html5中,在新增加和废除很多元素的同时,也增加和废除了很多属性。
一、新增属性
1、表单属性
a、autofocus
对input[所有类型]、select、textarea与button指定autofocus属性。它以指定属性的方式让元素在页面加载后自动获得焦点。一个页面只能有一个元素有autofocus属性,同时设置多个,则第一个生效。
这个属性对登录页面很有用,可提升用户体验,有时登录页面就一个用户名,密码,页面加载后用户要手动定位到输入框,才能输入,有了autofocus,页面打开即可直接输入。
举例:
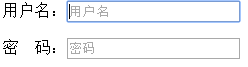
<form> <p>用户名:<input type="text" autofocus /></p> <p>密 码:<input type="password"/></p> </form>

b、placeholder
对input[text, search, url, telephone, email 以及 password]、textarea指定placeholder属性,它会对用户的输入进行提示,提示用户期待什么样的输入。
当输入框获取焦点时,提示字符消失。
这个属性也能提升用户体验,用的已经相当普遍了。
举例:

<form> <p>用户名:<input type="text" autofocus placeholder="用户名"/></p> <p>密 码:<input type="password" placeholder="密码"/></p> </form>
c、form属性
对input[所有类型]、output、select、textarea、button与fieldset指定form属性。它声明属于哪个表单,然后将其放置在页面的任何位置,都在表单之内。这个属性解放了form表单里的元素,给我们在复杂的布局时带来方便。
Note:
一个输入域可以属于一个或多个表单,多个表单用空格分隔开。
输入域的form属性必须引用所属表单的id,这点有点像<label>标签的for属性。
举例:
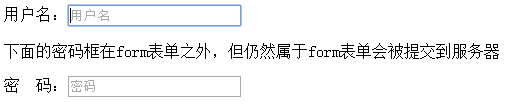
<form action="" method="" id="user_form"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" autofocus placeholder="用户名"/></p> </form> <p>下面的密码框在form表单之外,但仍然属于form表单会被提交到服务器</p> <p>密 码:<input type="password" placeholder="密码" form="user_form"/></p>
d、required属性
该属性表示用户提交时检查该元素输入域不能为空。
适用于以下类型的 input[text, search, url, telephone, email, password, date pickers, number, checkbox, radio, file]。
举例:
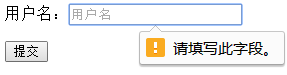
<form action="" method="" id="user_form"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" autofocus placeholder="用户名" required/></p> <p><input type="submit" value="提交"/></p> </form>
e、autocomplete属性。
autocomplete:适用于form,input[text,search,url,telephone,email,password,datepickers,range,color]。
设置"autocomplete"属性为"on",则用户在自动完成域输入时,浏览器会在该域内显示填写的选项。
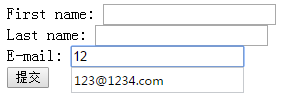
<form action="" method="get" autocomplete="on"> First name: <input type="text" name="fname" /><br /> Last name: <input type="text" name="lname" /><br /> E-mail: <input type="email" name="email"autocomplete="on"/><br /> <input type="submit" /> </form>
f、重置表单默认行为的新属性
html5中表单的自由度非常高,因为html5为input[submit,image]、button元素增加formaction、formenctype、formmethod、formnovalidate与formtarget几个新属性,能对form元素的某些属性重置,比如能做到表单1的提交按钮提交表单2等。
formaction:重写表单action属性
formenctype:重写表单enctype属性
formmethod:重写表单method属性
formnovalidate:重写表单novalidate属性
formtarget:重写表单target属性
举例:formaction和formmethod
html中,一个表单内的所有元素都通过表单的action属性统一提交到另一个页面。html5中可通过formaction属性实现点击不同提交按钮,将表单提交到不同的页面。
html中一个表单只有一个action属性来对表单内所有元素统一指定提交页面,每个表单只有一个method属性统一指定提交方法。html5中新增的formmethod方法,可以实现不同按钮指定不同提交方法,比如post,get等。
<form action="server.jsp" method="get" id="user_form"> E-mail: <input type="email" name="useremail" /><br /> <input type="submit" formmethod="get" formaction="s1.jsp" value="get方法提交到s1.jsp" /><br /> <input type="submit" formmethod="post" formaction="s2.jsp" value="post方法提交到s2.jsp" /><br /> </form>
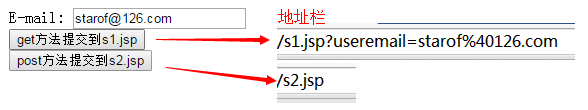
点"get方法提交到s1.jsp"按钮,将表单以get方法提交到s1.jsp页面,从url也可以看出地址栏显示提交参数。
点"post方法提交到s2.jsp"按钮,将表单以post方法提交到s2.jsp页面。
举例:formnovalidate属性,可以取消提交时进行的有关检查,表单可以被无条件地提交[哪怕form里有required,min,max等]。
<form action="demo_form.jsp" method="get" id="user_form"> E-mail: <input type="email" required name="useremail" /><br /> <input type="submit" formnovalidate="true" value="Submit without validation" /> </form>
点击“Submit without validation”按钮时,Form 不会做任何校验,虽然有required属性,表单空仍然可以提交。
g、image提交按钮新增width,height属性
width和height来设置image类型的input标签的图像的宽高。
举例:用 来作为提交按钮,通过width和height设置其宽高。
来作为提交按钮,通过width和height设置其宽高。
<form action="server.jsp" method="get" id="user_form"> E-mail: <input type="email" name="useremail" /><br /> <input type="image" src="img/submit.png" width="30px" height="30px"/> </form>

