0. NioEventLoop简介
NioEventLoop如同它的名字,它是一个无限循环(Loop),在循环中不断处理接收到的事件(Event)
在Reactor模型中,NioEventLoop就是Worker的角色,关联于多个Channel,监听这些Channel上的read/write事件,一旦有事件发生,就做出相应的处理
1. NioEventLoop类图
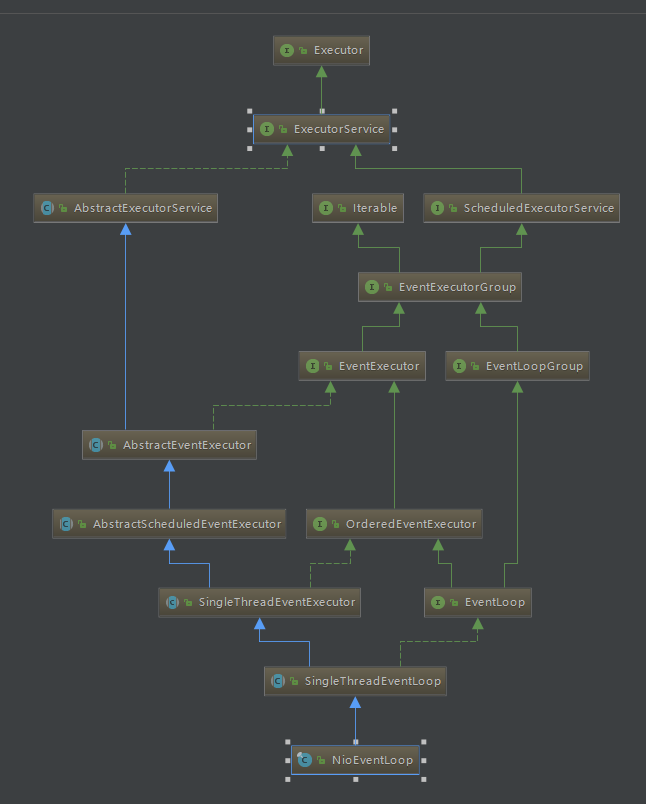
继承关系可以说是相当复杂了,我们慢慢分析
2. NioEventLoop的构造方法
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider, SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) { super(parent, executor, false, DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS, rejectedExecutionHandler); if (selectorProvider == null) { throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider"); } if (strategy == null) { throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy"); } provider = selectorProvider; final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector(); selector = selectorTuple.selector; unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector; selectStrategy = strategy; } private SelectorTuple openSelector() { final Selector unwrappedSelector; try { unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();//利用JDK提供的SelectorProvider直接创建一个Selector } catch (IOException e) { throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e); } if (DISABLE_KEYSET_OPTIMIZATION) {//如果没有开启KEYSET优化,将上面的那个Selector直接返回 return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector); } final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();//创建一个专门存放SelectionKey的Set对象 Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { try {//用反射的方式创建一个SelectorImpl对象 return Class.forName( "sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl", false, PlatformDependent.getSystemClassLoader()); } catch (Throwable cause) { return cause; } } }); if (!(maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Class) || // ensure the current selector implementation is what we can instrument. !((Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass).isAssignableFrom(unwrappedSelector.getClass())) { if (maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Throwable) { Throwable t = (Throwable) maybeSelectorImplClass; logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, t); } return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector); } final Class<?> selectorImplClass = (Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass; Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { try { Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys"); Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys"); Throwable cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(selectedKeysField); if (cause != null) { return cause; } cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(publicSelectedKeysField); if (cause != null) { return cause; } selectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);//强制将SelectorImpl中的selectedKeys域替换为优化版的SelectedSelectionKeySet对象 publicSelectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);//强制将SelectorImpl中的publicSelectedKeys域替换为优化版的SelectedSelectionKeySet对象 return null; } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { return e; } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { return e; } } }); if (maybeException instanceof Exception) { selectedKeys = null; Exception e = (Exception) maybeException; logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, e); return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector); } selectedKeys = selectedKeySet; logger.trace("instrumented a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector); return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector, new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet)); }
构造方法的主要作用是创建了一个SelectorImpl对象,如果没有设置DISABLE_KEYSET_OPTIMIZATION属性,SelectorImpl中类型为Set<SelectionKey>的selectedKeys与publicSelectedKeys域会被替换为一个SelectedSelectionKeySet对象。
为什么搞得这么麻烦呢?因为默认的域是Set类型,插入元素的开销是o(log n),而优化版的SelectedSelectionKeySet继承了AbstractSet,具有Set的功能,但是内部是用数组实现,只具有add功能,而且其开销为o(1)。
3. NioEventLoop.run()
run方法是NioEventLoop的核心,此方法会在无限循环中监听关联的Channel上是否有新事件产生
@Override protected void run() { for (;;) {//无限循环 try { switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {//如果任务队列中有任务,调用selectNow()方法,如果没有,则直接返回SelectStrategy.SELECT case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE://没搞懂这个分支的目的是什么,全局搜了一下SelectStrategy.CONTINUE,没发现有赋这个值的地方 continue; case SelectStrategy.SELECT: select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));//调用select()方法,尝试从关联的channel里读取IO事件。需要注意的是这个select方法相当复杂,因为它悄悄的解决了老版本的JDK的select方法存在的bug,有兴趣的可以仔细分析一下相关源码 if (wakenUp.get()) { selector.wakeup(); } default: } cancelledKeys = 0; needsToSelectAgain = false; final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;//ioRatio代表EventLoop会花多少时间在IO事件上 if (ioRatio == 100) { try { processSelectedKeys();//处理IO事件 } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. runAllTasks();//处理CPU事件 } } else { final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); try { processSelectedKeys();//处理IO事件 } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;//本次循环处理IO事件的耗时 runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);//分给CPU事件的耗时 } } } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } // Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception. try { if (isShuttingDown()) { closeAll(); if (confirmShutdown()) { return; } } } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } } } private void processSelectedKeys() { if (selectedKeys != null) { processSelectedKeysOptimized();//处理IO事件。