Problem Description
A simple mathematical formula for e is
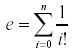
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
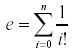
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using relatively small values of n.
Output
Output the approximations of e generated by the above formula for the values of n from 0 to 9. The beginning of your output should appear similar to that shown below.
Sample Output
n e - ----------- 0 1 1 2 2 2.5 3 2.666666667 4 2.708333333
Source
Greater New York 2000
一开始以为题目错了,怎么没有输入样例,仔细一读,哎,原来是不用输入的,直接输出就行。根据公式求n为0到9时的值,题目关键为求阶层,可以编写一个专门求阶层的函数,用来主函数调用,开一个数组用来存放n为0到9时的值,在循环赋值的时候可以利用前一次计算的结果,边计算边赋值,数组中的值赋完以后就好办了,输出。题目输出样例中发现当n从3开始保留了9位小数,因此3以后的数都是为9位小数,输出的时候需要判断一下,当n大于等于3时,控制一下输出格式。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>//控制输出格式的头文件
using namespace std;
double gcd(int n)//递归求阶层
{
double sum=1;
if(n==0||n==1) sum=1;
else
sum=gcd(n-1)*n;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
double num[10];
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
sum+=(1/gcd(i));
num[i]=sum;
}//边计算边赋值
cout<<"n"<<" "<<"e"<<endl;
cout<<"-"<<" "<<"-----------"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
if(i>=3)//别忘了判断一下
cout<<i<<" "<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<setprecision(9)<<num[i]<<endl;//9位小数
else
cout<<i<<" "<<num[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行截图:
