1、栈
栈又名堆栈,是允许在同一端进行插入和删除操作的特殊线性表。其中,允许进行插入和删除操作的一端叫做栈顶(Top),另一端叫做栈底,栈底固定,栈顶浮动。
栈是后进先出的线性表,数据结构如下:
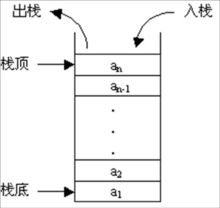
实现一个栈,需要实现以下核心方法:
(1)push():向栈中压入一个数据,先入栈的数据放在最下面。
(2)pop():移除栈顶数据。
(3)peek():返回当前的栈顶数据。
栈的具体实现过程:
package com.jzq.structure.Stack; public class Stack<E> { private Object[] data = null; private int maxSize = 0;//栈的容量 private int top = -1;//栈顶指针 Stack() { this(10);//默认的栈大小为10 } Stack(int initialSize) { if (initialSize >= 0) { this.maxSize = initialSize; data = new Object[initialSize]; top = -1; }else { throw new RuntimeException("初始化大小不能小于0: "+initialSize); } } //进栈,向栈顶压入一个数据,第一个元素top=0 public boolean push(E e){ if (top == maxSize -1){ throw new RuntimeException("栈已满,无法将元素入栈;"); }else { data[++top] = e;//先分配栈空间,再放入元素 return true; } } //出栈,移除栈顶第一个元素 public E pop(){ if (top == -1){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空"); }else { return (E)data[top--]; } } //查看栈顶元素 public E peek(){ if (top == -1){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空"); }else { return (E)data[top]; } } }
2、队列
队列是一种只允许在表的前端进行删除操作且在表的后端进行插入操作的线性表。其中执行插入操作(入队)的端叫做队尾,执行删除操作(出队)的端叫做队头。
队列是先进先出的线性表,具体结构如图:
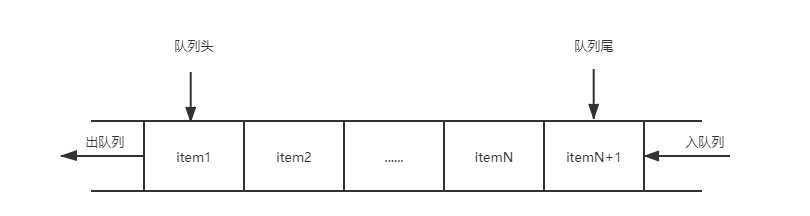
实现一个队列,需要实现以下核心方法:
(1)add():向队尾加入一个元素。
(2)pop():删除队列头部元素。
(3)peek():取出队列头部元素。
队列的具体实现过程:
package com.jzq.structure.Queue; public class Queue<E> { private Object[] data = null; private int maxSize;//队列长度 private int front;//队列头 private int rear;//队列尾 public Queue() { this(10); } public Queue(int initialSize) { if (initialSize >= 0) { this.maxSize = initialSize; data = new Object[initialSize]; front = rear = 0; } else { throw new RuntimeException("初始化大小不能小于0: " + initialSize); } } public boolean empty() { return maxSize == 0; } //在队尾插入数据 public boolean add(E e) { if (rear == maxSize) { throw new RuntimeException("队列已满,无法插入新的元素"); } else { data[rear++] = e; return true; } } //删除队列头部数据 public E poll() { if (empty()) { throw new RuntimeException("空队列异常"); } else { E value = (E) data[front]; data[front++] = null; return value; } } //查看队列头部数据 public E peek() { if (empty()) { System.out.println("asd"); throw new RuntimeException("空队列异常"); } else { return (E) data[front]; } } }
3、链表
链表是由一系列节点组成的数据结构,节点可以在运行过程中动态生成。每个节点都包括两个部分内容:存储数据的数据域和存储下一个节点的指针域。
链表有3种不同类型:单向链表、双向链表和循环链表。
3.1 单向链表
单向链表的特点是链表的链接方向是单向的。访问链表时要从头部开始顺序读取。
具体结构如图:
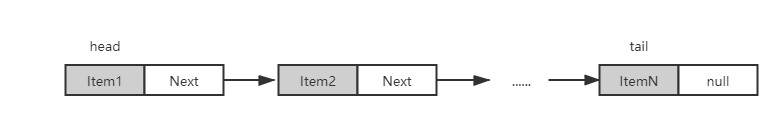
单向链表,需要实现以下操作:
(1)查找:单向链表只可向一个方向遍历,一般从第一个节点开始。
(2)插入:将插入的节点设置为头节点,将Next指针指向原来的头节点即可。
(3)删除:将要删除节点的上一个节点的Next指针指向该节点的下一个节点,然后删除该节点即可。
单向链表的具体实现过程:
package com.jzq.structure.LinkedList.SingleLinkedList; public class SingleLinkedList { private int length; private Node head; public SingleLinkedList() { length = 0; head = null; } private class Node { private Object data; private Node next; public Node(Object data) { this.data = data; } } //插入新节点 public Object addHead(Object obj) { Node newhead = new Node(obj); if (length == 0) { head = newhead; } else { head = newhead; newhead.next = head; } length++; return obj; } //删除单向链表数据 public boolean delete(Object value) { if (length == 0) { return false; } Node current = head; Node previous = head; while (current.data == value) { if (current.next == null) { return false; } else { previous = current; current = current.next; } } if (current == head) { head = current.next; } else { previous.next = current.next; } length--; return true; } //单向链表查询 public Node find(Object obj) { Node current = head; int tempSize = length; System.out.println(length); while (tempSize > 0) { if (obj.equals(current.data)) { System.out.println(current.data); return current; } else { current = current.next; } tempSize--; } return null; } }
3.2 双向链表
双向链表的每个数据都有两个指针,分别指向其直接后继节点和直接前驱节点。
双向链表数据结构如图所示:
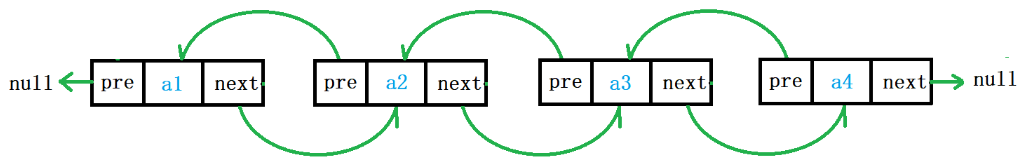
双向链表的具体实现过程:
package com.jzq.structure.LinkedList.TwoWayLinkedList; public class TwoWayLinkedList { private Node head;//表示链表头 private Node tail;//表示链表尾 private int length;//表示链表长度 private class Node { private Object data; private Node next; private Node prev; public Node(Object data) { this.data = data; } } public TwoWayLinkedList() { length = 0; head = null; tail = null; } //在链表头部增加节点 public void addHead(Object value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); if (length == 0) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; length++; } else { head.prev = newNode; newNode.next = head; head = newNode; length++; } } //在链表尾部增加节点 public void addTail(Object value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); if (length == 0) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; length++; } else { tail.next = newNode; newNode.prev = tail; tail = newNode; length++; } } //删除链表头部节点 public boolean deleteHead() { if (length == 0) { return false; } if (head.next == null) {//表明链表中有一个节点 head = null; tail = null; } else { head = head.next; } length--; return true; } //删除链表尾部节点 public boolean deleteTail() { if (length == 0) { return false; } if (tail.prev == null) {//表明链表中有一个节点 head = null; tail = null; } else { tail = tail.prev; } length--; return true; } }
3.3 循环链表
循环列表中的最后一个节点的指针域指向头节点,整个链表形成一个环。循环列表与单向链表十分相似。
具体数据结构如图:
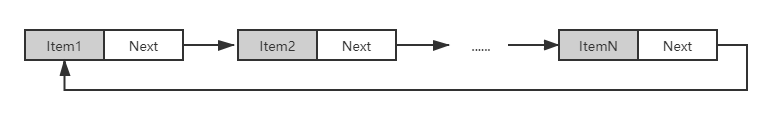
由于与单向链表相似,只展示循环链表部分代码:
public CircleLinkedList() { length = 0; head.next = head; }
4、散列表
散列表,也称哈希表,是根据键值对(Key-Value)对数据进行存取的数据结构。
散列表通过映射函数把键值对映射到表中的一个位置来加快查找。
具体数据结构如图:
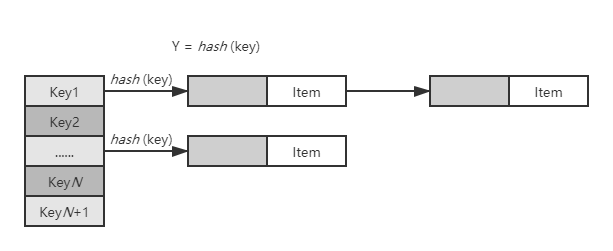
4.1 常用的构造散列算法
(1)直接定址法:取k或者k的某个线性函数为Hash值。
(2)平方取值法:取关键字平方后的中间几位为散列地址。
(3)折叠法:将关键字分割成位数相同的几部分,然后取这几部分的叠加和作为散列地址。
(4)除留取余法:取关键字被某个不大于Hash表长度m的数p除后所得的余数为Hash地址 。
(5)随机数法:选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值作为Hash地址。
4.2 散列冲突
散列冲突是指由关键字得到的哈希地址的位置上已存有记录,则“处理冲突”就是为该关键字的记录找到另一个“空”的哈希地址。
解决散列冲突的方法有:开放寻址法(Open Addressing)和链表法(Chaining),以及再哈希法和公共溢出法。
5、二叉排序树
二叉排序树,又称二叉搜索树,二叉排序树满足以下条件的树:
- 若左子树不为空,则左子树上的所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值。
