(;;) { 5 try { 6 Object object = blockingQ.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //防止死锁 7 if(object == null) { 8 //TODO 9 continue; //或者进行其他操作 10 } 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 break; 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 };