一、线程的休眠
一种控制线程行为的方法使调用sleep()方法,sleep()方法需要一个参数用于指定该线程休眠的时间,该时间以毫秒为单位
sleep()方法的语法如下:
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
上述代码会使线程在2秒之内不会进入就绪状态。由于sleep()方法的执行有可能抛出InterruptedException异常,所以将sleep()方法的调用放在try-catch块中。虽然使用sleep()方法的线程在一段时间内会醒来,但是并不能保证它醒来后进入运行状态,只能保证它进入就绪状态。

1 package com.lzw; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.util.*; 5 6 import javax.swing.*; 7 public class SleepMethodTest extends JFrame { 8 /** 9 * 10 */ 11 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 12 private Thread t; 13 // 定义颜色数组 14 private static Color[] color = { Color.BLACK, Color.BLUE, Color.CYAN, 15 Color.GREEN, Color.ORANGE, Color.YELLOW, Color.RED, 16 Color.PINK, Color.LIGHT_GRAY }; 17 private static final Random rand = new Random();// 创建随机对象 18 19 private static Color getC() {// 获取随机颜色值的方法 20 return color[rand.nextInt(color.length)]; 21 } 22 23 public SleepMethodTest() { 24 t = new Thread(new Runnable() {// 创建匿名线程对象 25 int x = 30;// 定义初始坐标 26 int y = 50; 27 28 public void run() {// 覆盖线程接口方法 29 while (true) {// 无限循环 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(100);// 线程休眠0.1秒 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 // 获取组件绘图上下文对象 36 Graphics graphics = getGraphics(); 37 graphics.setColor(getC());// 设置绘图颜色 38 // 绘制直线并递增垂直坐标 39 graphics.drawLine(x, y, 100, y++); 40 if (y >= 80) { 41 y = 50; 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }); 46 t.start();// 启动线程/ 47 } 48 49 public static void main(String[] args) { 50 init(new SleepMethodTest(), 100, 100); 51 } 52 // 初始化程序界面的方法 53 public static void init(JFrame frame, int width, int height) { 54 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 55 frame.setSize(width, height); 56 frame.setVisible(true); 57 } 58 }
二、线程的加入
如果当前某程序为多线程序,加入存在一个线程A,现在需要插入线程B,并要求线程B先执行完毕,然后再继续执行线程A,此时可以使用Thread类中的join()方法来完成。
当某个线程使用join()方法加入到另一个线程时,另一个线程会等待该线程执行完毕后再继续执行。

1 package com.lzw; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class JoinTest extends JFrame { 7 /** 8 * 9 */ 10 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 11 private Thread threadA; // 定义两个线程 12 private Thread threadB; 13 final JProgressBar progressBar = new JProgressBar(); // 定义两个进度条组件 14 final JProgressBar progressBar2 = new JProgressBar(); 15 int count = 0; 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 init(new JoinTest(), 100, 100); 19 } 20 21 public JoinTest() { 22 super(); 23 // 将进度条设置在窗体最北面 24 getContentPane().add(progressBar, BorderLayout.NORTH); 25 // 将进度条设置在窗体最南面 26 getContentPane().add(progressBar2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 27 progressBar.setStringPainted(true); // 设置进度条显示数字字符 28 progressBar2.setStringPainted(true); 29 // 使用匿名内部类形式初始化Thread实例子 30 threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() { 31 int count = 0; 32 33 public void run() { // 重写run()方法 34 while (true) { 35 progressBar.setValue(++count); // 设置进度条的当前值 36 try { 37 Thread.sleep(100); // 使线程A休眠100毫秒 38 threadB.join(); // 使线程B调用join()方法 39 } catch (Exception e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }); 45 threadA.start(); // 启动线程A 46 threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() { 47 int count = 0; 48 49 public void run() { 50 while (true) { 51 progressBar2.setValue(++count); // 设置进度条的当前值 52 try { 53 Thread.sleep(100); // 使线程B休眠100毫秒 54 } catch (Exception e) { 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 } 57 if (count == 100) // 当count变量增长为100时 58 break; // 跳出循环 59 } 60 } 61 }); 62 threadB.start(); // 启动线程B 63 } 64 65 // 设置窗体各种属性方法 66 public static void init(JFrame frame, int width, int height) { 67 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 68 frame.setSize(width, height); 69 frame.setVisible(true); 70 } 71 }
三、线程的中断
以往有的时候回使用stop()方法停止线程,但当前版本的JDK早已废除了stop()方法,不建议使用stop()方法来停止一个线程的运行。现在提倡在run()方法中使用无线循环的形式,然后使用一个布尔型标记控制循环的停止。
如果线程因为使用了sleeo()方法或wait()方法进入了就绪状态,可以使用Thread类中的interrupt()方法时线程离开run()方法,同时结束线程,但程序会抛出InterruptedException异常,用户可以在处理该异常时完成线程的中断业务处理,如终止while循环。

1 package com.lzw; 2 3 public class InterruptedTest implements Runnable{ 4 private boolean isContinue = false; //设置一个编辑变量,默认值为false 5 6 public void run() { 7 while(true) { 8 //... 9 if(isContinue) //当isContinue变量为true时,停止线程 10 break; 11 } 12 } 13 14 public void setContinue() { 15 this.isContinue = true; //定义设置isContinue变量为true的方法 16 } 17 }

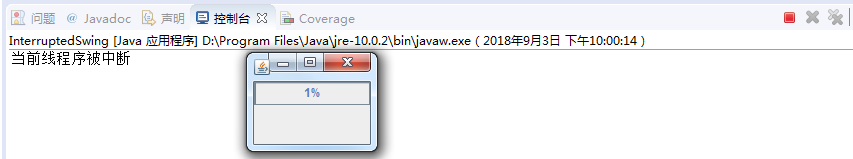
1 package com.lzw; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 public class InterruptedSwing extends JFrame { 7 /** 8 * 9 */ 10 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 11 Thread thread; 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 init(new InterruptedSwing(), 100, 100); 15 } 16 17 public InterruptedSwing() { 18 super(); 19 final JProgressBar progressBar = new JProgressBar(); // 创建进度条 20 // 将进度条放置在窗体合适位置 21 getContentPane().add(progressBar, BorderLayout.NORTH); 22 progressBar.setStringPainted(true); // 设置进度条上显示数字 23 thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { 24 int count = 0; 25 26 public void run() { 27 while (true) { 28 progressBar.setValue(++count); // 设置进度条的当前值 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(1000); // 使线程休眠1000豪秒 31 // 捕捉InterruptedException异常 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 System.out.println("当前线程序被中断"); 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 }); 39 thread.start(); // 启动线程 40 thread.interrupt(); // 中断线程 41 } 42 43 public static void init(JFrame frame, int width, int height) { 44 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 45 frame.setSize(width, height); 46 frame.setVisible(true); 47 } 48 49 }
四、线程的礼让
Thread类中提供了一种礼让方法,使用yield()方法表示,它只是给当前正处于运行状态的线程一个提醒,告知它可以将资源礼让给其它线程,但这仅是一种暗示,没有任何一种机制保证当前线程会将资源礼让。
yield()方法使具有同样优先级的线程有进入可执行状态的机会,当当前线程放弃执行权时会再度回到就绪状态。对于支持多任务的操作系统来说,不需要调用yield()方法,因为操作系统会为线程自动分配CPU时间片来执行。
