1、
application.xml 中容器管理bean需要去扫描
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 扫描指定包下的带有Component标签的类,纳入spring管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mashibing.spring"></context:component-scan> </beans>
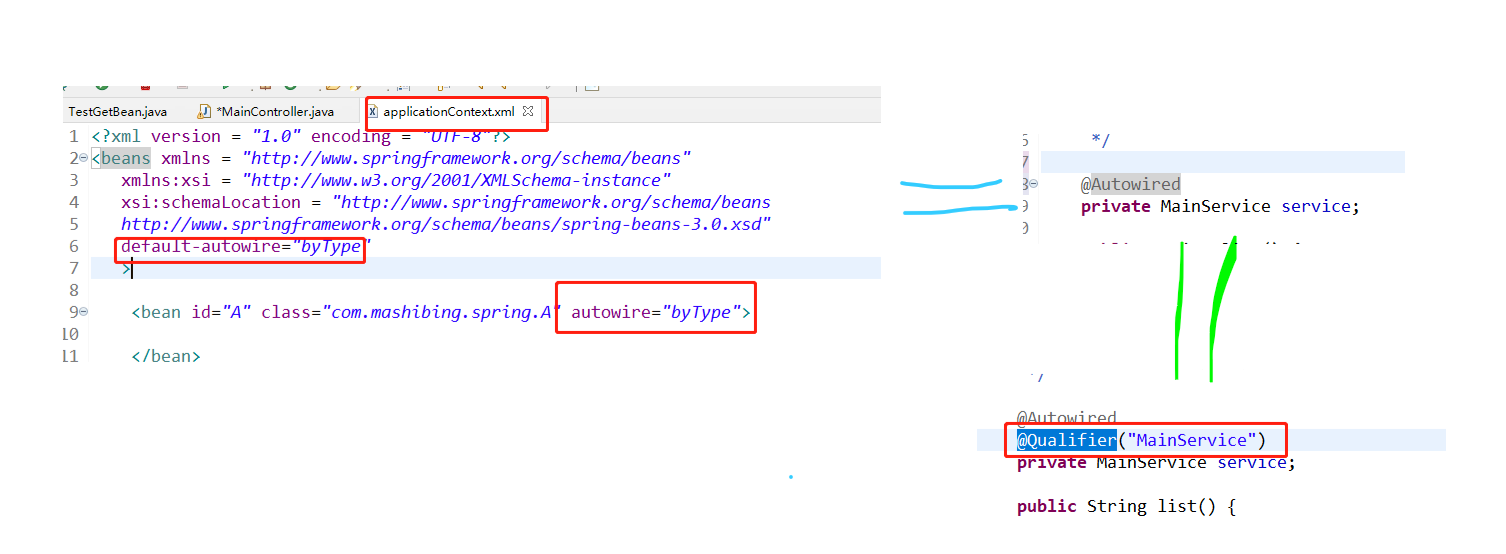
先通过类型去装配类,如果类型找不到,比如这个类型为某一个接口,但是它的实现类有多个,那么在这个类型下面再用@Qualifier指定实现类名称。
使用场景:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36567005/article/details/80611139
2、问为什么实体类不能用单例?
考虑线程安全问题:
从表到usr对象之间的映射叫ORM图
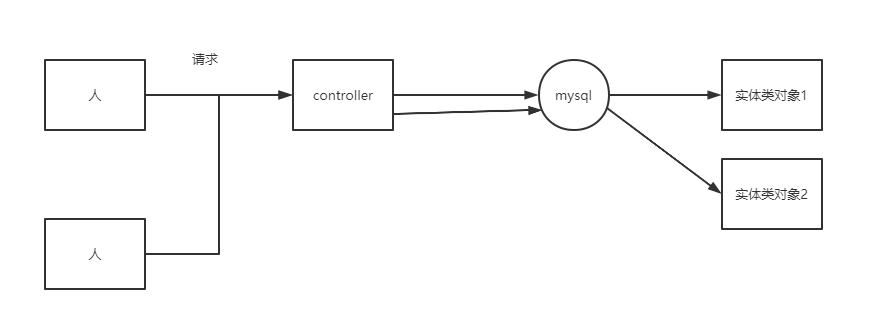
一次请求一个线程,一定是创建两个实体类对象,如果参数写成不是private的,那么变量可能会被改变,存在线程安全问题。
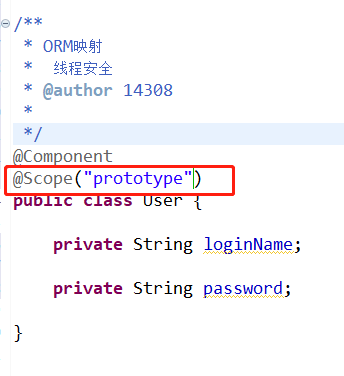
实体类对象用“prototype”,每次都是new出来的。
/** * ORM映射 * 线程安全 * @author 14308 * */ @Component @Scope("prototype") public class User { //设置默认值 简单的属性注入 @Value("zhangsan") private String loginName; @Value("123123") private String password; //注入对象引用的 @Autowired private Pet pet; }
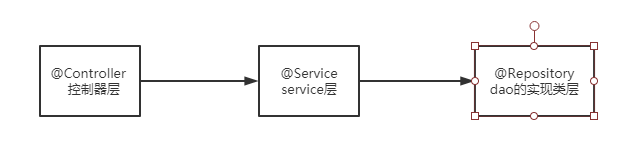
都可以用@Component代替
3、静态代理

package com.mashibing.spring; public interface Human { public void eat(); } _______________________________________________ package com.mashibing.spring; public class Girl implements Human{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Em mmm... mm.."); } } ________________________________________________ package com.mashibing.spring; public class ProxyGirl implements Human{ private Human human; public ProxyGirl() { } public ProxyGirl(Human human) { super(); this.human = human; } @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("chiqian"); human.eat(); System.out.println("chihou"); } } __________________________________________ package com.mashibing.spring; import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.ToStringStyle; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestGetBean { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Girl girl = new Girl(); Human proxyGirl = new ProxyGirl(girl); proxyGirl.eat(); } }
从静态代理的使用上来看:1.代理类一般要持有一个被代理的对象的引用。2.对于我们不关心的方法,全部委托给被代理的对象处理。3.自己处理我们关心的方法。
其优点表现为:在不修改目标对象的前提下,可以通过代理对象对目标对象功能扩展
代理使客户端不需要知道实现类是什么,怎么做的,而客户端只需知道代理即可(解耦合),对于如上的客户端代码,RealInterner() 可以应用工厂将它隐藏。
缺点为:代理类和委托类实现了相同的接口,代理类通过委托类实现了相同的方法。这样就出现了大量的代码重复。如果接口增加一个方法,除了所有实现类需要实现这个方法外,所有代理类也需要实现此方法。增加了代码维护的复杂度。
代理对象只服务于一种类型的对象,如果要服务多类型的对象。势必要为每一种对象都进行代理,静态代理在程序规模稍大时就无法胜任了。
4、动态代理
