(一)定义
是只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表
与栈相反,队列是先进先出(First In First Out:FIFO)的线性表、
与栈相同:队列也是一种重要的线性结构,实现一个队列同样需要顺序表或者链表来作为基础
(二)结构

(三)队列的抽象数据类型
ADT 队列(Queue)
Data
同线性表。元素具有相同的类型,相邻元素具有前驱和后继的关系。
Operation
InitQueue( *Q): 初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q
ClearQueue( *Q): 将队列清空
QueueEmpty( Q): 若队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
QueueLength( Q): 返回队列Q的元素个数
GetHead( Q, *e): 若是队列存在且非空,用e返回Q的队头元素
EnQueue( *Q, e):若是队列存在,则插入新的元素e入队为队尾
DeQueue( *Q, *e):若是队列存在且非空,进行出队操作,用e接收数据
DestroyQueue( *Q): 若是队列存在,则销毁他
endADT
(四)存储结构
队列既可以使用链表实现,也可以使用顺序表来实现。跟栈相反的是,栈一般使用顺序表来实现,而队列常使用链表来实现,简称链队列
//设置队列的数据结点
typedef struct QNode
{
ElemType data; //存放队列中的数据
struct QNode* next; //队列结点的指针域
}QNode, *QNodePtr;
//设置队列的结构体
typedef struct
{
QNodePtr front,rear; //队列头尾指针
}LinkQueue;
(五)队列的链式存储结构
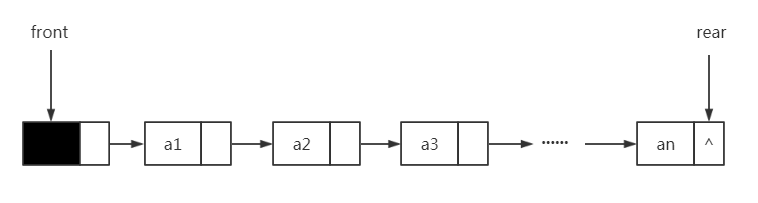
我们将个队头指针指向链队列的头结点,而队尾指针指向终端结点(注:头结点不是必须的,这里为了操作结点使用了)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
//设置队列的数据结点
typedef struct QNode
{
ElemType data; //存放队列中的数据
struct QNode* next; //队列结点的指针域
}QNode, *QNodePtr;
//设置队列的结构体
typedef struct
{
QNodePtr front,rear; //队列头尾指针
}LinkQueue;
//四个基础操作
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q); //初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q
Status ClearQueue(LinkQueue *Q);//将队列清空
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q); //若队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
int QueueLength(LinkQueue Q); //返回队列Q的元素个数
Status GetHead(LinkQueue Q, ElemType *e); //若是队列存在且非空,用e返回Q的队头元素
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType e); //若是队列存在,则插入新的元素e入队为队尾
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType *e); //若是队列存在且非空,进行出队操作,用e接收数据
Status DestroyQueue(LinkQueue *Q); //若是队列存在,则销毁他
int main()
{
LinkQueue lq;
ElemType e;
int i;
//初始化一个空的队列
InitQueue(&lq);
printf("2.EnQueue 1-5
");
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
EnQueue(&lq, i);
printf("3.DeQueue number for three times
");
for (i = 1; i <= 3;i++)
{
DeQueue(&lq, &e);
printf("DeQueue %d: %d
",i, e);
}
GetHead(lq, &e);
printf("4.Get Head:%d
",e);
printf("5.EnQueue 6-10
");
for (i = 6; i <= 10; i++)
EnQueue(&lq, i);
printf("6.Get queue length:%d
", QueueLength(lq));
printf("7.DeQueue number for six times
");
for (i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
DeQueue(&lq, &e);
printf("DeQueue %d: %d
",i, e);
}
if (!QueueEmpty(lq))
{
printf("8.Queue is not Empty
");
ClearQueue(&lq);
printf("9.Queue is Clear
");
}
printf("10.Queue Empty:%d
", QueueEmpty(lq));
printf("11.destroy Queue");
