BlogEngine.Net 是个功能点很全面的开源博客系统,容易安装和实现定制,开放接口支持TrackBack,可以定义主题配置数据源等等。可谓五脏俱全,这里先记录一下它基于Membership的权限管理(一般只说到角色就没了)。
Membership是.net2.0的时候就出来了,现在的最新版本是Identity(微软已经将这个Asp.net项目开源 https://github.com/aspnet/Identity )。权限管理就是处理用户、角色、和具体权限的关系。用户和角色是多对多的关系,角色和权限也是多对多的关系。 用户通过拥有角色来间接获得权限。但为什么要使用Membership呢,我们可以在数据库中建几张表就可以搞定这些关系了,因为想用Asp.Net自带的账户管理,比自己实现的要安全方便。废话不多说了,切入正题。
一、MembershipProvider 用户/账户管理
功能:用户注册,登陆,账户管理
Membership是基于Provider实现,在Asp.Net中到处可以见到Provider的身影。MembershipProvider是一个抽象类,主要负责给Membership提供用户账户验证方面的方法。BlogEngine实现了XmlMembershipProvider和DbMembershipProvider。再通过Webconfig的配置来决定启用哪一种MembershipProvider。
1. 以XmlMembershipProvider为例,比较重要的一些方法是CreateUser,ValidateUser,ChangePassword 等。
(完整的源码可以去官网下载,这里不列出了)

public class XmlMembershipProvider : MembershipProvider { //.... /// <summary> /// Creates the user. /// </summary> /// <param name="username">The username.</param> /// <param name="password">The password.</param> /// <param name="email">The email.</param> /// <param name="passwordQuestion">The password question.</param> /// <param name="passwordAnswer">The password answer.</param> /// <param name="approved">if set to <c>true</c> [approved].</param> /// <param name="providerUserKey">The provider user key.</param> /// <param name="status">The status.</param> /// <returns>A Membership User.</returns> public override MembershipUser CreateUser( string username, string password, string email, string passwordQuestion, string passwordAnswer, bool approved, object providerUserKey, out MembershipCreateStatus status) { this.ReadMembershipDataStore(); if (this.users[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].ContainsKey(username)) { throw new NotSupportedException("The username is already in use. Please choose another username."); } var doc = new XmlDocument(); doc.Load(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); XmlNode xmlUserRoot = doc.CreateElement("User"); XmlNode xmlUserName = doc.CreateElement("UserName"); XmlNode xmlPassword = doc.CreateElement("Password"); XmlNode xmlEmail = doc.CreateElement("Email"); XmlNode xmlLastLoginTime = doc.CreateElement("LastLoginTime"); xmlUserName.InnerText = username; string passwordPrep = this.passwordFormat == MembershipPasswordFormat.Hashed ? Utils.HashPassword(password) : password; xmlPassword.InnerText = passwordPrep; xmlEmail.InnerText = email; xmlLastLoginTime.InnerText = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", CultureInfo.InvariantCulture); xmlUserRoot.AppendChild(xmlUserName); xmlUserRoot.AppendChild(xmlPassword); xmlUserRoot.AppendChild(xmlEmail); xmlUserRoot.AppendChild(xmlLastLoginTime); doc.SelectSingleNode("Users").AppendChild(xmlUserRoot); doc.Save(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); status = MembershipCreateStatus.Success; var user = new MembershipUser( this.Name, username, username, email, passwordQuestion, passwordPrep, approved, false, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now, DateTime.MaxValue); this.users[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].Add(username, user); return user; } /// <summary> /// Removes a user from the membership data source. /// </summary> /// <param name="username">The name of the user to delete.</param> /// <param name="deleteAllRelatedData">true to delete data related to the user from the database; false to leave data related to the user in the database.</param> /// <returns> /// true if the user was successfully deleted; otherwise, false. /// </returns> public override bool DeleteUser(string username, bool deleteAllRelatedData) { this.ReadMembershipDataStore(); var doc = new XmlDocument(); doc.Load(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); foreach (XmlNode node in doc.GetElementsByTagName("User").Cast<XmlNode>().Where(node => node.ChildNodes[0].InnerText.Equals(username, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))) { doc.SelectSingleNode("Users").RemoveChild(node); doc.Save(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); this.users[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].Remove(username); return true; } return false; } /// <summary> /// Processes a request to update the password for a membership user. /// </summary> /// <param name="username">The user to update the password for.</param> /// <param name="oldPassword">The current password for the specified user.</param> /// <param name="newPassword">The new password for the specified user.</param> /// <returns> /// true if the password was updated successfully; otherwise, false. /// </returns> public override bool ChangePassword(string username, string oldPassword, string newPassword) { var doc = new XmlDocument(); doc.Load(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); var nodes = doc.GetElementsByTagName("User"); foreach (XmlNode node in nodes) { if (!node["UserName"].InnerText.Equals(username, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { continue; } if (!this.CheckPassword(node["Password"].InnerText, oldPassword)) { continue; } string passwordPrep = this.passwordFormat == MembershipPasswordFormat.Hashed ? Utils.HashPassword(newPassword) : newPassword; node["Password"].InnerText = passwordPrep; doc.Save(XmlFullyQualifiedPath); this.users = null; this.ReadMembershipDataStore(); return true; } return false; } //...... }
2.webconfig配置:
在system.web目录下。通过defaultProvider来指定。
<membership defaultProvider="XmlMembershipProvider"> <providers> <clear /> <add name="XmlMembershipProvider" type="BlogEngine.Core.Providers.XmlMembershipProvider, BlogEngine.Core" description="XML membership provider" passwordFormat="Hashed" /> <add name="SqlMembershipProvider" type="System.Web.Security.SqlMembershipProvider" connectionStringName="BlogEngine" applicationName="BlogEngine" /> <add name="DbMembershipProvider" type="BlogEngine.Core.Providers.DbMembershipProvider, BlogEngine.Core" passwordFormat="Hashed" connectionStringName="BlogEngine" /> </providers> </membership>
这里看到的SqlMembershipProvider是在.net2.0中就自带的一个Provider。
3.那这样就可以在我们的AccountController中调用了。
[HttpPost] [AllowAnonymous] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public ActionResult Register(RegisterModel model) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { // 尝试注册用户 try { Membership.CreateUser(model.UserName, model.Password, model.Email); FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(model.UserName, false); return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } catch (MembershipCreateUserException e) { ModelState.AddModelError("", ErrorCodeToString(e.StatusCode)); } } // 如果我们进行到这一步时某个地方出错,则重新显示表单 return View(model); }
另外还封装了一个UsersRepository,并通过API的方式供外部使用。

