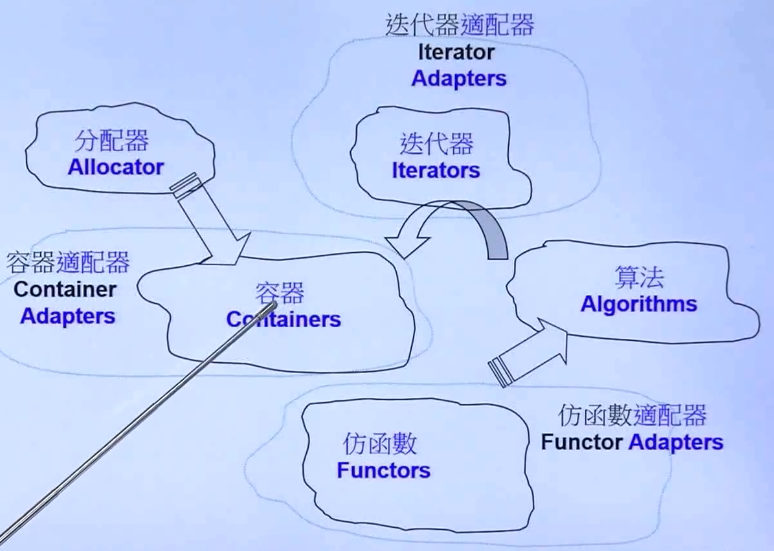
STL 六大部件
- 容器
- 分配器
- 算法
- 迭代器
- 适配器
- 仿函式
#include <algorithm> #include <functional> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { /* code */ int ia[6] = {27,210,12 ,47,109,83}; vector<int,allocator<int> > vi(ia,ia+6); /* 默认就有分配器 不写也行 设定数组ia的起始到 ia+6*/ /*count_if给定条件下符合条件元素的个数*/ cout << count_if(vi.begin(), vi.end(),/*begin和end会传回iterator 处理 整个vi中的元素*/ not1(bind2nd(less<int>(),40))); /*bind2nd适配器绑定 小于40的元素 加not表示大于等于40*/ return 0; }
容器(不一定是连续空间) 指的是前闭后开区间 begin指的第一个元素开头 end指的是最后一个元素的下一个元素的开头
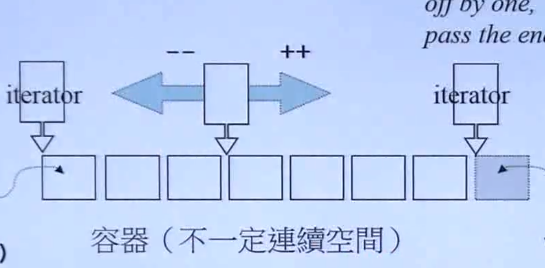
遍历迭代
for (int i : {2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 14})遍历迭代数组中的每一个元素 { std::cout << i << std::endl; /* code */ } std::vector<int> vec; for (auto elem : vec){ auto会去自动寻找vec中的类型 std::cout << elem <<std::endl; } for (auto& elem : vec){ elem *= 3; 使用引用传值 把每个元素都乘以3 }