逻辑回归模型(Logistic Regression)及Python实现
1.模型
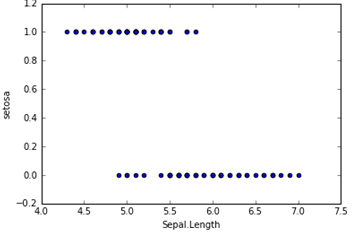
在分类问题中,比如判断邮件是否为垃圾邮件,判断肿瘤是否为阳性,目标变量是离散的,只有两种取值,通常会编码为0和1。假设我们有一个特征X,画出散点图,结果如下所示。这时候如果我们用线性回归去拟合一条直线:hθ(X) = θ0+θ1X,若Y≥0.5则判断为1,否则为0。这样我们也可以构建出一个模型去进行分类,但是会存在很多的缺点,比如稳健性差、准确率低。而逻辑回归对于这样的问题会更加合适。
逻辑回归假设函数如下,它对θTX作了一个函数g变换,映射至0到1的范围之内,而函数g称为sigmoid function或者logistic function,函数图像如下图所示。当我们输入特征,得到的hθ(x)其实是这个样本属于1这个分类的概率值。也就是说,逻辑回归是用来得到样本属于某个分类的概率。
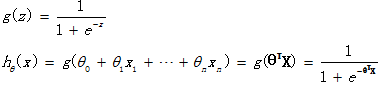

2.评价
回想起之前线性回归中所用到的损失函数:
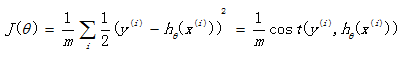
如果在逻辑回归中也运用这种损失函数,得到的函数J是一个非凸函数,存在多个局部最小值,很难进行求解,因此需要换一个cost函数。重新定义个cost函数如下:
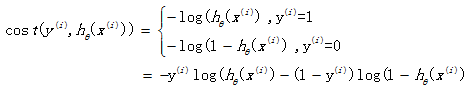
当实际样本属于1类别时,如果预测概率也为1,那么损失为0,预测正确。相反,如果预测为0,那么损失将是无穷大。这样构造的损失函数是合理的,并且它还是一个凸函数,十分方便求得参数θ,使得损失函数J达到最小。
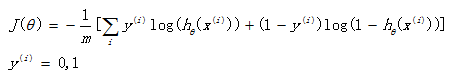
3.优化
我们已经定义好了损失函数J(θ),接下来的任务就是求出参数θ。我们的目标很明确,就是找到一组θ,使得我们的损失函数J(θ)最小。最常用的求解方法有两种:批量梯度下降法(batch gradient descent), 牛顿迭代方法((Newton's method)。两种方法都是通过迭代求得的数值解,但是牛顿迭代方法的收敛速度更加快。
批量梯度下降法: ![]()
牛顿迭代方法: ![]() (H为海瑟矩阵)
(H为海瑟矩阵)
4.python代码实现
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Wed Feb 24 11:04:11 2016 4 5 @author: SumaiWong 6 """ 7 8 import numpy as np 9 import pandas as pd 10 from numpy import dot 11 from numpy.linalg import inv 12 13 iris = pd.read_csv('D:iris.csv') 14 dummy = pd.get_dummies(iris['Species']) # 对Species生成哑变量 15 iris = pd.concat([iris, dummy], axis =1 ) 16 iris = iris.iloc[0:100, :] # 截取前一百行样本 17 18 # 构建Logistic Regression , 对Species是否为setosa进行分类 setosa ~ Sepal.Length 19 # Y = g(BX) = 1/(1+exp(-BX)) 20 def logit(x): 21 return 1./(1+np.exp(-x)) 22 23 temp = pd.DataFrame(iris.iloc[:, 0]) 24 temp['x0'] = 1. 25 X = temp.iloc[:,[1,0]] 26 Y = iris['setosa'].reshape(len(iris), 1) #整理出X矩阵 和 Y矩阵 27 28 # 批量梯度下降法 29 m,n = X.shape #矩阵大小 30 alpha = 0.0065 #设定学习速率 31 theta_g = np.zeros((n,1)) #初始化参数 32 maxCycles = 3000 #迭代次数 33 J = pd.Series(np.arange(maxCycles, dtype = float)) #损失函数 34 35 for i in range(maxCycles): 36 h = logit(dot(X, theta_g)) #估计值 37 J[i] = -(1/100.)*np.sum(Y*np.log(h)+(1-Y)*np.log(1-h)) #计算损失函数值 38 error = h - Y #误差 39 grad = dot(X.T, error) #梯度 40 theta_g -= alpha * grad 41 print theta_g 42 print J.plot() 43 44 # 牛顿方法 45 theta_n = np.zeros((n,1)) #初始化参数 46 maxCycles = 10 #迭代次数 47 C = pd.Series(np.arange(maxCycles, dtype = float)) #损失函数 48 for i in range(maxCycles): 49 h = logit(dot(X, theta_n)) #估计值 50 C[i] = -(1/100.)*np.sum(Y*np.log(h)+(1-Y)*np.log(1-h)) #计算损失函数值 51 error = h - Y #误差 52 grad = dot(X.T, error) #梯度 53 A = h*(1-h)* np.eye(len(X)) 54 H = np.mat(X.T)* A * np.mat(X) #海瑟矩阵, H = X`AX 55 theta_n -= inv(H)*grad 56 print theta_n 57 print C.plot()
代码所用的数据下载地址:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/sumai/iris.rar