public class UsersRepository : IUsersRepository { /// <summary> /// Post list /// </summary> /// <param name="filter">Filter expression</param> /// <param name="order">Order expression</param> /// <param name="skip">Records to skip</param> /// <param name="take">Records to take</param> /// <returns>List of users</returns> public IEnumerable<BlogUser> Find(int take = 10, int skip = 0, string filter = "", string order = "") { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.AccessAdminPages)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); var users = new List<BlogUser>(); int count; var userCollection = Membership.Provider.GetAllUsers(0, 999, out count); var members = userCollection.Cast<MembershipUser>().ToList(); foreach (var m in members) { users.Add(new BlogUser { IsChecked = false, UserName = m.UserName, Email = m.Email, Profile = GetProfile(m.UserName), Roles = GetRoles(m.UserName) }); } var query = users.AsQueryable().Where(filter); // if take passed in as 0, return all if (take == 0) take = users.Count; return query.OrderBy(order).Skip(skip).Take(take); } /// <summary> /// Get single post /// </summary> /// <param name="id">User id</param> /// <returns>User object</returns> public BlogUser FindById(string id) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.AccessAdminPages)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); var users = new List<BlogUser>(); int count; var userCollection = Membership.Provider.GetAllUsers(0, 999, out count); var members = userCollection.Cast<MembershipUser>().ToList(); foreach (var m in members) { users.Add(new BlogUser { IsChecked = false, UserName = m.UserName, Email = m.Email, Profile = GetProfile(m.UserName), Roles = GetRoles(m.UserName) }); } return users.AsQueryable().Where("UserName.ToLower() == "" + id.ToLower() + """).FirstOrDefault(); } /// <summary> /// Add new user /// </summary> /// <param name="user">Blog user</param> /// <returns>Saved user</returns> public BlogUser Add(BlogUser user) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.CreateNewUsers)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); if (user == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.UserName) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.Email) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.Password)) { throw new ApplicationException("Error adding new user; Missing required fields"); } if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(Rights.CreateNewUsers)) throw new ApplicationException("Not authorized"); // create user var usr = Membership.CreateUser(user.UserName, user.Password, user.Email); if (usr == null) throw new ApplicationException("Error creating new user"); UpdateUserProfile(user); UpdateUserRoles(user); user.Password = ""; return user; } /// <summary> /// Update user /// </summary> /// <param name="user">User to update</param> /// <returns>True on success</returns> public bool Update(BlogUser user) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.EditOwnUser)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); if (user == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.UserName) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.Email)) throw new ApplicationException("Error adding new user; Missing required fields"); if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(Rights.EditOwnUser)) throw new ApplicationException("Not authorized"); // update user var usr = Membership.GetUser(user.UserName); if (usr == null) return false; usr.Email = user.Email; Membership.UpdateUser(usr); UpdateUserProfile(user); UpdateUserRoles(user); return true; } /// <summary> /// Save user profile /// </summary> /// <param name="user">Blog user</param> /// <returns>True on success</returns> public bool SaveProfile(BlogUser user) { return UpdateUserProfile(user); } /// <summary> /// Delete user /// </summary> /// <param name="id">User ID</param> /// <returns>True on success</returns> public bool Remove(string id){ if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(id)) return false; if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.DeleteUserSelf)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); bool isSelf = id.Equals(Security.CurrentUser.Identity.Name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase); if (isSelf && !Security.IsAuthorizedTo(Rights.DeleteUserSelf)) throw new ApplicationException("Not authorized"); else if (!isSelf && !Security.IsAuthorizedTo(Rights.DeleteUsersOtherThanSelf)) throw new ApplicationException("Not authorized"); // Last check - it should not be possible to remove the last use who has the right to Add and/or Edit other user accounts. If only one of such a // user remains, that user must be the current user, and can not be deleted, as it would lock the user out of the BE environment, left to fix // it in XML or SQL files / commands. See issue 11990 bool adminsExist = false; MembershipUserCollection users = Membership.GetAllUsers(); foreach (MembershipUser user in users) { string[] roles = Roles.GetRolesForUser(user.UserName); // look for admins other than 'id' if (!id.Equals(user.UserName, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) && (Right.HasRight(Rights.EditOtherUsers, roles) || Right.HasRight(Rights.CreateNewUsers, roles))) { adminsExist = true; break; } } if (!adminsExist) throw new ApplicationException("Can not delete last admin"); string[] userRoles = Roles.GetRolesForUser(id); try { if (userRoles.Length > 0) { Roles.RemoveUsersFromRoles(new string[] { id }, userRoles); } Membership.DeleteUser(id); var pf = AuthorProfile.GetProfile(id); if (pf != null) { BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.DeleteProfile(pf); } } catch (Exception ex) { Utils.Log("Error deleting user", ex.Message); return false; } return true; } #region Private methods static Profile GetProfile(string id) { if (!Utils.StringIsNullOrWhitespace(id)) { var pf = AuthorProfile.GetProfile(id); if (pf == null) { pf = new AuthorProfile(id); pf.Birthday = DateTime.Parse("01/01/1900"); pf.DisplayName = id; pf.EmailAddress = Utils.GetUserEmail(id); pf.FirstName = id; pf.Private = true; pf.Save(); } return new Profile { AboutMe = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.AboutMe) ? "" : pf.AboutMe, Birthday = pf.Birthday.ToShortDateString(), CityTown = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.CityTown) ? "" : pf.CityTown, Country = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.Country) ? "" : pf.Country, DisplayName = pf.DisplayName, EmailAddress = pf.EmailAddress, PhoneFax = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.PhoneFax) ? "" : pf.PhoneFax, FirstName = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.FirstName) ? "" : pf.FirstName, Private = pf.Private, LastName = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.LastName) ? "" : pf.LastName, MiddleName = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.MiddleName) ? "" : pf.MiddleName, PhoneMobile = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.PhoneMobile) ? "" : pf.PhoneMobile, PhoneMain = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.PhoneMain) ? "" : pf.PhoneMain, PhotoUrl = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.PhotoUrl) ? "" : pf.PhotoUrl.Replace(""", ""), RegionState = string.IsNullOrEmpty(pf.RegionState) ? "" : pf.RegionState }; } return null; } static List<Data.Models.RoleItem> GetRoles(string id) { var roles = new List<Data.Models.RoleItem>(); var userRoles = new List<Data.Models.RoleItem>(); roles.AddRange(System.Web.Security.Roles.GetAllRoles().Select(r => new Data.Models.RoleItem { RoleName = r, IsSystemRole = Security.IsSystemRole(r) })); roles.Sort((r1, r2) => string.Compare(r1.RoleName, r2.RoleName)); foreach (var r in roles) { if (System.Web.Security.Roles.IsUserInRole(id, r.RoleName)) { userRoles.Add(r); } } return userRoles; } static bool UpdateUserProfile(BlogUser user) { if (user == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.UserName)) return false; var pf = AuthorProfile.GetProfile(user.UserName) ?? new AuthorProfile(user.UserName); try { pf.DisplayName = user.Profile.DisplayName; pf.FirstName = user.Profile.FirstName; pf.MiddleName = user.Profile.MiddleName; pf.LastName = user.Profile.LastName; pf.EmailAddress = user.Email; // user.Profile.EmailAddress; DateTime date; if (user.Profile.Birthday.Length == 0) user.Profile.Birthday = "1/1/1001"; if (DateTime.TryParse(user.Profile.Birthday, out date)) pf.Birthday = date; pf.PhotoUrl = user.Profile.PhotoUrl.Replace(""", ""); pf.Private = user.Profile.Private; pf.PhoneMobile = user.Profile.PhoneMobile; pf.PhoneMain = user.Profile.PhoneMain; pf.PhoneFax = user.Profile.PhoneFax; pf.CityTown = user.Profile.CityTown; pf.RegionState = user.Profile.RegionState; pf.Country = user.Profile.Country; pf.AboutMe = user.Profile.AboutMe; pf.Save(); UpdateProfileImage(pf); } catch (Exception ex) { Utils.Log("Error editing profile", ex); return false; } return true; } static bool UpdateUserRoles(BlogUser user) { try { // remove all user roles and add only checked string[] currentRoles = Roles.GetRolesForUser(user.UserName); if (currentRoles.Length > 0) Roles.RemoveUserFromRoles(user.UserName, currentRoles); if (user.Roles.Count > 0) { string[] roles = user.Roles.Where(ur => ur.IsChecked).Select(r => r.RoleName).ToArray(); if(roles.Length > 0) Roles.AddUsersToRoles(new string[] { user.UserName }, roles); else Roles.AddUsersToRoles(new string[] { user.UserName }, new string[] { BlogConfig.AnonymousRole }); } return true; } catch (Exception ex) { Utils.Log("Error updating user roles", ex); return false; } } /// <summary> /// Remove any existing profile images /// </summary> /// <param name="profile">User profile</param> static void UpdateProfileImage(AuthorProfile profile) { var dir = BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.GetDirectory("/avatars"); if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(profile.PhotoUrl)) { foreach (var f in dir.Files) { var dot = f.Name.IndexOf("."); var img = dot > 0 ? f.Name.Substring(0, dot) : f.Name; if (profile.UserName == img) { f.Delete(); } } } else { foreach (var f in dir.Files) { var dot = f.Name.IndexOf("."); var img = dot > 0 ? f.Name.Substring(0, dot) : f.Name; // delete old profile image saved with different name // for example was admin.jpg and now admin.png if (profile.UserName == img && f.Name != profile.PhotoUrl.Replace(""", "")) { f.Delete(); } } } } #endregion }

unity.RegisterType<UsersController>(); unity.RegisterType<IUsersRepository, UsersRepository>(new HierarchicalLifetimeManager()); //...... public class UsersController : ApiController { readonly IUsersRepository repository; public UsersController(IUsersRepository repository) { this.repository = repository; } //.......... }
最后的结构图如下:
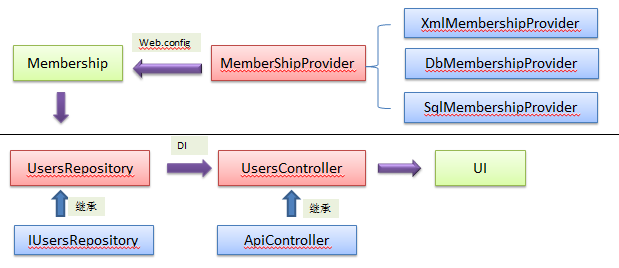
二、RoleProvider 角色管理
功能:提供用户角色的管理、验证相关方法。
同上,BlogEngine提供了DbRoleProvider和XmlRoleProvider。而且通过配置文件加入了系统角色。在BlogConfig.cs文件中可以看到,他提供了三个系统角色,管理员,匿名用户和编辑。

#region AdministratorRole private static string _administrativeRole; /// <summary> /// The role that has administrator persmissions /// </summary> public static string AdministratorRole { get { return _administrativeRole ?? (_administrativeRole = WebConfigurationManager.AppSettings["BlogEngine.AdminRole"] ?? "administrators"); } } #endregion #region AnonymousRole private static string _anonymousRole; /// <summary> /// The role that represents all non-authenticated users. /// </summary> public static string AnonymousRole { get { return _anonymousRole ?? (_anonymousRole = WebConfigurationManager.AppSettings["BlogEngine.AnonymousRole"] ?? "Anonymous"); } } #endregion #region EditorsRole private static string _editorsRole; /// <summary> /// The role that represents all non-authenticated users. /// </summary> public static string EditorsRole { get { return _editorsRole ?? (_editorsRole = WebConfigurationManager.AppSettings["BlogEngine.EditorsRole"] ?? "Editors"); } } #endregion
在Web.config的AppSettings的节点可以看到,且这样可以比较方便的修改默认名称。
<add key="BlogEngine.AdminRole" value="Administrators" /> <!-- The name of the role for anonymous(non-authenticated) users. --> <add key="BlogEngine.AnonymousRole" value="Anonymous" /> <!-- The name of the role for Editors --> <add key="BlogEngine.EditorsRole" value="Editors" />
1.以XmlRoleProvider为例。(先不必纠结代码中Blog.CurrentInstance.Id)

public class XmlRoleProvider : RoleProvider { //............... public override void AddUsersToRoles(string[] usernames, string[] roleNames) { ReadRoleDataStore(); var currentRoles = new List<string>(this.GetAllRoles()); if (usernames.Length != 0 && roleNames.Length != 0) { foreach (var rolename in roleNames.Where(rolename => !currentRoles.Contains(rolename) && !rolename.Equals(BlogConfig.AnonymousRole, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))) { this.roles[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].Add(new Role(rolename, new List<string>(usernames))); } foreach (var role in this.roles[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id]) { var role1 = role; foreach (var s in from name in roleNames where role1.Name.Equals(name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) from s in usernames where !role1.Users.Contains(s) select s) { role.Users.Add(s); } } } this.Save(); } /// <summary> /// Adds a new role to the data source for the configured applicationName. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"> /// The name of the role to create. /// </param> public override void CreateRole(string roleName) { ReadRoleDataStore(); // This needs to be fixed. This will always return false. if (this.roles[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].Contains(new Role(roleName))) { return; } this.roles[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id].Add(new Role(roleName)); this.Save(); } }
