★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)
➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/ )
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/9866561.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
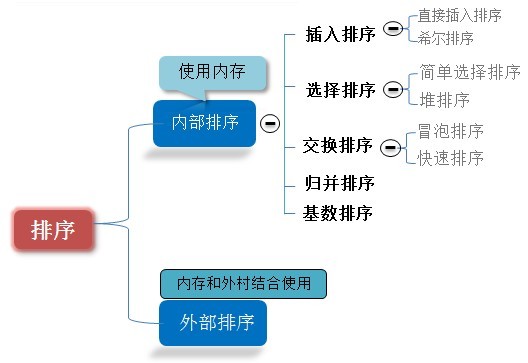
排序分为内部排序和外部排序。
内部排序:是指待排序列完全存放在内存中所进行的排序过程,适合不太大的元素序列。
外部排序:指的是大文件的排序,即待排序的记录存储在外存储器上,待排序的文件无法一次装入内存,需要在内存和外部存储器之间进行多次数据交换,以达到排序整个文件的目的。
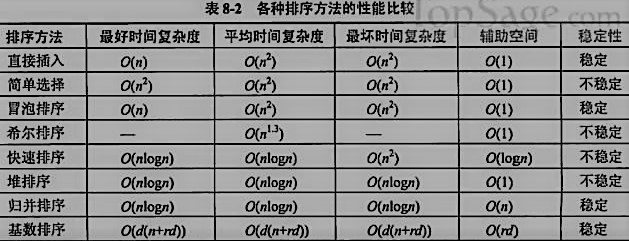
当N小于20的时候,插入排序具有最好的性能。
当N大于20时,快速排序具有最好的性能,尽管归并排序(merge sort)和堆排序(heap sort)复杂度都为nlog2(n)。
归并排序
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
算法描述
归并操作的工作原理如下:
第一步:申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列
第二步:设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置
第三步:比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置
重复步骤3直到某一指针超出序列尾,将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾
ViewController.swift文件:运行时间(7.7611s)
1 import UIKit 2 3 class ViewController: UIViewController { 4 //属性1:用来存储需要排序的数组 5 var result : Array<Int> = Array<Int>() 6 //属性2:排序时使用到的临时二维数组 7 var tempArray: Array<Array<Int>> = [] 8 //属性3:统计排序花费的时间 9 var date : Date! 10 11 override func viewDidLoad() { 12 super.viewDidLoad() 13 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 14 //初始化一个整形数组 15 var array : Array<Int> = Array<Int>() 16 //将1至100的100个整数,存入到该数组中 17 for i in 1...100 18 { 19 array.append(i) 20 } 21 //添加一个循环语句, 22 //用来生成一个由100个随机整数组成的数组 23 for _ in 1...100 24 { 25 //首先根据数组的长度, 26 //获得一个1至100的随机整数 27 let temp = Int(arc4random() % UInt32(array.count))+1 28 //根据随机值从数组中获得指定位置的整数, 29 //并存储在用来排序的数组中 30 let num = array[temp-1] 31 result.append(num) 32 //从原数组中移该随机数,以避免获得重复的数字 33 array.remove(at: temp-1) 34 } 35 //添加一个循环语句, 36 //用来生成100个自定义视图对象 37 for i in 1...100 38 { 39 //初始化自定义视图对象 40 let num = result[i-1] 41 //并设置它的显示区域。 42 //其中视图的高度,是当前数组中的数字的两倍大小 43 let view = SortView(frame: CGRect(x: 10+i*3, y: 200, 2, height: num * 2)) 44 view.backgroundColor = .black 45 //设置视图的标识值 46 view.tag = i 47 //并将视图添加到当前视图控制器的根视图 48 self.view.addSubview(view) 49 } 50 //然后添加一个按钮 51 //当用户点击该按钮时对数组进行排序 52 let bt = UIButton(frame: CGRect(x: 10, y: 340, 300, height: 40)) 53 //设置背景按钮的背景颜色为橙色 54 bt.backgroundColor = .orange 55 //设置按钮在正常状态下的标题文字 56 bt.setTitle("Sort", for: .normal) 57 //给按钮对象绑定点击事件, 58 bt.addTarget(self, action: #selector(reOrderView), for: .touchUpInside) 59 //将按钮添加到当前视图控制器的根视图 60 self.view.addSubview(bt) 61 } 62 63 //添加一个方法,用来响应按钮的点击事件 64 @objc func reOrderView() 65 { 66 //获得当前的日期和时间 67 date = Date() 68 //在一个全局队列中,以异步的方式对数组进行排序 69 //并实时调整和数组中的数值相对应的视图的位置 70 DispatchQueue.global().async 71 { 72 //调用实例方法,用来进行可视化的插入排序。 73 //该方法在下方的代码中实现 74 self.sort(items: self.result) 75 //获得排序后的系统时间, 76 //并在控制台输出两个时间的差值, 77 //从而获得排序所花费的大致时间。 78 //考虑线程休眠的影响,此数据仅做参考 79 let endDate = Date() 80 print(endDate.timeIntervalSince(self.date)) 81 } 82 } 83 84 //添加一个方法,用来实现具体的可视化的归并排序的功能 85 func sort(items: Array<Int>) 86 { 87 //首先清除临时数组中的所有元素 88 tempArray.removeAll() 89 //然后通过一个循环语句, 90 //将需要排序的数组中的每一个元素, 91 //都转换为包含一元素的数组, 92 //并将该数组添加到临时数组中 93 for item in items 94 { 95 var subArray: Array<Int> = [] 96 subArray.append(item) 97 tempArray.append(subArray) 98 } 99 //接着对临时数组进行归并排序操作, 100 //直到它的长度为1 101 while tempArray.count != 1 102 { 103 var i = 0 104 while i < tempArray.count - 1 105 { 106 //将每两个左右相邻的子数组进行合并, 107 //(合并之后又在子数组中进行了排序,合并的方法将在下方的代码中实现) 108 //合并后的结果存入左侧的子数组中, 109 //右侧的子数组则在合并之后,从临时数组中删除 110 tempArray[i] = mergeArray(firstList: tempArray[i], secondList: tempArray[i + 1]) 111 tempArray.remove(at: i + 1) 112 //然后对合并后的子数组进行遍历, 113 //用来及时更新在合并和排序之后的每个子数组中的元素所对应的视图的高度 114 for subIndex in 0..