几个要点
- HashTable底层的数据结构基于链表(O(n))的数组;
- HashTable不允许空key和空value;
- HashMap元素非按照写入时顺序排序,而是按Key的hash取n模来排序(算法优化采用(n - 1) & hash)
- HashTable线程安全类,但它是直接在方法上使用synchronized,是利用阻塞式的内部锁(整表上锁)保证线程安全的,其并发效率低。可考虑Concurrent包,如ConcurrentHashMap;
- Hashtable和HashMap一样,都有初始容量和加载因子两个影响性能的参数,并且加载因子默认也是0.75;
- 初始容量initialCapacity是11,不要求必须是2的指数倍数,而不是HashMap的16;
- hash算法直接使用object的hashcode(键的哈希码),没有HashMap的优化(高低16位异或);
- Hashtable在初始化时就创建了数组,HashMap是懒加载;
- 定位算法是(e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length。由于HashMap中桶的个数必须是2的指数倍数,因此得到桶索引处的方法可以优化为hash & (length-1);
- Hashtable插入效率低下,每次插入都要遍历一次链表,每次都是O(n),效率比HashMap要低下,HashMap一般为直接定位则为O(1),红黑树内少量元素的O(LogN),链表内内少量元素的O(n),链表而且是低于8的;
- Hashtable读取效率也低下,每次读取都要遍历一次链表,每次都是O(n),HashMap几乎为O(1),直接定位h & (length-1),加上红黑树内的O(LogN),所以几乎为O(1);
类定义
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
属性
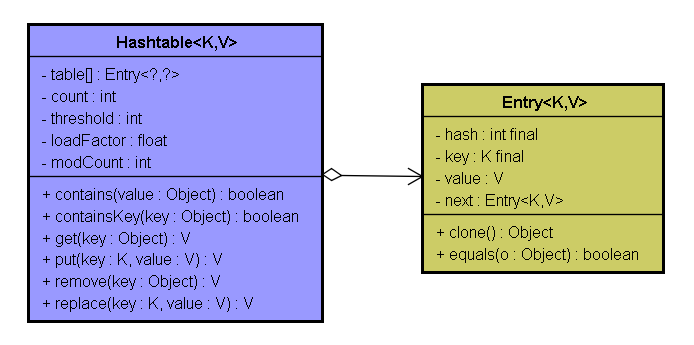
- Entry<?,?>[] table :Entry类型的数组,用于存储Hashtable中的键值对;
- int count :存储hashtable中有多少个键值对
- int threshold :当count值大于该值是,哈希表扩大容量,进行rehash()
- float loadFactor :threshold=哈希表的初始大小*loadFactor,初始容量默认为11,loadFactor值默认为0.75
- int modCount :此HashTable结构修改次数,每次添加,更新,删除元素时,这个值就加1。实现"fail-fast"机制,在并发集合中对Hashtable进行迭代操作时,若其他线程对Hashtable进行结构性的修改,迭代器会通过比较expectedModCount和modCount是否一致,如果不一致则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
构造器
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor); if (initialCapacity==0) initialCapacity = 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor; table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity]; threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); } public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, 0.75f); } public Hashtable() { this(11, 0.75f); } public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) { this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f); putAll(t); }
modCount一致性
public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable<Integer, String> tb = new Hashtable<Integer,String>(); tb.put(1, "BUPT"); tb.put(2, "PKU"); tb.put(3, "THU"); Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = tb.entrySet().iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry<?, ?>) iter.next(); //此处会抛出异常 System.out.println(entry.getValue()); if("THU".equals(entry.getValue())){ tb.remove(entry.getKey()); } } } /* 输出结果如下: THU Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.Hashtable$Enumerator.next(Hashtable.java:1367) at ali.Main.main(Main.java:16) */
ConcurrentModificationException异常,每一次修改hashtable中的数据都更新modCount的值,而迭代器Enumerator<T>的next方法会判断modCount != expectedModCount
public T next() { //首先判断modCount和expectedModCount是否相等 //由于在主程序中Hashtable对象通过tb.remove()方法修改了modCount的值,使得expectedModCount和modCount不相等而抛出异常 //解决办法就是将tb.remove()方法替换为iter.remove()方法 if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); return nextElement(); }
//该方法在remove元素的同时修改了modCount和expectedModCount的值 public void remove() { if (!iterator) throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Hashtable Enumerator"); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); synchronized(Hashtable.this) { Entry<?,?>[] tab = Hashtable.this.table; int index = (lastReturned.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; for(Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) { if (e == lastReturned) { modCount++; expectedModCount++; if (prev == null) tab[index] = e.next; else prev.next = e.next; count--; lastReturned = null; return; } } throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
主要方法
put
可以看出,每次插入都要遍历一次链表,每次都是O(n),效率比HashMap要低下,HashMap一般为红黑树内O(LogN),链表内O(n),直接定位则为1
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { //值不允许为null if (value == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; //得到键的hash int hash = key.hashCode(); //得到对应hash在数组中的桶索引 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") //得到桶中链表头节点 Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; //从头开始遍历 for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { //一旦hash值相等并且键相等,替换旧值 if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { V old = entry.value; entry.value = value; return old; } } //如果没有找到相同键,那么添加新节点 addEntry(hash, key, value, index); return null; }
addEntry
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) { modCount++; Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; //如果尺寸超过了阈值,进行rehash if (count >= threshold) { // Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded rehash(); tab = table; hash = key.hashCode(); index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; } // Creates the new entry. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); count++; }
get
public synchronized V get(Object key) { Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; //遍历所有元素,哈希值和key一致,则返回 for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { return (V)e.value; } } return null; }