前言
BitSet实现了一个按需增长的位向量,每一位都是一个boolean值,可以对每一位进行设置或清除,常用场景就是判断一个数据在一个大数据集中是否存在。
使用
有1千万个随机数,随机数的范围在1到1亿之间。现在要求写出一种算法,将1到1亿之间没有在随机数中的数求出来?
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.Random;
public class Client2 {
//一亿
private static final int HUNDRED_MILLION = 100_000_000;
//一千万
private static final int TEN_MILLION = 10_000_000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
BitSet bitSet = new BitSet(HUNDRED_MILLION);
for (int i = 0; i < TEN_MILLION; i++) {
//将指定索引设置为true
bitSet.set(random.nextInt(HUNDRED_MILLION));
}
for (int i = 0; i < HUNDRED_MILLION; i++) {
//获取指定索引为false表示不存在
if (!bitSet.get(i)) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
原理
/**
* This class implements a vector of bits that grows as needed. Each
* component of the bit set has a {@code boolean} value. The
* bits of a {@code BitSet} are indexed by nonnegative integers.
* Individual indexed bits can be examined, set, or cleared. One
* {@code BitSet} may be used to modify the contents of another
* {@code BitSet} through logical AND, logical inclusive OR, and
* logical exclusive OR operations.
*
* <p>By default, all bits in the set initially have the value
* {@code false}.
*
* <p>Every bit set has a current size, which is the number of bits
* of space currently in use by the bit set. Note that the size is
* related to the implementation of a bit set, so it may change with
* implementation. The length of a bit set relates to logical length
* of a bit set and is defined independently of implementation.
*
* <p>Unless otherwise noted, passing a null parameter to any of the
* methods in a {@code BitSet} will result in a
* {@code NullPointerException}.
*
* <p>A {@code BitSet} is not safe for multithreaded use without
* external synchronization.
*
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @author Michael McCloskey
* @author Martin Buchholz
* @since 1.0
*/
public class BitSet implements Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
/**
* 存储数据的数组
*/
private long[] words;
/**
* 将位索引转换成数组索引
*/
private static int wordIndex(int bitIndex) {
return bitIndex >> ADDRESS_BITS_PER_WORD;
}
/**
* 构造器
*/
public BitSet() {
initWords(BITS_PER_WORD);
sizeIsSticky = false;
}
/**
* 根据位长度构造
*/
public BitSet(int nbits) {
// nbits can't be negative; size 0 is OK
if (nbits < 0)
throw new NegativeArraySizeException("nbits < 0: " + nbits);
initWords(nbits);
sizeIsSticky = true;
}
/**
* 根据位长度创建数组 可以看做求分页的总页数 页面大小64 64就是1页 65就是2页
*/
private void initWords(int nbits) {
words = new long[wordIndex(nbits-1) + 1];
}
}
BitSet内部是使用long数组来存储所有数据的,相比HashMap还是很节省内存的。


可以看到ArrayList的removeIf()方法实现也是实现了一个简单的BitSet。
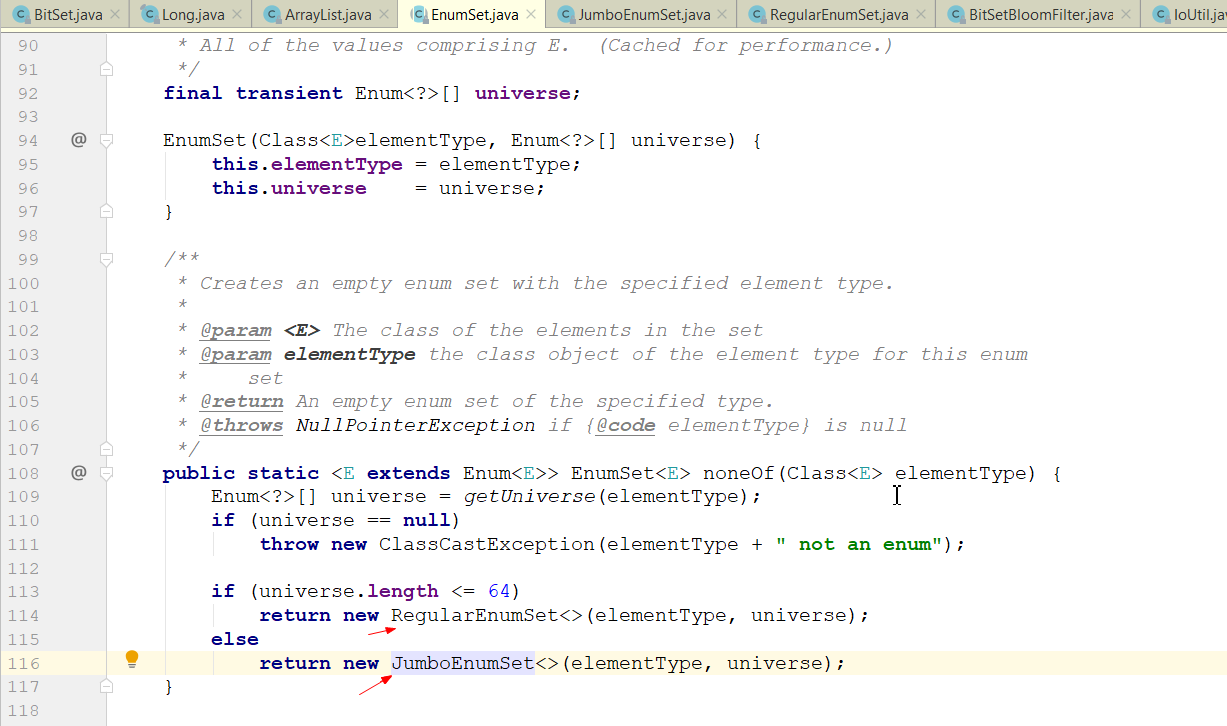
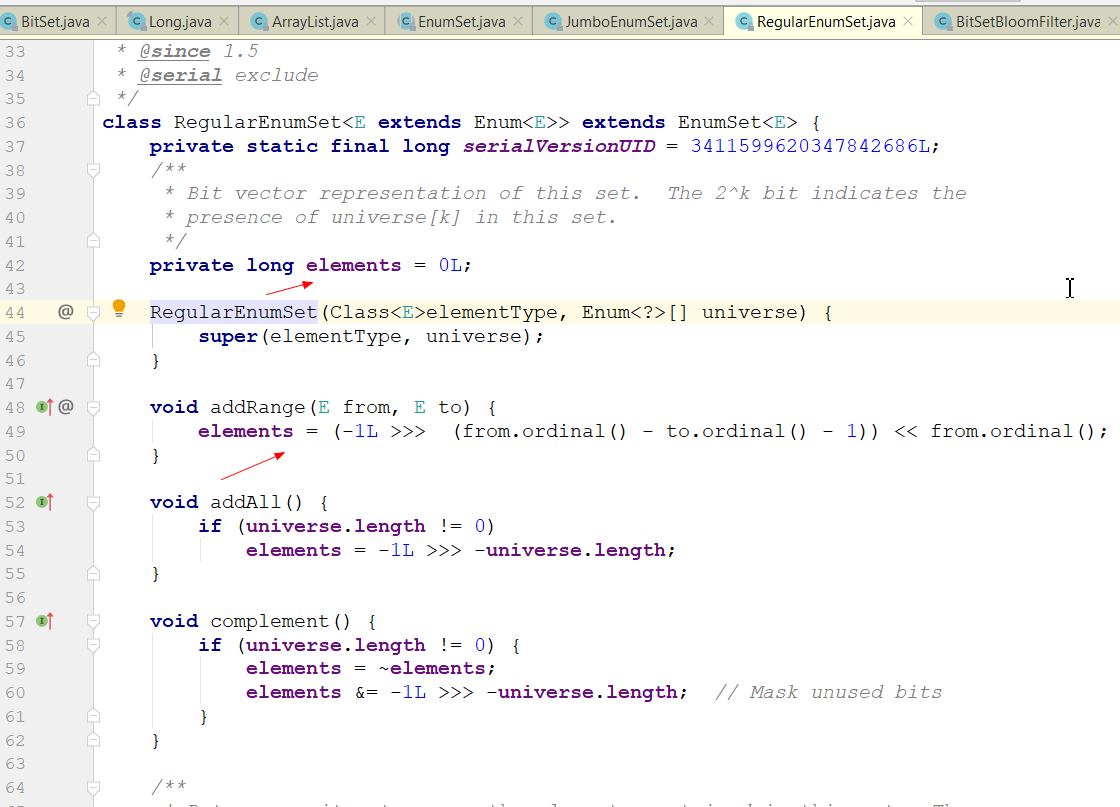

EnumSet的两种实现RegularEnumSet和JumboEnumSet也是通过BitSet的思想实现的。
总结
BitSet的原理主要就是将对一个int值或字符串的操作转换成位运算,相应的占用空间就少了。