h、list属性
list属性与 datalist标签配合使用,用来规定输入域的datalist。datalist是输入域的选项列表,该元素类似<select>,但是比select更好的一点在,当用户要设定的值不在选择列表内时,允许自行输入,该元素本身不显示,当文本框获得焦点时以提示输入的方式显示。
list属性适用于input[text,search,url,telephone,email,datepickers,numbers,range,color]
Note:
list值为文档中的 datalist 的 id,又看到了熟悉的id,回想一下form属性引用的是表单的id,都类似label属性引用input的id一样。
举例:
<form action="demo_form.jsp" method="get"> 主页:<input type="url" list="url_list" name="link" /> <datalist id="url_list"> <option label="baidu" value="http://www.baidu.com" /> <option label="qq" value="http://www.qq.com" /> <option label="Microsoft" value="http://www.microsoft.com" /> </datalist> <input type="submit" /> </form>
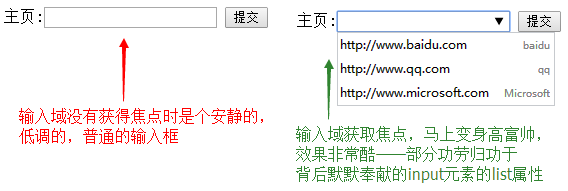
举例:顺便说一下datalist和autocomplete配合使用
前面讲了autocomplete属性可以让用户完成域输入时,浏览器在该域内显示填写的选项。现在datalist元素与autocomplete属性配合使用可更好的提升用户体验。
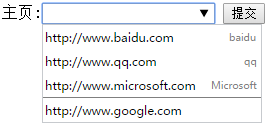
在上面代码基础上给datalist增加autocomplete属性,即<datalist id="url_list" autocomplete>。
用户第一次输入http:www.google.com提交后,再次输入时会同时给出datalist的option提示和autocomplete增加的提示。
i、max,min和step属性
max,min和step属性用来为包含数字或日期的input类型规定限定或者说约束。
max属性规定输入域所允许的最大值。
min属性规定输入域允许的最小值。
step属性为输入域规定合法的数字间隔。(假如 step="3",则合法数字应该是 -3、0、3、6,以此类推)step 属性可以与 max 以及 min 属性配合使用,以创建合法值的范围。
max,min,step属性适用于input[datepickers,number,range]。
举例:
这是一个非常好的属性,之前有人问我用<input type="time">来输入时间,奈何firefox浏览器不支持怎么办。可以通过min max 模拟实现一个时间输入框,小时允许输入[0~23],分钟允许输入[0~59]。
<form action="demo_form.jsp" method="get"> <label>time小时,分钟:<input type="time" name="user_time"></label> <p>input类型time在firefox下不支持,给出模拟实现方案</p> <label><input type="number" min="0" max="23" step="1">时</label> <label><input type="number" min="0" max="59">分</label> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form>
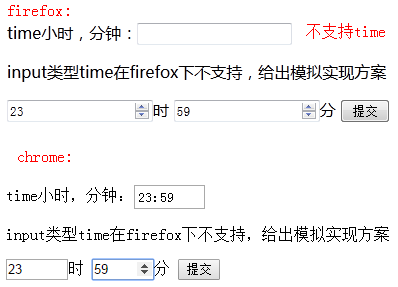
超出max提交时给出提示。