DestroyQueue(&lq);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
Q->front = Q->rear = (QNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!Q->front)
return ERROR;
Q->front->next = Q->rear->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
//将队列清空,保留头结点,注意队尾指针
Status ClearQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
QNodePtr head = Q->front->next; //获取开始结点
QNodePtr cur; //游标指针
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
while (head) //将数据全部释放
{
cur = head;
head = head->next;
free(cur);
}
Q->rear = Q->front; //将队尾指向队头
Q->rear->next = Q->front->next = NULL; //记得:重点
return OK;
}
//若队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q)
{
if (!Q.front->next)
return TRUE;
return FALSE;
}
//返回队列Q的元素个数
int QueueLength(LinkQueue Q)
{
QNodePtr head = Q.front; //获取头结点
QNodePtr end = Q.rear; //获取终端结点
int length = 0;
while (head!=end)
{
length++;
head = head->next;
}
return length;
}
//若是队列存在且非空,用e返回Q的队头元素
Status GetHead(LinkQueue Q, ElemType *e)
{
QNodePtr head;
if (!e||QueueEmpty(Q))
return ERROR;
head = Q.front->next;
*e = head->data;
return OK;
}
//注意:对于队列,我们更多关心队尾指针多余队头指针
//若是队列存在,则插入新的元素e入队为队尾,注意还要考虑队尾指针
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType e)
{
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
QNodePtr q = (QNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!q)
return ERROR;
q->data = e;
q->next = Q->rear->next;
Q->rear->next = q;
Q->rear = q;
return OK;
}
//若是队列存在且非空,进行出队操作,用e接收数据,注意还要考虑队尾指针
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType *e)
{
QNodePtr q;
if (!Q || !e || QueueEmpty(*Q))
return ERROR;
q = Q->front->next; //开始结点
*e = q->data;
Q->front->next = q->next; //指针后移(这一步注意:重点,且易错)
if (Q->rear == q) //若是我们队列中只有一个结点,删除后需要修改队尾指针
Q->rear = Q->front;
free(q); //释放结点
return OK;
}
//若是队列存在,则销毁他,包含头结点
Status DestroyQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
if (!Q)
return OK;
if (ClearQueue(Q))
{
free(Q->front);
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
return OK;
}
return ERROR;
}
(六)队列的顺序存储结构(了解思想即可)
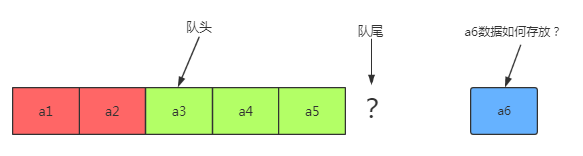
(1)顺序队列:队头指针不变

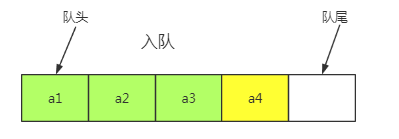
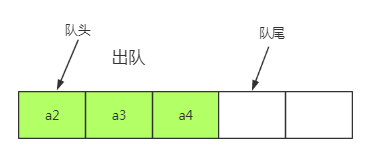
上面的顺序队列:在出队时需要移动顺序队列中所有的元素,时间复杂度O(n),需要改进
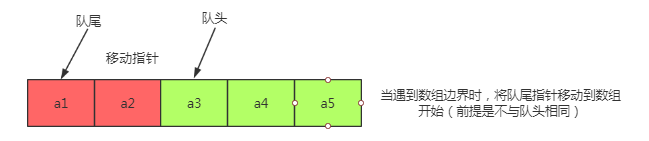
(2)顺序队列:队头指针移动



缺点:队尾指针逐渐增加,而队头也增加,那么数组的可用空间会减少。前面的红色区域会造成空间浪费。
(3) 顺序队列:循环队列
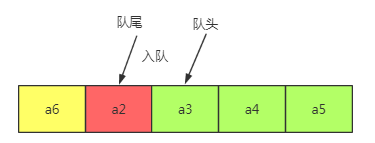
成功解决上面两种情况的缺点,不足之处是对于数组溢出没有办法
注意:和链队列相比
链队列的队尾指针是执行最后的那个元素结点。
而循环链表则是指向下一个空数组下标。(当然我们也可以执行最后一个有数据的下标)
(七)实现循环队列(可以使用堆,也可以使用数组,这里直接使用数组)
注意:考虑对于队尾在队头后面和前面两种情况下的长度,如何使用一种方法来表示?还有判断队满是否也可以使用一种方法表示?还有判断队尾,队头下标方法是否一致?
