题面
Time limit per test: 2 seconds
Memory limit per test: 256 megabytes
Description
You are given a regular polygon with 2⋅n vertices (it's convex and has equal sides and equal angles) and all its sides have length 1. Let's name it as 2n-gon.
Your task is to find the square of the minimum size such that you can embed 2n-gon in the square. Embedding 2n-gon in the square means that you need to place 2n-gon in the square in such way that each point which lies inside or on a border of 2n-gon should also lie inside or on a border of the square.
You can rotate 2n-gon and/or the square.
Input
The first line contains a single integer T (1≤T≤200) — the number of test cases.
Next T lines contain descriptions of test cases — one per line. Each line contains single odd integer n (3≤n≤199). Don't forget you need to embed 2n-gon, not an n-gon.
Output
Print T real numbers — one per test case. For each test case, print the minimum length of a side of the square 2n-gon can be embedded in. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10^−6^.
Example
input
3
3
5
199
output
1.931851653
3.196226611
126.687663595
题意
给定一个边长为 1 的正 2n 边形
求外接正方形的最小面积
解题思路
因为本题给定的 n 是奇数
又因为外接正方形要求面积最小
所以不会有边与正方形重合,只存在四个点会位于外接正方形的四条边上
以正十边形为例
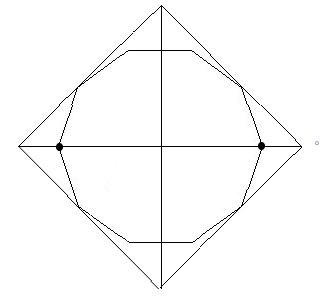
外接正方形的作图方法为
选择一对 连线能够通过正十边形中心点 的点对,连接两点,并向两端延长
然后从正十边形中心点开始作垂直于前面那条边的边,并向两端延长
然后以这两条线为准作一个斜45°正方形
为将正方形缩小到最小,所以要保证正十边形上有点会落在正方形上
故作出来的图如上图所示
具体作图法放在了文章末尾
只看其四分之一部分
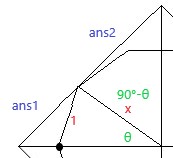
首先可以通过 360°/(2*n) 来求出每份角的角度 ang
因为边长为 1 ,所以可以通过一个顶角为 ang ,底边为 1 的等腰三角形来求出腰长 x = 0.5/sin(ang/2)