更多细节可参考HTML5 number类型文本框step属性的验证机制
j、pattern属性
pattern属性用于验证输入字段的模式,其实就是正则表达式,不用再写js绑定正则验证了,非常方便。
pattern属性适用于input[text,search,url,telephone,email,password]
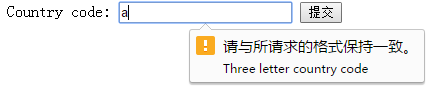
举例:给输入框定义了 Pattern 为“[A-z]{3}”,也就是包含三个字母的正则表达式约束,如果输入不合法,我们会看到如下效果。
<form action="#" method="get" id="user_form">
Country code:
<input type="text" name="country_code" pattern="[A-z]{3}"title="Three letter country code" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
k、multiple属性
multiple属性规定输入域中可选择多个值。
multiple属性适用于input[email,file]。
举例:允许上传时一次上传多个文件。
<form action="demo_form.jsp" method="get"> 选择图片:<input type="file" name="img" multiple="multiple" /> <input type="submit" /> </form>

l、<fieldset>增加disabled属性
html5为 fieldset元素增加了disabled属性,可以把它的子元素设为disabled状态,但是注意不包括legend里的元素。
举例:点击legend中的checkbox,切换filed子元素的disabled状态。
<form> <fieldset name="userInfo"> <legend> <label><input type="checkbox" checked name="enableUserInfo" onchange="form.userInfo.disabled=!checked">启用用户信息</label> </legend> <p> <label>姓名:<input name="userName" required></label> </p> <fieldset name="personalInfo"> <legend> <label><input type="checkbox" checked name="enablePersonalInfo" onchange="form.personalInfo.disabled=!checked">个人信息</label> </legend> <p> <label>生日:<input name="birthday" required></label> </p> </fieldset> <fieldset name="companyInfo"> <legend> <label><input type="checkbox" checked name="enableCompanyInfo" onchange="form.companyInfo.disabled=!checked">公司信息</label> </legend> <p> <label>公司名称:<input name="companyName" required></label> </p> </fieldset> </fieldset> </form>

m、<label>增加control属性
html5中为标签新增了control属性,在标签内部放置一个表单元素,通过标签的control属性访问该表单元素。
举例:
<script> function setValue(){ var label=document.getElementById("label"); var textbox=label.control; textbox.value="718308"; } </script> <form> <label id="label"> 邮编: <input id="txt_zip" maxlength="6"> <small>请输入6位数字</small> </label> <input type="button" value="设置默认值" onclick="setValue()"> </form>

分析:通过label的control属性控制input输入框的value,所以点“设置默认值”按钮,将邮编输入框值初始化为"718308"。
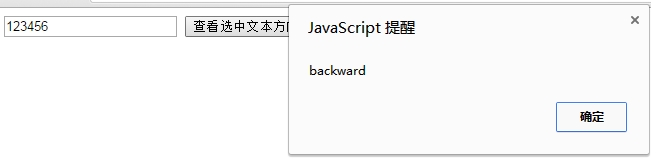
n、新增SelectionDirection属性
selectionDirection适用于input元素和textarea元素。
用户在input元素或textarea元素中用鼠标选取部分文字时,可以使用该属性来获取选取方向。当用户正向选取文字时,该属性值为"forward",反向选取值为“backward”,且当用户没有选取任何文字时,该属性值为"forward"。
举例:
<script type="text/javascript"> function alertSelectionDirection(){ var testInput=document.getElementById("test"); var direction=testInput.selectionDirection; alert(direction); } </script> <form> <input type="text" name="text" id="test"> <input type="button" value="查看选中文本方向" onclick="alertSelectionDirection()"> </form>
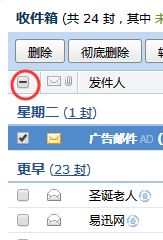
o、复选框的indeterminate属性
这个属性用来表示复选框部分选中,像qq邮箱中,邮件部分选中就有这样的效果。
举例:经测试,貌似还是必须通过脚本控制indetermidate属性。
<form> <input type="checkbox" checked/> <input type="checkbox" indeterminate/>只写一个indeterminate不起作用 <input type="checkbox" id="test"/> <input type="checkbox" /> </form> <script> document.getElementById('test').indeterminate = true; </script>

indeterminate属性主要是在复选框嵌套时使用,了解更多可参考css-tricks indetermidate-checkboxes
2、链接属性
a、media属性
为a、area增加media属性。规定目标 URL 是为哪种类型的媒介/设备进行优化的,只能在href属性存在时使用。该属性用于规定目标 URL 是为特殊设备(比如 iPhone)、语音或打印媒介设计的,可接受多个值。
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" media="print and (resolution:300dpi)" >查询</a>
取值如下:【没懂这个media到底有什么样的优化措施】

运算符:[and]and运算符,[not]not运算符,[,]or运算符。
设备:
all:默认,适合所有设备。
aural:语音合成器
braille:盲文反馈装置
handheld:手持设备(小屏幕,有限的带宽)
projection:投影机
print:打印预览模式/打印页面
screen:计算机屏幕
tty:电传打字机以及使用等宽字符网格的类似媒介
tv:电视类型设备(低分辨率,有限的分页能力)
值:
规定目标显示区域的宽度,可使用"min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (min-500px)"
height:同width,用来设置高度。
device-规定目标显示器/纸张的宽度。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (device-500px)"
device-height:同device-height,用来设置高度。
orientation:英文意思"方向",用来规定目标显示器/纸张的取向。可能的值:"portrait" 或 "landscape"。例:media="all and(orientation: landscape)"
aspect-ratio:规定目标显示区域的宽高比。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (aspect-ratio:16/9)"
device-aspect-ratio:规定目标显示器/纸张的 device-width/device-height 比率。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (aspect-ratio:16/9)"
color:规定目标显示器的 bits per color。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (color:3)"
color-index:规定目标显示器能够处理的颜色数。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (min-color-index:256)"
monochrome:规定在单色帧缓冲中的每像素比特。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="screen and (monochrome:2)"
resolution:规定目标显示器/纸张的像素密度 (dpi or dpcm)。可使用 "min-" 和 "max-" 前缀。例:media="print and (resolution:300dpi)"
scan:规定 tv 显示器的扫描方法。可能的值是:"progressive" 和 "interlace"。例:media="tv and (scan:interlace)"
grid:规定输出设备是网格还是位图。可能的值:"1" 代表网格,"0" 是其他。例:media="handheld and (grid:1)"
更多可参考w3c media
b、<area>新增herflang、media、rel、type属性
herflang,media,rel,type为了保证a元素和link元素的一致性。
hreflang【取值language_code】规定在被链接文档中的文本的语言。只有当设置了 href 属性时,才能使用该属性。注释:该属性是纯咨询性的。
media【取值media query】:对何种设备优化。【具体怎么优化?】
举例:
<a media="handheld" href="#">手持设备</a> <a media="tv" href="#">电视</a>
rel 【取值alternate, author, bookmark, external, help, license, next, nofollow, noreferrer, prefetch, prev, search, sidebar, tag】规定当前文档与被链接文档/资源之间的关系。只有当使用 href 属性时,才能使用 rel 属性。
举例:
<a href=http://www.mukewang.com/" hreflang="zh" rel="external">
表示超链接使用的是中文,并且这个超链接是个外部的超链接。
type【mime_type】规定目标 URL 的 MIME 类型。
c、<link>新增sizes属性
为link增加sizes属性。sizes 属性规定被链接资源的尺寸。只有当被链接资源是图标时 (rel="icon"),才能使用该属性。该属性可接受多个值。值由空格分隔。
网上千篇一律都是这样写的:
<link rel="icon" href="img/demo_icon.ico" type="image/gif" sizes="16x16" />
但是经过测试用不用sizes都一样,没看出sizes有什么作用。查了一下目前几乎没有主流浏览器支持 sizes 属性。
d、<base>新增target属性
为base元素增加target属性,主要是保持与a元素的一致性。
举例:target表示页面中超链接都将使用_blank在新窗口中打开页面,且加上http://localhost地址,后面相当于相对地址。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>base element target</title> <base href="http://localhost/ " target="_blank"> </head> <body> <a href="a.html" >a.html页面</a> </body> </html>
点a.html页面将在新窗口中打开链接:http://localhost/a.html
3、其他属性
a、ol新增reversed属性
reversed是个bool属性,规定有序列表倒序。
举例:有序列表起始值50,倒序。
<ol start="50" reversed> <li>coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Milk</li> </ol>

b、meta新增charset属性
为meta增加charset属性
c、menu新增type和label属性
menu在html4.01中废弃,后在html5中重新定义,为menu增加type和label属性。label为菜单定义一个菜单的标注,type属性让才当可以以上下文菜单、工具条与列表右键菜单三种形式出现。
label取值是文本,表示菜单名称。
type取值三个:
popup:浏览器不支持。
toolbar:浏览器不支持。
context:右键菜单。仅firefox支持。
可通过w3c menu元素了解更多。
举例:toolbar
<menu type="toolbar" label="menu"> <li><input type="checkbox" />red</li> <li><input type="checkbox">blue</li> </menu>
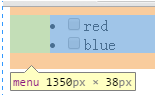
可见menu的浏览器默认样式为:
menu { display: block; list-style-type: disc; margin-top: 1em; margin-bottom: 1em; margin-left: 0; margin-right: 0; padding-left: 40px; }
举例:context
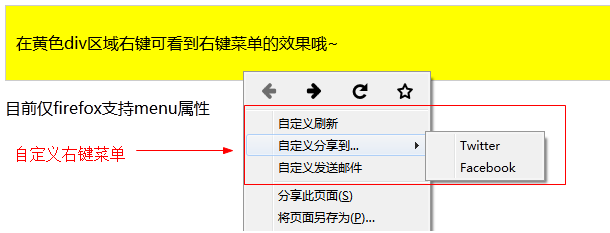
<div contextmenu="mymenu"> <p>在黄色div区域右键可看到右键菜单的效果哦~</p> <menu type="context" id="mymenu"> <menuitem label="自定义刷新" onclick="window.location.reload();" icon="ico_reload.png"></menuitem> <menu label="自定义分享到..."> <menuitem label="Twitter" icon="ico_twitter.png" onclick="window.open('//twitter.com/intent/tweet?text=' + window.location.href);"></menuitem> <menuitem label="Facebook" icon="ico_facebook.png" onclick="window.open('//facebook.com/sharer/sharer.php?u=' + window.location.href);"></menuitem> </menu> <menuitem label="自定义发送邮件" onclick="window.location='mailto:?body='+window.location.href;"></menuitem> </menu> </div> <p>目前仅firefox支持menu属性</p>
d、style新增scoped属性
html5为style增加scoped属性。有了一个样式作用域的概念,它允许我们为文档的指定部分定义样式,而不是整个文档。如果使用 "scoped" 属性,那么所规定的样式只能应用到 style 元素的父元素及其子元素。 scoped为开发单页面样式带来方便,但不能常用,否则css难以维护。
举例:
<!-- 这个article正常使用head里声明的style --> <article> <h1>h1标签内容</h1> <p>p标签内容</p> </article> <article> <!-- 这里声明的style只能让该article以及子元素使用 --> <style scoped> h1,p{ color: hotpink; } article { border: solid 1px hotpink; } </style> <h1>h1标签内容,受局部作用域的样式控制</h1> <p>p标签内容,受局部作用域的样式控制</p> </article>

