Subprocess模块
subprocess.run(args, *, stdin=None, input=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, shell=False, timeout=None, check=False)
>>>res2 = subprocess.run(["ls", "-l"]) # 输出结果,返回执行状态,(接收命令为列表)
>>> res2
CompletedProcess(args=['ls', '-l'], returncode=0)
# 返回结果与执行状态,(接收命令为列表)
# 屏幕输出结果,返回状态,加|时要加shell=True,表示在shell环境下执行
subprocess.run(["df", "-h","|", "grep", "hhe"], shell=True)

#执行命令,如果命令结果为0,就正常返回,否则抛异常(接收命令为列表)>>> subprocess.check_call(["ls", "-l"])
0
#接收字符串格式命令,返回元组形式,第1个元素是执行状态,第2个是命令结果
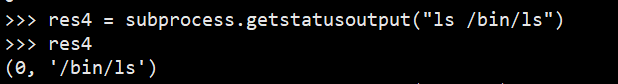
#接收字符串格式命令,并返回结果
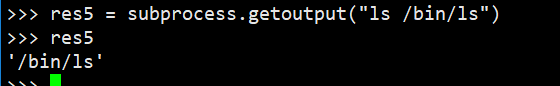
#执行命令,并返回结果,注意是返回结果

a = subprocess.call(["ls","-l"]) # 命令过程中如果出错,a会返回报错(结果输出屏幕)
>>> res1 = subprocess.call(["ls", "-l"]) # 输出结果,返回执行状态
>>> res1
0
#上面那些方法,底层都是封装的subprocess.Popen
>>> p = subprocess.Popen("df -h | grep dev", stdin=subprocess.PIPE,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
>>> p
<subprocess.Popen object at 0x7f3084fcb5c0>
>>> p.stdout.read()
b'/dev/xvda1 40G 7.9G 30G 22% /
devtmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev
tmpfs 920M 0 920M 0% /dev/shm
'
# poll()执行完成才返回状态码,否则返回空
>>> p = subprocess.Popen("sleep 10; echo hello world",shell=True)
>>>
>>> p.poll()
>>> hello world
>>> p.poll()
0
terminate() 杀掉所启动进程
poll() : Check if child process has terminated. Returns returncode
>>> p = subprocess.Popen("sleep 10; echo hello world",shell=True)
>>> p.terminate()
>>> p.poll()
-15
#communicate() 等待任务结束Popen.communicate(input=None)
与子进程进行交互。向stdin发送数据,或从stdout和stderr中读取数据。可选参数input指定发送到子进程的参数。 Communicate()返回一个元组:(stdoutdata, stderrdata)。注意:如果希望通过进程的stdin向其发送数据,在创建Popen对象的时候,参数stdin必须被设置为PIPE。同样,如 果希望从stdout和stderr获取数据,必须将stdout和stderr设置为PIPE。
>>> p = subprocess.Popen("sleep 10; echo hello world", stdin=subprocess.PIPE,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
>>>
>>> p.communicate()
(b'hello world
', b'')
>>> >>> >>>
Popen.pid
获取子进程的进程ID。
Popen.stdin
如果在创建Popen对象是,参数stdin被设置为PIPE,Popen.stdin将返回一个文件对象用于策子进程发送指令。否则返回None。
Popen.stdout
如果在创建Popen对象是,参数stdout被设置为PIPE,Popen.stdout将返回一个文件对象用于策子进程发送指令。否则返回 None。
Popen.stderr
如果在创建Popen对象是,参数stdout被设置为PIPE,Popen.stdout将返回一个文件对象用于策子进程发送指令。否则返回 None。
Popen.returncode
获取进程的返回值。如果进程还没有结束,返回None。
下面是一个非常简单的例子,来演示supprocess模块如何与一个控件台应用程序进行交 互。
import subprocess
p = subprocess.Popen(“app2.exe”, stdin = subprocess.PIPE, /
stdout = subprocess.PIPE, stderr = subprocess.PIPE, shell = False)
p.stdin.write(’3/n’)
p.stdin.write(’4/n’)
print p.stdout.read()
#—- 结果 —-
input x:
input y:
3 + 4 = 7
app2.exe也是一个非常简单的控制台程序,它从界面上接收两个数值,执行加操作,并将结 果打印到控制台上。代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char *artv[])
{
int x, y;
cout << “input x: ” << endl;
cin >> x;
cout << “input y: ” << endl;
cin >> y;
cout << x << ” + ” << y << ” = ” << x + y << endl;
return 0;
}