一个角色可以包含多个用户。Role对象如下,便于存储。

public class Role { #region Constructors and Destructors /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="Role"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="name"> /// A name of the role. /// </param> public Role(string name) : this(name, new List<string>()) { } /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref = "Role" /> class. /// </summary> public Role() : this(null, new List<string>()) { } /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="Role"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="name"> /// A name of the role. /// </param> /// <param name="userNames"> /// A list of users in role. /// </param> public Role(string name, List<string> userNames) { if (userNames == null) { throw new System.ArgumentNullException("userNames"); } else { this.Name = name; this.Users = userNames; } } #endregion #region Properties /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the name. /// </summary> /// <value>The name of the role.</value> public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets the users. /// </summary> /// <value>The users.</value> public List<string> Users { get; private set; } #endregion }
生成的xml文档:每个角色下面有那些用户 一目了然。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="yes"?> <roles> <role> <name>Administrators</name> <users> <user>Admin</user> </users> </role> <role> <name>Editors</name> <users /> </role> <role> <name>Anonymous</name> <users /> </role> <role> <name>COCO</name> <users> <user>stoneniqiu</user> </users> </role> </roles>
但呈现在UI上的每一个Role转换成RoleItem(相当于一个视图模型)。

/// <summary> /// Json friendly Role wrapper /// </summary> public class RoleItem { /// <summary> /// If checked in the UI(是否选中) /// </summary> public bool IsChecked { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Role Name /// </summary> public string RoleName { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Is System Role /// </summary> public bool IsSystemRole { get; set; } }
2.Web.config配置:
在system.web的rolManager节点中。
<roleManager defaultProvider="XmlRoleProvider" enabled="true" cacheRolesInCookie="false"> <providers> <clear /> <add name="XmlRoleProvider" type="BlogEngine.Core.Providers.XmlRoleProvider, BlogEngine.Core" description="XML role provider" /> <add name="SqlRoleProvider" type="System.Web.Security.SqlRoleProvider" connectionStringName="BlogEngine" applicationName="BlogEngine" /> <add name="DbRoleProvider" type="BlogEngine.Core.Providers.DbRoleProvider, BlogEngine.Core" connectionStringName="BlogEngine" /> </providers> </roleManager>
同样,有一个现成的SqlRoleProvider以供选择。
3.如MembershipProvider对应Membership一样,RoleProvider对应的是System.Web.Security.Roles。
在RolesRepository中 通过Roles来操作。
public class RolesRepository : IRolesRepository { //.... public IEnumerable<RoleItem> Find(int take = 10, int skip = 0, string filter = "", string order = "") { var roles = new List<RoleItem>(); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filter)) filter = "1 == 1"; if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(order)) order = "RoleName"; roles.AddRange(System.Web.Security.Roles.GetAllRoles().Select(r => new RoleItem { RoleName = r, IsSystemRole = Security.IsSystemRole(r) })); roles.Sort((r1, r2) => string.Compare(r1.RoleName, r2.RoleName)); return roles; } public RoleItem Add(Data.Models.RoleItem role) { try { Roles.CreateRole(role.RoleName); return FindById(role.RoleName); } catch (Exception ex) { Utils.Log(string.Format("Error adding role", ex)); throw new ApplicationException("Error adding new role"); } } //.... }
在界面中,可以方便的给我们的用户指定角色。
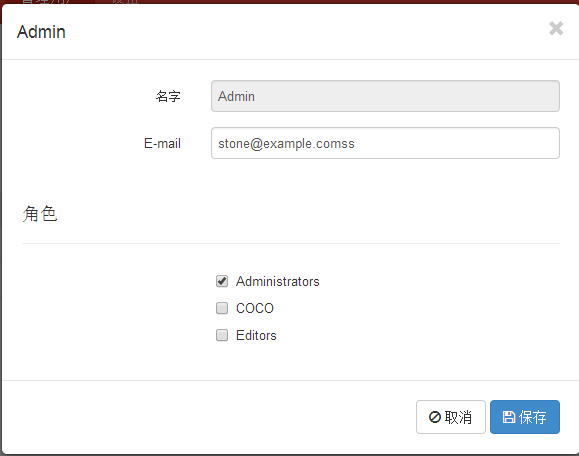
3.最后封装在RolesRepository中,通过Api的方式公布了出去 图如下
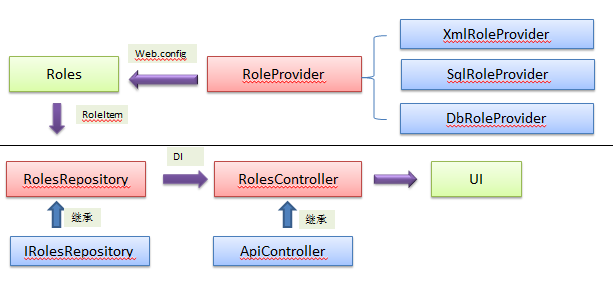
三、Right 权限管理
功能:权限和角色的管理
用户和角色都有自带的Provider。而权限没有,在BlogEngine中,定义了枚举类型Rights、权限类型RightCategory、以及特性RightDetailsAttribute

public enum Rights { /// <summary> /// Represents a user that has no rights or permissions. This flag should not be used in combination with any other flag. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// /// This value isn't meant for public consumption. /// /// </remarks> None = 0, #region Misc /// <summary> /// A user is allowed to view exception messages. /// </summary> [RightDetails(Category = RightCategory.General)] ViewDetailedErrorMessages, /// <summary> /// A user is allowed to access administration pages. /// Typically, a blog where self-registration is allowed /// would restrict this right from guest users. /// </summary> [RightDetails(Category = RightCategory.General)] AccessAdminPages, /// <summary> /// A user is allowed to access admin settings pages. /// </summary> [RightDetails(Category = RightCategory.General)] AccessAdminSettingsPages, /// <summary> /// A user is allowed to manage widgets. /// </summary> [RightDetails(Category = RightCategory.General)] ManageWidgets, #endregion #region "Comments" //............. [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field, AllowMultiple=false, Inherited=false)] public sealed class RightDetailsAttribute : Attribute { /// <summary> /// Default constructor. /// </summary> public RightDetailsAttribute() { } #region "Properties" /// <summary> /// Key for grabbing a description from a resource file. /// </summary> public string DescriptionResourceLabelKey { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Key for grabbing a name from a resource file. /// </summary> public string NameResourceLabelKey { get; set; } /// <summary> /// The category a Right is for. /// </summary> public RightCategory Category { get; set; } #endregion } /// <summary> /// Categories for Rights. /// </summary> public enum RightCategory { /// <summary> /// No category /// </summary> None, /// <summary> /// General category /// </summary> General, /// <summary> /// Comments category /// </summary> Comments, /// <summary> /// Pages category /// </summary> Pages, /// <summary> /// Post category /// </summary> Posts, /// <summary> /// Users category /// </summary> Users, /// <summary> /// Roles /// </summary> Roles } }
1.权限管理的核心类是Right,实现了IHttpModule接口,提供静态的验证方法,同时又是作为一个存储模型(即和其他模型一样按照用户指定的方式存储,不像用户和角色需要配置)。这个类稍微有点复杂,刚开始看,容易搞晕。做几点说明。