e、script新增async属性
html5为script新增了一个async属性,用来定义脚本是否异步执行。async仅适用于外部脚本(只有在使用src属性时)。
和async【异步执行】相近的还有一个属性defer【推迟执行】,defer属性过去也有,但在html5中进行了更好的支持。
使用:
如果 async="async":脚本相对于页面的其余部分异步地执行,因为async表示下载脚本文件,之后马上运行,运行的同时并不阻止浏览器去解析下面的内容,所以称之为异步。
如果不使用 async 且 defer="defer":脚本将在页面完成解析时执行,因为defer表示脚本下载完并不执行而是等页面全部加载完之后再执行。
如果既不使用 async 也不使用 defer:在浏览器继续解析页面之前,立即读取并执行脚本。
举例:
在jquery官网有两个jquery文件,如下。
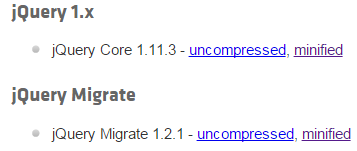
我们就拿这两个文件举例,jquery-1.11.3.min.js是 标准库文件,93.7k。jquery-migrate-1.2.1.min.js是jquery向后兼容的文件,7.03k。代码如下。
<!DOCTYPE> <meta charset="utf-8"></meta> <meta http-equiv="prama" content="no-cache"><!--禁止掉页面缓存--> <script defer src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.11.3.min.js" onload="alert('a')"></script> <script async src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-migrate-1.2.1.min.js" onload="alert('b')"></script>
运行效果,先弹出b,后弹出a。
f、html元素新增manifest属性
html5为html元素增加manifest,指向一个用于结合离线web应用API的应用程序缓存清单。开发离线web应用程序时他与API结合使用,定义一个URL,在这个URL上描述文档的缓存信息。
访问一次以后下次就是断网了也能看到以前的内容。
用法:
首先,创建mainfest文件
CACHE MANIFEST
#This is a comment
CACHE #需要缓存的文件
index.html
style.css
NETWORK: #不需要缓存的文件
search.php
login.php
FALLBACK: #资源不可用的情况下,重定向的地址
/api offline.html
然后将该mainfest文件的地址加到html属性中。
<html manifest="/offline.manifest">
详细步骤可参考:How to create offline HTML5 web apps in 5 easy steps
了解更多可参考:w3c manifests
g、iframe元素新增sandbox、seamless、srcdoc属性
为iframe增加三个属性,sandbox、seamless、srcdoc。用来提高页面安全性,防止不信任的web页面执行某些操作。
seamless:有这个属性,表示iframe框架没有边框,没有边距。
srcdoc:用来指定内嵌框架的内容,srcdoc和src属性有顺序区分,有了srcdoc,后面src的内容被忽略。
举例:
<iframe srcdoc="<h1>srcdoc出现,后面src内容被忽略</h1>" src="http://www.baidu.com"></iframe>

sandbox:是个安全沙箱。有了sandbox,内嵌框架就有了严格的安全限制,禁止提交表单,禁止运行js脚本,且内嵌页面和外面页面不同源。等。
当然可以通过给sandbox设置来取消限制。可选值:
"":应用以下所有限制。
allow-scripts:运行运行JavaScript。
allow-same-origin:允许iframe内容被视为与包含文档有相同的源。
allow-top-navigation:允许iframe内容从包含文档导航(加载)内容。
allow-forms:运行提交表单。
二、删除属性
删除了一些可以用css代替的属性,多余属性和其他属性。
|
在HTML 4中使用的属性 |
使用该属性的元素 |
在HTML 5中的替代方案 |
|
rev |
link、a |
rel |
|
charset |
link、a |
在被链接的资源的中使用HTTP Content-type头元素 |
|
shape、coords |
a |
使用area元素代替a元素 |
|
longdesc |
img、iframe |
使用a元素链接到校长描述 |
|
target |
link |
多余属性,被省略 |
|
nohref |
area |
多余属性,被省略 |
|
profile |
head |
多余属性,被省略 |
|
version |
html |
多余属性,被省略 |
|
name |
img |
id |
|
scheme |
meta |
只为某个表单域使用scheme |
|
archive、chlassid、codebose、codetype、declare、standby |
object |
使用data与typc属性类调用插件。需要使用这些属性来设置参数时,使用param属性 |
|
valuetype、type |
param |
使用name与value属性,不声明之的MIME类型 |
|
axis、abbr |
td、th |
使用以明确简洁的文字开头、后跟详述文字的形式。可以对更详细内容使用title属性,来使单元格的内容变得简短 |
|
scope |
td |
在被链接的资源的中使用HTTP Content-type头元素 |
|
align |
caption、input、legend、div、h1、h2、h3、h4、h5、h6、p |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
alink、link、text、vlink、background、bgcolor |
body |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、bgcolor、border、cellpadding、cellspacing、frame、rules、width |
table |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、char、charoff、height、nowrap、valign |
tbody、thead、tfoot |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、bgcolor、char、charoff、height、nowrap、valign、width |
td、th |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、bgcolor、char、charoff、valign |
tr |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、char、charoff、valign、width |
col、colgroup |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、border、hspace、vspace |
object |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
clear |
br |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
compace、type |
ol、ul、li |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
compace |
dl |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
compace |
menu |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
width |
pre |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、hspace、vspace |
img |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、noshade、size、width |
hr |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
align、frameborder、scrolling、marginheight、marginwidth |
iframe |
使用CSS样式表替代 |
|
autosubmit |
menu |
