Step 0: Load data
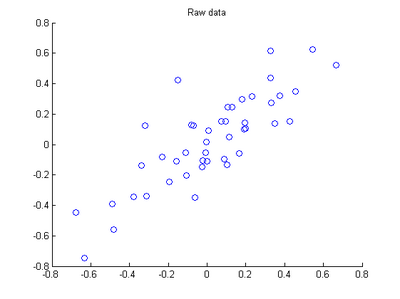
The starter code contains code to load 45 2D data points. When plotted using the scatter function, the results should look like the following:
Step 1: Implement PCA
In this step, you will implement PCA to obtain xrot, the matrix in which the data is "rotated" to the basis comprising
made up of the principal components
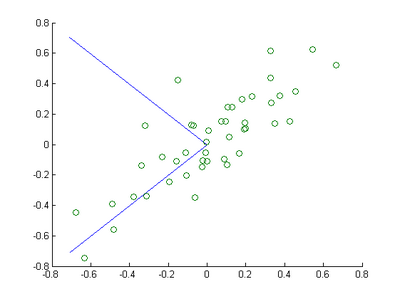
Step 1a: Finding the PCA basis
Find
and
, and draw two lines in your figure to show the resulting basis on top of the given data points.
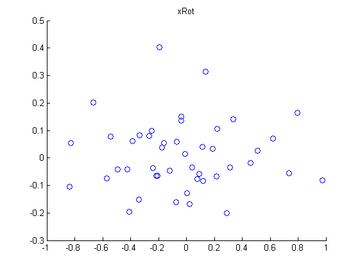
Step 1b: Check xRot
Compute xRot, and use the scatter function to check that xRot looks as it should, which should be something like the following:
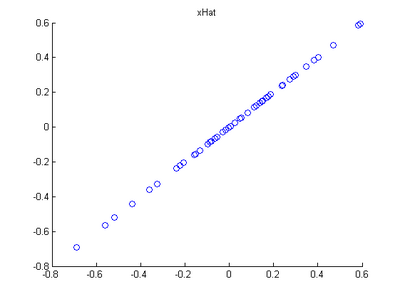
Step 2: Dimension reduce and replot
In the next step, set k, the number of components to retain, to be 1
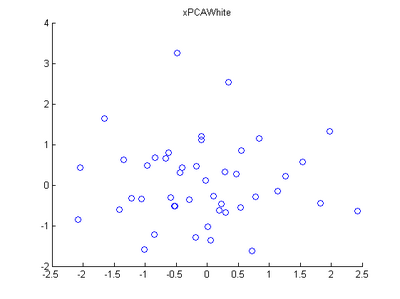
Step 3: PCA Whitening
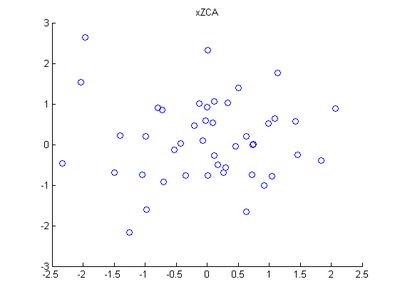
Step 4: ZCA Whitening
Code
close all %%================================================================ %% Step 0: Load data % We have provided the code to load data from pcaData.txt into x. % x is a 2 * 45 matrix, where the kth column x(:,k) corresponds to % the kth data point.Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x. % You do not need to change the code below. x = load('pcaData.txt','-ascii'); % 载入数据 figure(1); scatter(x(1, :), x(2, :)); % 用圆圈绘制出数据分布 title('Raw data'); %%================================================================ %% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain U % Implement PCA to obtain the rotation matrix U, which is the eigenbasis % sigma. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- u = zeros(size(x, 1)); % You need to compute this [n m]=size(x); % x=x-repmat(mean(x,2),1,m); %预处理,均值为零 —— 2维,每一维减去该维上的均值 sigma=(1.0/m)*x*x'; % 协方差矩阵 [u s v]=svd(sigma); % -------------------------------------------------------- hold on plot([0 u(1,1)], [0 u(2,1)]); % 画第一条线 plot([0 u(1,2)], [0 u(2,2)]); % 画第二条线 scatter(x(1, :), x(2, :)); hold off %%================================================================ %% Step 1b: Compute xRot, the projection on to the eigenbasis % Now, compute xRot by projecting the data on to the basis defined % by U. Visualize the points by performing a scatter plot. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- xRot = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this xRot=u'*x; % -------------------------------------------------------- % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the % diagonal against a blue background. figure(2); scatter(xRot(1, :), xRot(2, :)); title('xRot'); %%================================================================ %% Step 2: Reduce the number of dimensions from 2 to 1. % Compute xRot again (this time projecting to 1 dimension). % Then, compute xHat by projecting the xRot back onto the original axes % to see the effect of dimension reduction % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- k = 1; % Use k = 1 and project the data onto the first eigenbasis xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this xHat = u*([u(:,1),zeros(n,1)]'*x); % 降维 % 使特征点落在特征向量所指的方向上而不是原坐标系上 % -------------------------------------------------------- figure(3); scatter(xHat(1, :), xHat(2, :)); title('xHat'); %%================================================================ %% Step 3: PCA Whitening % Complute xPCAWhite and plot the results. epsilon = 1e-5; % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this xPCAWhite = diag(1./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % 每个特征除以对应的特征向量,以使每个特征有一致的方差 % -------------------------------------------------------- figure(4); scatter(xPCAWhite(1, :), xPCAWhite(2, :)); title('xPCAWhite'); %%================================================================ %% Step 3: ZCA Whitening % Complute xZCAWhite and plot the results. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this xZCAWhite = u*diag(1./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % -------------------------------------------------------- figure(5); scatter(xZCAWhite(1, :), xZCAWhite(2, :)); title('xZCAWhite'); %% Congratulations! When you have reached this point, you are done! % You can now move onto the next PCA exercise. :)