1).Fields里面有很多集合,主要是rihtsByRole(每个角色有哪些权限) rightsbyName(权限名称对应的Right对象集合)rightsByFlag(枚举类型的权限对应的Right对象集合)。allRightInstances(所有Right实例) _rolesWithRight(拥有当前权限的角色)
2) 以上集合是多在静态构造函数中初始化,可以不必在意EnsureBlogInstanceDataLoaded 函数。
3) RefreshAllRights初始化角色和权限。比如AdministratorRole 默认拥有所有权限都是在这里完成的。

public sealed class Right : IHttpModule { #region "Static" #region "Fields" // These dictionaries would probably be better condensed into something else. private static readonly object staticLockObj = new Object(); private static readonly ReadOnlyCollection<Rights> rightFlagValues; private static readonly ReadOnlyCollection<Right> allRightInstances; // This is a static collection so that there's no need to constantly remake a new empty collection // when a user has no rights. private static readonly ReadOnlyCollection<Right> noRights = new ReadOnlyCollection<Right>(new List<Right>()); // Once rightsByFlag is set it should not be changed ever. private static readonly Dictionary<Rights, Right> rightsByFlag = new Dictionary<Rights, Right>(); private static readonly Dictionary<string, Right> rightsByName = new Dictionary<string, Right>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); private static readonly Dictionary<Guid, Dictionary<string, HashSet<Right>>> rightsByRole = new Dictionary<Guid, Dictionary<string, HashSet<Right>>>(); #endregion #region "IHttpModule" /// <summary> /// Initializes a module and prepares it to handle requests. /// </summary> /// <param name="context">An <see cref="T:System.Web.HttpApplication"/> that provides access to the methods, properties, and events common to all application objects within an ASP.NET application</param> public void Init(HttpApplication context) { context.BeginRequest += ContextBeginRequest; } /// <summary> /// Handles the BeginRequest event of the context control. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"> /// The source of the event. /// </param> /// <param name="e"> /// The <see cref="System.EventArgs"/> instance containing the event data. /// </param> private static void ContextBeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { //var context = ((HttpApplication)sender).Context; EnsureBlogInstanceDataLoaded(); } /// <summary> /// Disposes of the resources (other than memory) used by the module that implements <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpModule"/>. /// </summary> public void Dispose() { // Nothing to dispose } #endregion static Right() { // Initialize the various dictionaries to their starting state. var flagType = typeof(Rights); rightFlagValues = Enum.GetValues(flagType).Cast<Rights>().ToList().AsReadOnly(); var adminRole = BlogEngine.Core.BlogConfig.AdministratorRole; var allRights = new List<Right>(); // Create a Right instance for each value in the Rights enum. foreach (var flag in rightFlagValues) { Rights curFlag = (Rights)flag; var flagName = Enum.GetName(flagType, curFlag); var curRight = new Right(curFlag, flagName); allRights.Add(curRight); // Use the Add function so if there are multiple flags with the same // value they can be caught quickly at runtime. rightsByFlag.Add(curFlag, curRight); rightsByName.Add(flagName, curRight); } allRightInstances = allRights.AsReadOnly(); EnsureBlogInstanceDataLoaded(); Blog.Saved += (s, e) => { if (e.Action == SaveAction.Delete) { Blog blog = s as Blog; if (blog != null) { // remove deleted blog from static 'rightsByRole' if (rightsByRole != null && rightsByRole.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) rightsByRole.Remove(blog.Id); // remove deleted blog from _readOnlyRoles/_rolesWithRight from // each of the Right instances. for (int i = 0; i < allRightInstances.Count; i++) { if (allRightInstances[i]._readOnlyRoles.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) allRightInstances[i]._readOnlyRoles.Remove(blog.Id); if (allRightInstances[i]._rolesWithRight.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) allRightInstances[i]._rolesWithRight.Remove(blog.Id); } } } }; } #region "Methods" /// <summary> /// Method that should be called any time Rights are changed and saved. /// </summary> public static void RefreshAllRights() { var flagType = typeof(Rights); lock (staticLockObj) { RightsByRole.Clear(); var allRoles = new HashSet<string>(System.Web.Security.Roles.GetAllRoles(), StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); foreach (var role in allRoles) { var curRole = PrepareRoleName(role); RightsByRole.Add(curRole, new HashSet<Right>()); allRoles.Add(curRole); } var adminRole = BlogConfig.AdministratorRole; var anonymousRole = BlogConfig.AnonymousRole; var editorsRole = BlogConfig.EditorsRole; foreach (var right in GetAllRights()) { // Clear the existing roles so any newly-deleted // roles are removed from the list. right.ClearRoles(); if (right.Flag != Rights.None) { right.AddRole(adminRole); } } foreach (var pair in BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.FillRights()) { // Ignore any values that are invalid. This is bound to happen // during updates if a value gets renamed or removed. if (Right.RightExists(pair.Key)) { var key = GetRightByName(pair.Key); foreach (var role in pair.Value) { var curRole = PrepareRoleName(role); // Ignore any roles that are added that don't exist. if (allRoles.Contains(curRole)) { key.AddRole(curRole); Right.RightsByRole[curRole].Add(key); } } } } // Note: To reset right/roles to the defaults, the data store can be // cleared out (delete rights.xml or clear DB table). Then these // defaults will be setup. bool defaultsAdded = false; // Check that the anonymous role is set up properly. If no rights // are found, then the defaults need to be set. if (!GetRights(anonymousRole).Any()) { List<Rights> defaultRoleRights = GetDefaultRights(anonymousRole); foreach (Rights rights in defaultRoleRights) { Right.rightsByFlag[rights].AddRole(anonymousRole); } defaultsAdded = true; } // Check that the editor role is set up properly. If no rights // are found, then the defaults need to be set. if (!GetRights(editorsRole).Any()) { List<Rights> defaultRoleRights = GetDefaultRights(editorsRole); foreach (Rights rights in defaultRoleRights) { Right.rightsByFlag[rights].AddRole(editorsRole); } defaultsAdded = true; } // This check is for autocreating the rights for the Administrator role. foreach (KeyValuePair<Rights, Right> kvp in rightsByFlag) { if (kvp.Key != Rights.None) { kvp.Value.AddRole(adminRole); // could set defaultsAdded to true if the right doesn't already // have the adminRole in it. since the admin always gets all // rights and they cannot be removed, we simply grant the admin // all rights without the need to persist that. } } if (defaultsAdded) { BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.SaveRights(); } } } /// <summary> /// Gets the list of default rights for the given role name. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName">The role for which we are obtaining rights.</param> /// <returns>If the role is found, a list of the appropriate rights. Otherwise, an empty list of rights.</returns> public static List<Rights> GetDefaultRights(string roleName) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(roleName)) { return new List<Rights>(); } if (roleName.Equals(BlogConfig.EditorsRole, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { return new List<Rights>() { Rights.AccessAdminPages, Rights.CreateComments, Rights.ViewPublicComments, Rights.ViewPublicPosts, Rights.ViewPublicPages, Rights.ViewRatingsOnPosts, Rights.SubmitRatingsOnPosts, Rights.ViewUnmoderatedComments, Rights.ModerateComments, Rights.ViewUnpublishedPages, Rights.ViewUnpublishedPosts, Rights.DeleteOwnPosts, Rights.PublishOwnPosts, Rights.CreateNewPages, Rights.CreateNewPosts, Rights.EditOwnPages, Rights.EditOwnPosts, Rights.EditOwnUser }; } else if (roleName.Equals(BlogConfig.AnonymousRole, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { return new List<Rights>() { Rights.CreateComments, Rights.ViewPublicComments, Rights.ViewPublicPosts, Rights.ViewPublicPages, Rights.ViewRatingsOnPosts, Rights.SubmitRatingsOnPosts }; } return new List<Rights>(); } /// <summary> /// Handles updating Role name changes, so Role names tied to Rights stay in sync. /// </summary> /// <param name="oldname">The old Role name.</param> /// <param name="newname">The new Role name.</param> public static void OnRenamingRole(string oldname, string newname) { IEnumerable<Right> rightsWithRole = Right.GetRights(oldname); if (rightsWithRole.Any()) { foreach (Right right in rightsWithRole) { right.RemoveRole(oldname); right.AddRole(newname); } BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.SaveRights(); } } /// <summary> /// Handles removing Roles tied to Rights when a Role will be deleted. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"></param> public static void OnRoleDeleting(string roleName) { IEnumerable<Right> rightsWithRole = Right.GetRights(roleName); if (rightsWithRole.Any()) { foreach (Right right in rightsWithRole) { right.RemoveRole(roleName); } BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.SaveRights(); } } /// <summary> /// Call this method for verifying role names and then trimming the string. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static string PrepareRoleName(string roleName) { if (Utils.StringIsNullOrWhitespace(roleName)) { throw new ArgumentNullException("roleName"); } else { return roleName.Trim(); } } /// <summary> /// Returns an IEnumerable of all of the Rights that exist on BlogEngine. /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Right> GetAllRights() { return Right.allRightInstances; } /// <summary> /// Returns a Right instance based on its name. /// </summary> /// <param name="rightName"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static Right GetRightByName(string rightName) { if (Utils.StringIsNullOrWhitespace(rightName)) { throw new ArgumentNullException("rightName"); } else { Right right = null; if (rightsByName.TryGetValue(rightName.Trim(), out right)) { return right; } else { throw new KeyNotFoundException("No Right exists by the name '" + rightName + "'"); } } } /// <summary> /// Returns a Right instance based on the flag. /// </summary> /// <param name="flag"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static Right GetRightByFlag(Rights flag) { Right right = null; if (rightsByFlag.TryGetValue(flag, out right)) { return right; } else { throw new KeyNotFoundException("Unable to find a corresponding right for the given flag"); } } private static IEnumerable<Right> GetRightsInternal(string roleName) { roleName = PrepareRoleName(roleName); if (RightsByRole.ContainsKey(roleName)) return RightsByRole[roleName]; else return new HashSet<Right>(); } /// <summary> /// Returns an IEnumerable of Rights that are in the given role. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Right> GetRights(string roleName) { return GetRightsInternal(roleName).ToList().AsReadOnly(); } /// <summary> /// Returns an IEnumerable of Rights that are in all of the given roles. /// </summary> /// <param name="roles"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Right> GetRights(IEnumerable<string> roles) { if (roles == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("roles"); } else if (!roles.Any()) { return noRights; } else { var rights = new List<Right>(); foreach (var role in roles) { rights.AddRange(GetRightsInternal(role)); } return rights.Distinct().ToList().AsReadOnly(); } } /// <summary> /// Gets whether or not a Right exists within any of the given roles. /// </summary> /// <param name="right"></param> /// <param name="roles"></param> /// <returns> /// /// Use this method instead of GetRights().Contains() as it'll be /// much faster than having to create a new collection of Right instances each time. /// /// </returns> public static bool HasRight(Rights right, IEnumerable<string> roles) { if (roles == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("roles"); } else if (!roles.Any()) { return false; } else { var validRoles = GetRightByFlag(right).Roles; if (roles.Count() == 1) { // This is faster than intersecting, so this is // special cased. return validRoles.Contains(roles.First(), StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); } else { return validRoles.Intersect(roles, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase).Any(); } } } /// <summary> /// Checks to see if a Right exists by the given name. /// </summary> /// <param name="rightName"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static bool RightExists(string rightName) { return rightsByName.ContainsKey(rightName); } #endregion #endregion #region "Instance" #region "Fields and Constants" private readonly object instanceLockObj = new Object(); private readonly Dictionary<Guid, ReadOnlyCollection<string>> _readOnlyRoles; private readonly Dictionary<Guid, List<string>> _rolesWithRight; #endregion #region "Constructor" /// <summary> /// Private constructor for creating a Right instance. /// </summary> /// <param name="Right"></param> /// <param name="RightEnumName"></param> private Right(Rights Right, string RightEnumName) { _flag = Right; _name = RightEnumName; _rolesWithRight = new Dictionary<Guid, List<string>>(); _readOnlyRoles = new Dictionary<Guid, ReadOnlyCollection<string>>(); } // empty constructor so Right can be an HttpModule. private Right() { } #endregion #region "Properties" private static void EnsureBlogInstanceDataLoaded() { Blog blog = Blog.CurrentInstance; // either all the right instances will be setup for the current blog instance, or none // of them will be. check just the first one to see if it is setup for the current // blog instance. if (!allRightInstances[0]._readOnlyRoles.