- 面向与接口,jdk的动态代理
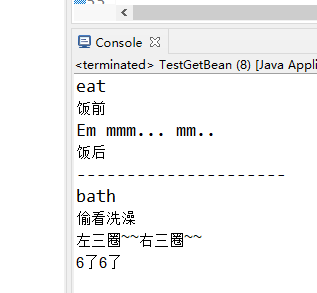
package com.mashibing.spring; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.ToStringStyle; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestGetBean { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ final Girl girl = new Girl(); /** * 参数1-Girl.class.getClassLoader()代表通过反射,Girl被new出来了,可以通过Girl的字节码文件反着找Girl类 * 参数2-Girl.class.getInterfaces()代表通过反射,找出Girl的所有接口 * 参数3-new InvocationHandler()是拦截方法执行的 * */ Human proxyGirl = (Human) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Girl.class.getClassLoader(), Girl.class.getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println(method.getName()); if (method.getName().equals("bath")) { System.out.println("偷看洗澡"); Object invoke = method.invoke(girl, args); System.out.println("6了6了"); return invoke; }else { System.out.println("饭前"); Object invoke = method.invoke(girl, args); System.out.println("饭后"); return invoke; } } }); proxyGirl.eat(); System.out.println("---------------------"); proxyGirl.bath(); } }
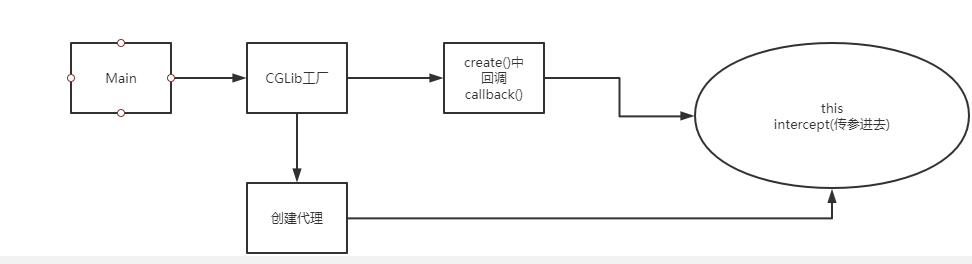
- CGlib动态代理
CGLibFactory类
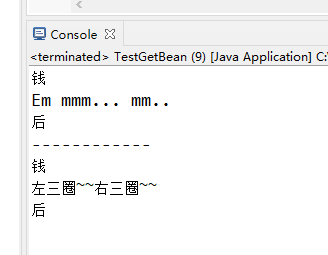
package com.mashibing.spring; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; public class CGLibFactory implements MethodInterceptor{ private Object target; public CGLibFactory() { super(); } public CGLibFactory(Object target) { this.target = target; } /** * 创建代理对象 * @return */ public Object createProxy() { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); //设置父类 enhancer.setSuperclass(Girl.class); enhancer.setCallback(this); return enhancer.create(); } /* * 拦截器 * Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy * obj是被传过来的,第二个method是动态代理对象要执行的方法,args是方法的参数,proxy是方法的代理 */ @Override public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("钱"); method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("后"); return null; } }
Test类
package com.mashibing.spring; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.ToStringStyle; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestGetBean { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Girl girl = new Girl(); Girl proxyGirl = (Girl)new CGLibFactory(girl).createProxy(); proxyGirl.eat(); System.out.println("------------"); proxyGirl.bath(); } }