因为总共有 10 个角,所以在四分之一图中平均有 10/4 = 2.5个角
因为这些正多边形都是凸多边形,所以与正方形的交点一定是最接近于中间位置的那个点 (文章末尾也会解释这一点)
所以实际的 θ = round(2.5/2)*ang
公式里表示为 ang2 = round(n/4)*ang
对于ans1,根据正弦定理
可以得到 ans1 / sinθ = x / sin45°
得到 ans1 = x / sin45° * sinθ
对于ans2,根据正弦定理
可以得到 ans2 / sin(90°-θ) = x / sin45°
得到 ans2 = x / sin45° * sin(90°-θ)
相加即为正方形边长
完整程序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const double epsilon=PI/180.0; //角度转弧度
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
double ang=180.0/n;
double ang2=round(n/4.0)*ang;
double x=1.0/(2.0*sin(ang/2.0*epsilon));
double ans1=x/sin(45.0*epsilon)*sin(ang2*epsilon);
double ans2=x/sin(45.0*epsilon)*sin((90.0-ang2)*epsilon);
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(9)<<ans1+ans2<<'
';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int T;cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
关于作图 - 最优作图法的证明
主要参考了 《正四边形内接正六边形》 才获得灵感
在不计数值的情况下,可以将正多边形外接最小正四边形转成正四边形内接最大正多边形的画法
因为正多边形一定保证所有边都位于一个圆心即正多边形中心的圆上
所以可以从作最大可能的圆入手
以正六边形为例
先画出一个正方形,连接对角线找出中点
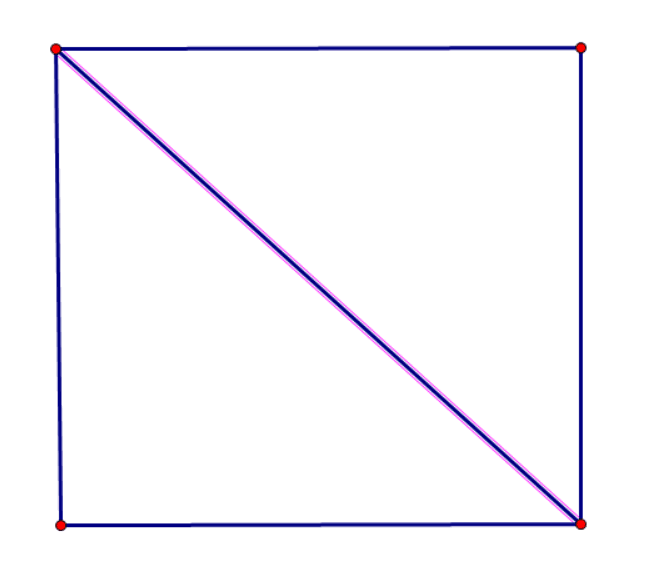
再选择其中一条对角线,每次绕中点旋转正多边形的单位角 θ ,旋转半圈
由于是正六边形,故将 360° 平分 6 份,每份 60°
所以每次旋转 60°,画图
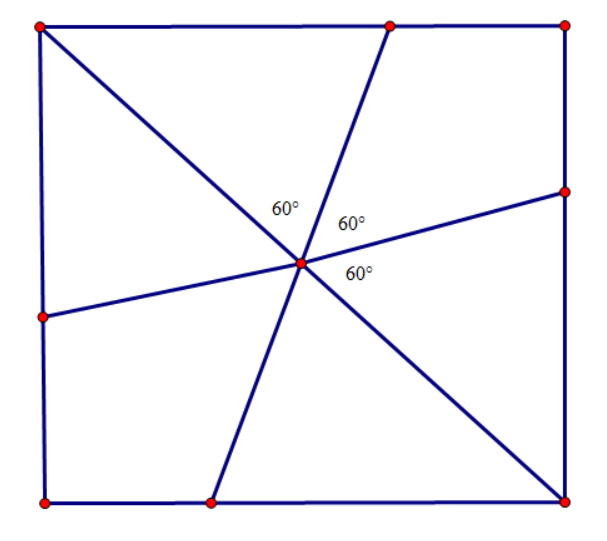
此时可以发现,加上对角线后得到的三条线
恰好与正方形交于 6 个点
故内接最大正六边形每个顶点都会落于这三条边上
为了使得内接正六边形最大,又因为正多边形每个顶点都会落在一个圆上
所以需要画出最大可能的圆
所以在画出的六个顶点中找出离中点最近的一个点
并以中点为圆心,中点到这个点的距离为半径画圆
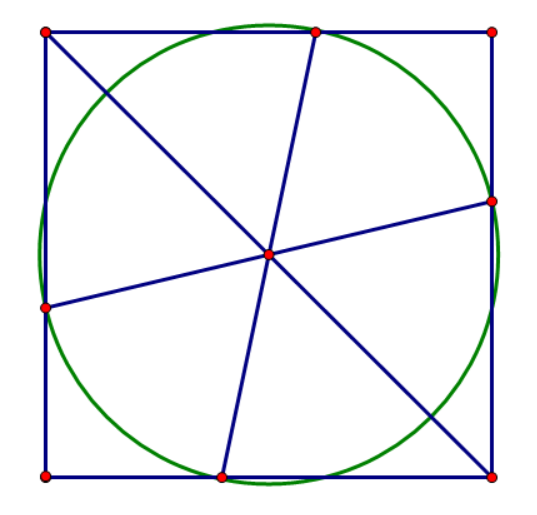
这个圆也许会超出正方形的边界,但可以保证正多边形在正方形内(因为选择的是离中点最近的点,所以与每条边的交点都在正方形内或正方形边界上)
最后,这个圆交三条线与六个点,连接后即获得内接最大正六边形
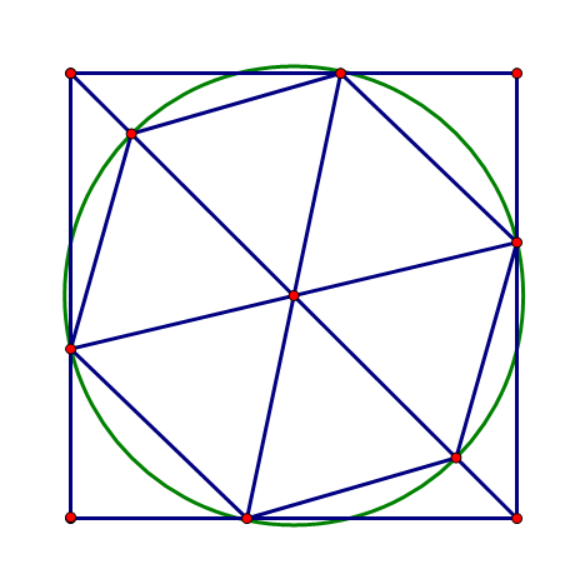
所以在思路部分(将上图旋转45°)
需要选取四分之一图中最接近中心的点来算得 ang2
也就是 round(n/4.0)*ang 的由来
这是因为距离正方形中心最近的点一定也距离正方形的边的中点最近