<tempArray[i].count 115 { 116 //通过实例方法,对子数组中的元素所对应的视图的高度进行更新, 117 //此方法在下方代码中实现 118 let index = self.countSubItemIndex(endIndex: i, subItemIndex: subIndex) 119 self.udpateView(j: index, height: tempArray[i][subIndex]) 120 } 121 //接着将索引值递增,直到循环结束 122 i = i + 1 123 } 124 } 125 } 126 127 //添加一个方法, 128 //用来实现两个相邻子数组的的合并,以及合并之后排序 129 func mergeArray(firstList: Array<Int>, secondList: Array<Int>) -> Array<Int> 130 { 131 //变量1:用于存储排序后的数组 132 var resultList: Array<Int> = [] 133 //变量2:用于辅助排序 134 var firstIndex = 0 135 //变量3:用于辅助排序 136 var secondIndex = 0 137 //添加一个循环语句 138 //用来对两个数组中的元素进行比较 139 while firstIndex < firstList.count && secondIndex < secondList.count 140 { 141 //如果第一个数组中的元素,小于第二个数组中的元素, 142 //则将较小值添加到结果数组中 143 if firstList[firstIndex] < secondList[secondIndex] 144 { 145 resultList.append(firstList[firstIndex]) 146 firstIndex += 1 147 } 148 else 149 { 150 //否则将第二个数组中的较小的值, 151 //添加到结果数组中 152 resultList.append(secondList[secondIndex]) 153 secondIndex += 1 154 } 155 } 156 //然后将第一个数组中的剩余元素, 157 //追加到结果数组中 158 while firstIndex < firstList.count 159 { 160 resultList.append(firstList[firstIndex]) 161 firstIndex += 1 162 } 163 //同样将第二个数组中的剩余元素,追加到结果数组中 164 while secondIndex < secondList.count 165 { 166 resultList.append(secondList[secondIndex]) 167 secondIndex += 1 168 } 169 //最后返回合并并且排序后的数组 170 return resultList 171 } 172 173 //添加一个方法 174 //用来计算并返回位于合并后的子数组中的元素的索引位置 175 func countSubItemIndex(endIndex: Int, subItemIndex: Int) -> Int 176 { 177 //定义一个整形变量, 178 //用来统计需要计算索引位置的元素之前的数组大小。 179 var sum = 0 180 //累加当前元素之前的所有数组的长度之和 181 for i in 0..<endIndex 182 { 183 sum += tempArray[i].count 184 } 185 //然后加上元素在其自身数组中的索引位置, 186 //就获得了元素在整个二维数组中的索引位置 187 return sum + subItemIndex 188 } 189 190 //添加一个方法,用来更新视图的高度 191 func udpateView(j: Int, height: Int) 192 { 193 //由于需要对界面元素进行调整, 194 //所以需要切换至主线程 195 weak var weak_self = self 196 DispatchQueue.main.async 197 { 198 //根据标识值, 199 //获得和需要交换顺序的数组元素相对应的视图对象 200 //并设置它的新的高度 201 let view = weak_self?.view.viewWithTag(j+1) 202 view?.frame.size.height = CGFloat(height*2) 203 } 204 //使线程休眠0.01秒, 205 //以方便观察排序的视觉效果 206 Thread.sleep(forTimeInterval: 0.01) 207 } 208 209 override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() { 210 super.didReceiveMemoryWarning() 211 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 212 } 213 }
SortView.swift文件
1 import UIKit 2 3 class SortView: UIView { 4 //首先重写父类的初始化方法 5 override init(frame: CGRect) 6 { 7 //设置自定义视图对象的显示区域 8 super.init(frame: frame) 9 self.frame = frame 10 } 11 12 //添加一个必须实现的初始化方法 13 required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) { 14 fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented") 15 } 16 17 //重写父类的重新布局子视图方法 18 //将在此视图中对视图进行外观设置 19 override func layoutSubviews() 20 { 21 //首先获得自定义视图在界面中对Y轴坐标 22 let y: CGFloat = 300 - frame.height 23 //然后重新设置自定义视图的位置 24 self.frame = frame 25 self.frame.origin.y = y 26 //根据自定义视图的高度,计算一个权重数值 27 //用于生成不同的背景颜色 28 let weight = frame.height / 200 29 //生成不同y色相的颜色对象,从而给自定义视图设置不同的背景颜色 30 //然后打开ViewController.swift文件 31 let color = UIColor(hue: weight, saturation: 1, brightness: 1, alpha: 1) 32 self.backgroundColor = color 33 } 34 /* 35 // Only override draw() if you perform custom drawing. 36 // An empty implementation adversely affects performance during animation. 37 override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) { 38 // Drawing code 39 } 40 */ 41 }