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) { for (int i = 0; i < allRightInstances.Count; i++) { allRightInstances[i]._rolesWithRight[blog.Id] = new List<string>(); allRightInstances[i]._readOnlyRoles[blog.Id] = new ReadOnlyCollection<string>(allRightInstances[i]._rolesWithRight[blog.Id]); } } if (!rightsByRole.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) { // touch RightsByRole to make sure data for current blog instance is loaded // in the static rightsByRole. var rr = RightsByRole; } } private List<string> RolesWithRight { get { return _rolesWithRight[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id]; } } private ReadOnlyCollection<string> ReadOnlyRoles { get { return _readOnlyRoles[Blog.CurrentInstance.Id]; } } private static Dictionary<string, HashSet<Right>> RightsByRole { get { Blog blog = Blog.CurrentInstance; if (!rightsByRole.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) { lock (staticLockObj) { if (!rightsByRole.ContainsKey(blog.Id)) { rightsByRole[blog.Id] = new Dictionary<string, HashSet<Right>>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); InitRightForBlogInstance(); } } } return rightsByRole[blog.Id]; } } private static void InitRightForBlogInstance() { // Make sure the Administrator role exists with the Role provider. if (!System.Web.Security.Roles.RoleExists(BlogConfig.AdministratorRole)) { System.Web.Security.Roles.CreateRole(BlogConfig.AdministratorRole); // if no one is in the admin role, and there is a user named "admin", add that user // to the role. if (System.Web.Security.Roles.GetUsersInRole(BlogConfig.AdministratorRole).Length == 0) { System.Web.Security.MembershipUser membershipUser = System.Web.Security.Membership.GetUser("Admin"); if (membershipUser != null) { System.Web.Security.Roles.AddUsersToRoles(new string[] { membershipUser.UserName }, new string[] { BlogConfig.AdministratorRole }); } } } // Make sure the Anonymous role exists with the Role provider. if (!System.Web.Security.Roles.RoleExists(BlogConfig.AnonymousRole)) { // Users shouldn't actually be in the anonymous role, since the role is specifically for people who aren't users. System.Web.Security.Roles.CreateRole(BlogConfig.AnonymousRole); } // Make sure the Editors role exists with the Role provider. if (!System.Web.Security.Roles.RoleExists(BlogConfig.EditorsRole)) { System.Web.Security.Roles.CreateRole(BlogConfig.EditorsRole); } var adminRole = BlogConfig.AdministratorRole; RefreshAllRights(); } // These should use attributes to set up the basic part. Perhaps DisplayNameAttribute // for getting a label key that can be translated appropriately. //public string ResourceLabelKey //{ // get // { // return _resourceLabelKey; // } //} //private readonly string _resourceLabelKey; /// <summary> /// Returns a display-friendly version of this Right's name. /// </summary> public string DisplayName { get { return Utils.FormatIdentifierForDisplay(Name); } } /// <summary> /// Returns the empty string. /// </summary> public string Description { get { return string.Empty; } } /// <summary> /// Gets the Right value for this Right instance. /// </summary> public Rights Flag { get { return _flag; } } private readonly Rights _flag; /// <summary> /// Gets the name of this right. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// /// This returns the string name of the Flag enum that this instance represents. /// /// This value should be the one that's serialized to the provider's data store as /// it's far less likely to change than the numerical value. /// /// </remarks> public string Name { get { return _name; } } private readonly string _name; /// <summary> /// Gets the Roles that currently have this Right. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// This returns a read only wrapper around the internal roles list. The Roles list is not allowed /// to be altered anywhere. Changes to the list need to go through the proper channels. /// </remarks> public IEnumerable<string> Roles { get { return ReadOnlyRoles; } } #endregion #region "Methods" /// <summary> /// Adds a role to the list of roles that have this Right. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"></param> /// <returns>True if the role doesn't already exist in the list of roles. Otherwise, false.</returns> /// <remarks> /// /// Use this method specifically to add roles to the internal list. This lets us keep track /// of what's added to it. /// /// </remarks> public bool AddRole(string roleName) { roleName = PrepareRoleName(roleName); lock (instanceLockObj) { if (!Roles.Contains(roleName, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { RolesWithRight.Add(roleName); return true; } else { return false; } } } /// <summary> /// Removes a Role from the collection of roles that allow this Right. /// </summary> /// <param name="roleName"></param> /// <returns>Returns true if the role was removed, false otherwise.</returns> /// <remarks> /// /// Use this method specifically to remove roles from the internal list. This lets us keep track /// of what's removed from it. /// /// </remarks> public bool RemoveRole(string roleName) { roleName = PrepareRoleName(roleName); if (roleName.Equals(BlogConfig.AdministratorRole, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { throw new System.Security.SecurityException("Rights can not be removed from the administrative role"); } lock (instanceLockObj) { return RolesWithRight.Remove(roleName); } } /// <summary> /// Clears all the roles in the roles list. This is only meant to be used during the static RefreshAllRoles method. /// </summary> private void ClearRoles() { lock (instanceLockObj) { RolesWithRight.Clear(); } } #endregion #endregion } }
2.权限的验证
在BlogEngine.Net中,封装了一个Security类,用于在仓库中验证。(代码没有贴全,源码在文章最下方)

public partial class Security : IHttpModule { //........ public static IEnumerable<Right> CurrentUserRights() { return Right.GetRights(Security.GetCurrentUserRoles()); } //验证当前用户是否拥有权限 public static bool IsAuthorizedTo(AuthorizationCheck authCheck, IEnumerable<Rights> rights) { //.... } //.... }
然后在仓库中进行验证。诸如此类。
public RoleItem FindById(string id) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(BlogEngine.Core.Rights.ViewRoles)) throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); //... }
那在MVC中,可以用Filter.