由于这里采用的是优化版的SelectorImpl,IO事件已经被写在selectedKeys属性里了,所以无需额外传参 } else { processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());//未优化版的SelectorImpl,需要调用selectedKeys()方法才能获取准备好的IO事件 } } private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() { for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {//遍历已经准备好的IO事件 final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i]; // null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363 selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;//手动将数组元素赋为null,以帮助gc(因为在系统压力大的时候,SelectionKey数组靠后的部分会被占用,如果不手动将用过的元素设置为null,那么在系统压力小的时候,这些元素是不会被释放的,也就是内存泄漏了) final Object a = k.attachment();//附件是这个事件所关联的Channel,后续的代码会直接从这个Channel上读取数据 if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);//处理某个IO事件 } else { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a; processSelectedKey(k, task); } if (needsToSelectAgain) { // null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363 selectedKeys.reset(i + 1); selectAgain(); i = -1; } } } private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) { final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe(); if (!k.isValid()) { final EventLoop eventLoop; try { eventLoop = ch.eventLoop(); } catch (Throwable ignored) { // If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this // because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority // to close ch. return; } // Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop // and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is // still healthy and should not be closed. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125 if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) { return; } // close the channel if the key is not valid anymore unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); return; } try { int readyOps = k.readyOps();//获取事件的类型 // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {//不太理解这段代码的原因 // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924 int ops = k.interestOps(); ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; k.interestOps(ops); unsafe.finishConnect(); } // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {//如果是可写事件,则flush缓存 // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write ch.unsafe().forceFlush(); } // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead // to a spin loop if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {//如果是可写事件,则调用unsafe.read()方法 unsafe.read();//此处的unsafe为NioSocketChannel.NioSocketChannelUnsafe } } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) { unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } }
代码很长,大概逻辑如下:
a. 在无限循环中调用Selector.select方法
b. 使用ioRatio控制IO事件与CPU事件的耗时比例(ioRatio的默认值为50)
c. 如果有IO事件发生,遍历所有IO事件并调用processSelectedKey方法
d. 在processSelectedKey中,如果发现事件是READ/ACCEPT类型,则调用NioSocketChannel.NioSocketChannelUnsafe.read()方法对事件进行处理。其实际实现位于AbstractNioByteChannel中:
@Override public final void read() { final ChannelConfig config = config(); final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();//获取用户注册的pipeline final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();//默认值为PooledByteBufAllocator,也就是申请direct memory final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle(); allocHandle.reset(config); ByteBuf byteBuf = null; boolean close = false; try { do { byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);//开辟一块内存作为buffer allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));//doReadBytes方法会从绑定的Channel里读取数据到buffer里。顺便记录一下本次读了多少字节的数据出来 if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) { // nothing was read. release the buffer. byteBuf.release(); byteBuf = null; close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0; break; } allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);//计数 readPending = false; pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);//触发pipeline的channelRead事件 byteBuf = null; } while (allocHandle.continueReading()); allocHandle.readComplete(); pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();//触发pipeline的channelReadComplete事件 if (close) { closeOnRead(pipeline); } } catch (Throwable t) { handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle); } finally { // Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet. // This could be for two reasons: // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254 if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) { removeReadOp(); } } } }
这段代码主要做了两件事情:
a. 在循环中将Channel可读的数据读到一个临时的ByteBuf中
b. 调用pipeline.fireChannelRead方法,处理读取到数据。(具体的处理逻辑在后续文章中阐述)
现在我们已经基本搞清楚NioEventLoop的工作逻辑了:
在无限循环中监听绑定的Channel上的事件,如果有ACCEPT/READ事件发生,则从Channel里读取数据,并调用关联的pipeline的fireChannelRead方法进行处理。
目前仍不清楚的地方是:NioEventLoop是如何与Channel/Pipeline绑定的?
且听后文分解。