从上面的循环队列分析:
长度可以使用-->(队尾下标-队头下标+数组长度)%数组长度
判断是否队满-->(队尾下标+1)%数组长度==队头下标
判断队尾,队头下标-->(队尾下标+1)%数组长度==新的队尾下标
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 10
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
//设置队列的结构体
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MAXSIZE];
int front; //队头下标
int rear; //队尾下标,若队列不为空,指向队列元素的下一个位置
}sqQueue;
//四个基础操作
Status InitQueue(sqQueue *Q); //初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q
Status ClearQueue(sqQueue *Q);//将队列清空
Status QueueEmpty(sqQueue Q); //若队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
int QueueLength(sqQueue Q); //返回队列Q的元素个数
Status GetHead(sqQueue Q, ElemType *e); //若是队列存在且非空,用e返回Q的队头元素
Status EnQueue(sqQueue *Q, ElemType e); //若是队列存在,则插入新的元素e入队为队尾
Status DeQueue(sqQueue *Q, ElemType *e); //若是队列存在且非空,进行出队操作,用e接收数据
Status DestroyQueue(sqQueue *Q); //若是队列存在,则销毁他
int main()
{
sqQueue lq;
ElemType e;
int i;
//初始化一个空的队列
InitQueue(&lq);
printf("2.EnQueue 1-5
");
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
EnQueue(&lq, i);
printf("3.DeQueue number for three times
");
for (i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
DeQueue(&lq, &e);
printf("DeQueue %d: %d
", i, e);
}
GetHead(lq, &e);
printf("4.Get Head:%d
", e);
printf("5.EnQueue 6-10
");
for (i = 6; i <= 10; i++)
EnQueue(&lq, i);
printf("6.Get queue length:%d
", QueueLength(lq));
printf("7.DeQueue number for six times
");
for (i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
DeQueue(&lq, &e);
printf("DeQueue %d: %d
", i, e);
}
if (!QueueEmpty(lq))
{
printf("8.Queue is not Empty
");
ClearQueue(&lq);
printf("9.Queue is Clear
");
}
printf("10.Queue Empty:%d
", QueueEmpty(lq));
printf("11.destroy Queue");
DestroyQueue(&lq);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q
Status InitQueue(sqQueue *Q)
{
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
Q->front = Q->rear = 0; //都指向下标0
return OK;
}
//将队列清空,和初始化一样即可
Status ClearQueue(sqQueue *Q)
{
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
Q->front = Q->rear = 0; //都指向下标0
return OK;
}
//若队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
Status QueueEmpty(sqQueue Q)
{
if (Q.front == Q.rear) //若是队头队尾指向一致,则为空
return TRUE;
return FALSE;
}
//返回队列Q的元素个数
int QueueLength(sqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.rear - Q.front + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE;
}
//若是队列存在且非空,用e返回Q的队头元素
Status GetHead(sqQueue Q, ElemType *e)
{
if (!e || QueueEmpty(Q))
return ERROR;
*e = Q.data[Q.front];
return OK;
}
//若是队列存在,且未满,则插入新的元素e入队为队尾
Status EnQueue(sqQueue *Q, ElemType e)
{
if (!Q || (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front) //判断队满
return ERROR;
Q->data[Q->rear] = e; //为队尾赋值
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE; //将队尾下标下移
return OK;
}
//若是队列存在且非空,进行出队操作,用e接收数据
Status DeQueue(sqQueue *Q, ElemType *e)
{
if (!Q || !e || QueueEmpty(*Q))
return ERROR;
*e = Q->data[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
//若是队列存在,则销毁他(和初始化一致),要不再加一个将数据清空吧
Status DestroyQueue(sqQueue *Q)
{
if (!Q)
return ERROR;
memset(Q, 0, MAXSIZE*sizeof(ElemType));
Q->front = Q->rear = 0; //都指向下标0
return OK;
}

(八)我们为什么选用链队列
1.若只是使用顺序存储,算法的时间性能不高,尤其是对于出队列时的相关操作。
2.即便我们使用了循环队列,也会面临数组溢出的问题。
总结:
所有我们使用不需要担心队列长度的链式存储结构即可