public class RightsAuthorizeAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute { public Rights ValidRights { get; set; } public RightsAuthorizeAttribute(Rights rights) { ValidRights = rights; } public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(ValidRights)) { filterContext.Result = new RedirectResult("~/Unauthorized.html"); } } }
放在指定的Action上面,没有权限的人访问就会跳转到指示页面。
[RightsAuthorize(Rights.EditProduct)] public ViewResult Edit(string name) { var file = _repository.Products.FirstOrDefault(n => n.Name == name); return View(file); }
3.权限存取。
权限是依附于角色而存在的,BlogEngine定义了Group和Permission两个视图模型。Group表示一个角色拥有哪些权限。Permission表示的就是权限名(在UI上不是直接用Right类)。

public class Group { /// <summary> /// Empty constructor needed for serialization /// </summary> public Group() { } /// <summary> /// Constractor /// </summary> /// <param name="title">Role title</param> public Group(string title) { Title = title; if (Permissions == null) Permissions = new List<Permission>(); } /// <summary> /// Role title /// </summary> public string Title { get; set; } /// <summary> /// List of rights /// </summary> public List<Permission> Permissions { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// Permission /// </summary> public class Permission { /// <summary> /// Right Id /// </summary> public string Id { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Title /// </summary> public string Title { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Checked if right allowed for the role /// </summary> public bool IsChecked { get; set; } }
在 RolesRepository中进行转换。BlogEngine的数据存储也是基于Provider模式,默认是xml格式存储。

public bool SaveRights(List<Data.Models.Group> rights, string id) { if (!Security.IsAuthorizedTo(Rights.EditRoles)) { throw new System.UnauthorizedAccessException(); } else if (Utils.StringIsNullOrWhitespace(id)) { throw new ApplicationException("Invalid role name"); } else if (rights == null) { throw new ApplicationException("Rights can not be null"); } else { var rightsCollection = new Dictionary<string, bool>(); foreach (var g in rights) { foreach (var r in g.Permissions) { if (r.IsChecked) { rightsCollection.Add(r.Id, r.IsChecked); } } } foreach (var right in Right.GetAllRights()) { if (right.Flag != Rights.None) { if (rightsCollection.ContainsKey(right.Name)) { right.AddRole(id); } else { right.RemoveRole(id); } } } BlogEngine.Core.Providers.BlogService.SaveRights(); return true; } }
配置界面:
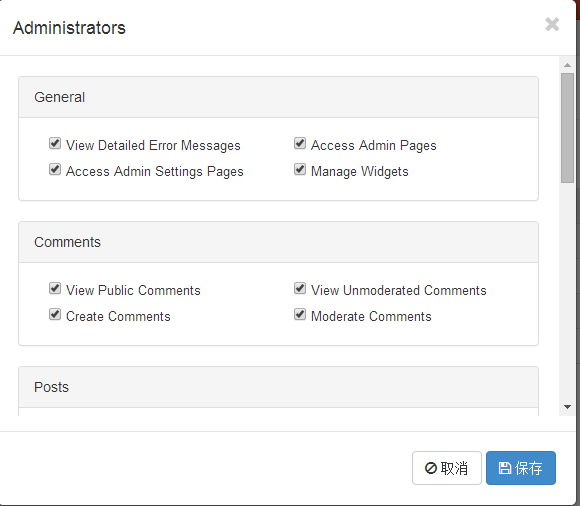
保存成xml后的格式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="yes"?> <rights> <right name="None" /> <right name="ViewDetailedErrorMessages"> <role name="Administrators" /> </right> <right name="AccessAdminPages"> <role name="Administrators" /> <role name="Editors" /> </right> .... </rights>
结构图大致如下:如果我们使用默认的MembershipProvider和RoleProvider,也可以这样加入我们的权限管理。
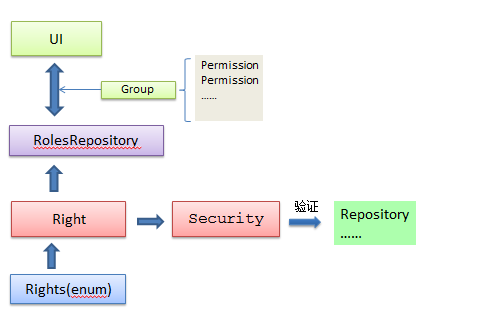
小结:文章有点长了,花了不少时间。这只是对知识的一个梳理,并不是要推荐用这种方式做权限管理,分享一下BlogEngine实现的方式。所以园友们各取所需。希望对你有帮助。tsk!
BlogEngine.Net源码:http://blogengine.codeplex.com/downloads/get/772826