- 若右子树不为空,则右子树上的所有节点的值均大于或等于它的根节点的值。
- 左右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
如图:
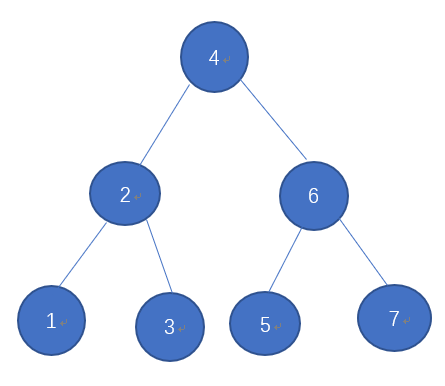
二叉排序树的具体操作包括插入操作、删除操作和查找操作
5.1 插入操作
目的:找到待插入的父节点,将数据插入。
(1)将待插入的新节点与当前节点进行比较,如果两个节点的值相同,则表示新节点已经存在于二叉排序树中,直接返回false。
(2)将待插入的新节点与当前节点进行比较,如果待插入的新节点的值小于当前结点的值,则在当前节点的左子树中寻找,直到左子树为空,则当前节点为要找的父节点,将新节点插入当前节点的左子树即可。
(3)将待插入的新节点与当前节点进行比较,如果待插入的新节点的值大于当前结点的值,则在当前节点的右子树中寻找,直到右子树为空,则当前节点为要找的父节点,将新节点插入当前节点的右子树即可。
5.2 删除操作
二叉排序树的删除操作主要分为三种情况:待删除节点没有子节点;待删除节点只有一个子节点;待删除节点有两个子节点。
(1)待删除节点没有子节点时,直接删除该节点。
(2)待删除节点只有一个子节点时,使用子节点替换当前节点,然后删除该节点即可。
(3)待删除节点有两个子节点时,删除该节点后,为保持其它元素之间的相对位置不变,选取左子树的最大值,进行替换,然后删除左子树的最大值节点,或者选取右子树的最小值进行替换,然后删除右子树的最小值节点。
5.3 查找操作
将要查找的数据与根节点的值比较,如果相等就返回,如果小于就到左子树中递归查找,如果大于就到右子树中递归查找。
5.4 具体实现过程
(1)定义二叉排序树的数据结构:
public class Node { private int value; private Node left; private Node right; public Node() { } public Node(int value, Node left, Node right) { this.value = value; this.left = left; this.right = right; } public Node(int value) { this(value, null, null); } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Node getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node left) { this.left = left; } public Node getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node right) { this.right = right; } private Node root; }
(2)定义二叉排序树的插入方法:
public void insert(int key) { Node p = root; //记录查找节点的父节点 Node prev = null; while (p != null) { prev = p; if (key < p.getValue()) { p = p.getLeft(); } else if (key > p.getValue()) { p=p.getRight(); }else { return; } } //判断二叉树根节点是否为null if(root == null){ root = new Node(key); }else if(key < prev.getValue()){ prev.setLeft(new Node(key)); }else { prev.setRight(new Node(key)); } }
(3)定义二叉排序树的删除方法:
public void deleteBST(int key){ deleteBST(root,key); } private boolean deleteBST(Node node, int key) { if(node == null){ return false; } if(key == node.getValue()){ return delete(node); }else if(key<node.getValue()){ return deleteBST(node.getLeft(),key); }else { return deleteBST(node.getRight(),key); } } private boolean delete(Node node) { Node temp = null; if(node.getRight() == null) { //右子树为空,重接左子树 temp = node; node = node.getLeft(); }else if(node.getLeft() == null){ //左子树为空,重接右子树 temp = node; node = node.getRight(); }else { //左右子树都不为空 temp = node; Node s = node; s = s.getLeft(); while (s.getRight() != null){ temp = s; s = s.getRight(); } node.setValue(s.getValue()); if(temp != null){ temp.setRight(s.getLeft()); }else { temp.setLeft(s.getLeft()); } } return true; }
(4)定义二叉排序树的查找方法:
public boolean searchBST(int key){ Node current = root; while(current!=null){ if(key == current.getValue()){ return true; }else if(key< current.getValue()){ current = current.getLeft(); }else { current = current.getRight(); } } return false; }
6、红黑树
红黑树是一种自平衡二叉排序树,在红黑树的每个节点上都多出一个存储位表示节点的颜色,且颜色只能是红或者黑。
6.1 红黑树的特性
- 每个节点或者是红色或者是黑色。
- 根节点是黑色的。
- 每个叶子节点(NIL)都是黑色的。
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
- 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点。
具体结构如图:
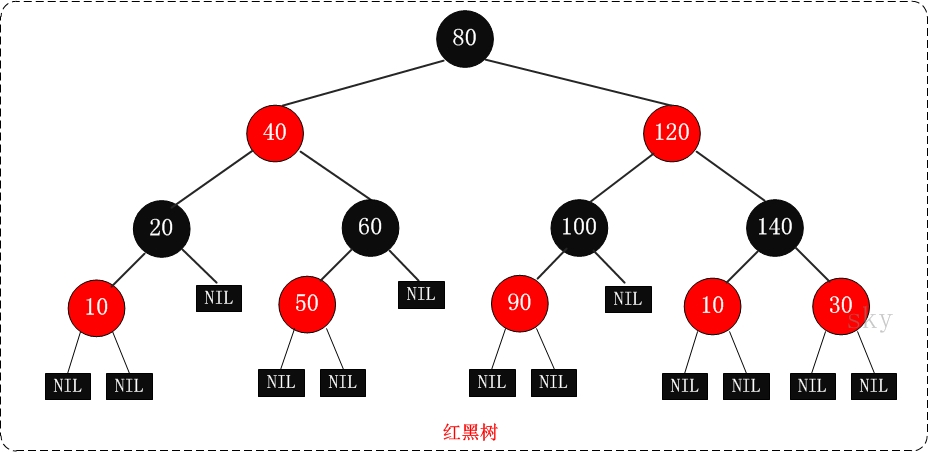
红黑树的基本操作是添加、删除和旋转。在对红黑树进行添加或删除后,会用到旋转方法。在添加或删除红黑树中的节点之后,红黑树就发生了变化,可能不满足红黑树的5条性质,也就不再是一颗红黑树了,而是一颗普通的树。而通过旋转,可以使这颗树重新成为红黑树。简单点说,旋转的目的是让树保持红黑树的特性。
6.2 红黑树的左旋
首先要说明的是节点本身是不会旋转的,旋转改变的是节点之间的关系,选择一个节点作为旋转的顶端,如果做一次左旋,这个顶端节点会向下和向左移动到它左子节点的位置,它的右子节点会上移到它原来的位置。左旋的顶端节点必须要有右子节点。
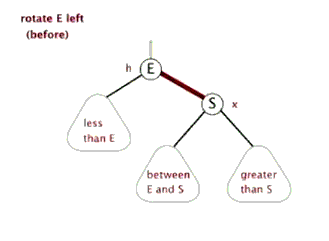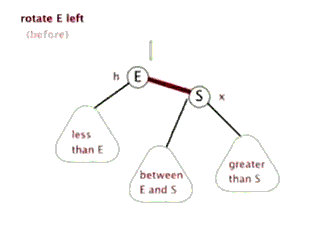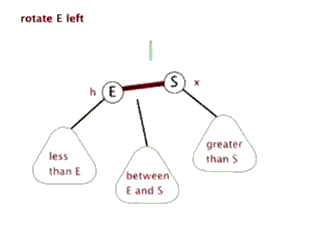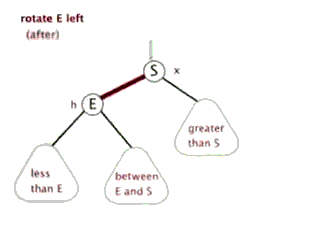
6.3 红黑树的右旋
右旋的顶端节点必须要有左子节点。
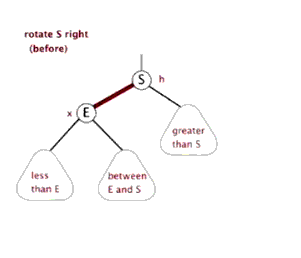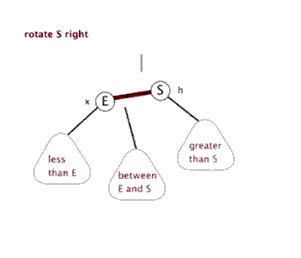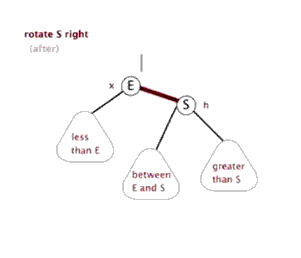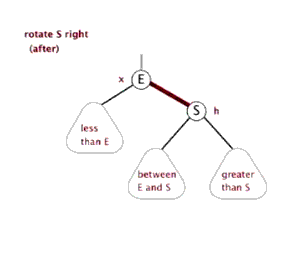
6.4 红黑树的添加
红黑树的添加分为3步:
(1)将红黑树看作是一颗二叉查找树,并以二叉树的插入规则插入新节点。
(2)将插入的节点涂为红色或者黑色。
(3)通过左旋、右旋或着色操作,使其重新成为一颗红黑树。
6.5 红黑树的删除
红黑树的删除分为2步:
(1)将红黑树看作是一颗二叉查找树,并以二叉树的删除规则删除节点。
(2)通过左旋、右旋或着色操作,使其重新成为一颗红黑树。