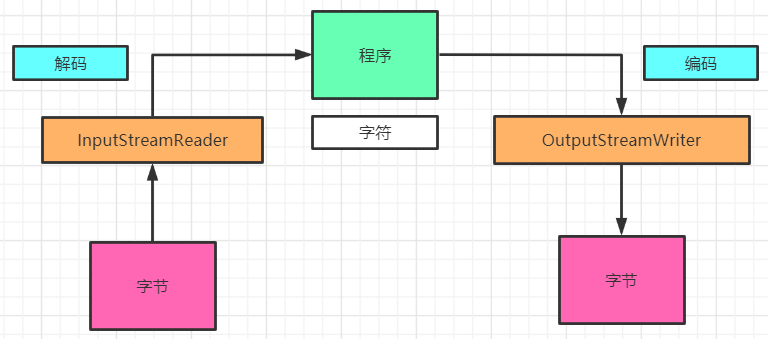
1、转换流InputStreamReader;OutputStreamWriter
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File("./txt")))); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter =new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(new File("./i.txt"))));
编码:字符串--->字节数组
解码:字节数组--->字符串
字节流的数据是字符时,转换成字符流更高效
InputStreamReader:用于将字节流解码成字符
OutputStreamWriter:将字节流中的字符按指定的字符集编码成字节
从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转换成大写输出,
然后继续进行输入操作,
直至输入e或者exit时推出程序
import java.io.*; public class Test819 { public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader bufferedReader=null; try { bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while(true){ String s=bufferedReader.readLine().toUpperCase(); if (s.equals("E")||s.equals("EXIT")){ System.out.println("退出"); return; } System.out.println(s); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try {//关闭连接,好习惯 bufferedReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
dsds
DSDS
dsds
DSDS
gtgt
GTGT
hyhy
HYHY
e
退出
************************大练习********************************************
项目4:考试管理软件 目标 •仿真实现一个基于文本界面的考试管理系统 •增量式开发,循序渐进完成项目 •建立查看使用API文档的习惯 •掌握编程技巧和调试技巧 •主要涉及以下主要知识点: –基础API –集合的存储与遍历 –I/O流基础知识 –I/O流的链接 –将散装数据合成对象 –控制台I/O 需求说明 •仿真实现基于文本界面的考试管理系统。 •应提供机上考试功能,并且能够自动判分。 •能够自动记录最后一次考试成绩。 •应尽量做到界面友好,操作方便。 •可选步骤,能够查询显示最后一次考试的答题情况和成绩。 软件设计结构 第1步 —使用基本I/O流读取文本文件 1.在IDE(例如eclipse)中创建Exam项目,在该项目下完成后续步骤。 2.编写ItemService类,提供public void readTextFile(String fileName)方法,该方法可读取参数指定的文本文件内容 (不使用包装) ,并打印输出到屏幕上; 3.Exam类的main方法中,创建ItemService对象并调用 readTextFile方法,来打印输出指定文本文件内容 第2步 —使用流的链接读取文本文件 1.改进ItemService类的readTextFile方法: public List<String> readTextFile(String filename),该方法使用流的链接,以文本行的方式读取参数指定的文本文件内容,并放置到集合中以作为该方法的返回值; 2.Exam类的main方法中,创建ItemService对象并调用 readTextFile方法,接收方法返回的List集合,在屏幕上打印集合内容。 知识点 — 将散装数据合成对象 •通常需要将文件中读取的内容封装到指定类型的对象中,以便于程序处理。 •例如:读取Teacher.txt中的数据,用来创建Teacher对象。 Teacher.txt文件内容如下: 张三 男 30 六班 第3步 —将散装数据合成对象 1.制作包含10道选择题的文本文件,选择题内容包括题目、4个选项和标准答案(均为单选); 2.定义题目Item类,属性与上述单选题对应,并提供对应的get/set方法; 3.在ItemService类中声明实例变量Item[] items;将ItemService类的readTextFile方法改为私有方法; 4.在ItemService 类中添加构造器,构造器中调用 readTextFile方法,将方法返回的字符串集合组装为 Item对象,并将所有 Item对象以数组形式保存在 items实例变量中; 5.添加getItem方法: public Item getItem(int no),该方法返回 ItemService中保存的由参数no指定的 Item对象; 6.Exam类的main方法中调用 getItem方法,接收方法返回的Item对象,在屏幕上打印对象。 第4步 —使用流的链接写入文本文件 1.在ItemService类中添加saveAnswer方法: public void saveAnswer(char[] answer),该方法创建answer.dat二进制文件,并将数组中的内容以对象形式写入到文件中保存; 提示:使用对象序列化机制 2.在Exam类的main方法中调用 saveAnswer方法,测试是否正常工作。 第5步 — 访问键盘设备 1.编写ExamView类,声明getUserAction方法:public char getUserAction(),在方法中读取键盘键入值(每次只取键入序列的第一个键值),判断键值应为a、b、c、d、n、p键(包括大小写)值之一时,将其作为方法返回值,否则忽略不计; 2.在Exam类的main方法中调用重复(循环)调用getUserAction方法,打印返回值,直到程序结束运行。 第6步 — 完善业务功能(一) 1.在ExamView类中,声明displayItem方法:public void displayItem(int no),该方法显示参数no指定的考题内容; 2.在ExamView类,声明testExam方法:public void testExam(),在方法中: –初始时,调用 displayItem显示考题第1题; –调用 getUserAction方法,判断当用户键入n时,显示下一题;当用户键入p时,显示上一题(如果当前不是第1题时); –在当前为最后一题时键入n,方法结束并返回。 3.在Exam类的main方法中调用 testExam方法,验证结果。 第7步 — 完善业务功能(二) 1.在ExamView类中,定义char[] answer属性,改进testExam方法,在原基础上: 1.调用 getUserAction方法,判断当用户键入a、b、c、d中的任意键时,将其记为当前题目的答案(记入 answer数组中); 2.在显示最后一题时键入n,方法结束, 调用ItemService中的saveAnswer保存所有答案,并返回。 2.在Exam类的main方法中调用 ExamView类的testExam方法,测试题目显示及按键操作是否正确。 第8步 — 进阶业务功能 1.在ExamView类中,继续改进testExam方法,在原基础上: 1.起始进入考试时,首先显示一页“帮助信息”,用来说明考试过程中的操作方法,尤其是各按键的使用。当键入n时,显示第一道题; 2.在显示每题题目的同时,如果之前考生已经选择了该题目的答案,则答案也同时显示以便考生查看; 3.键入f表示结束考试,程序应提示用户进行确认。如确认则自动判分,并调用ItemService中的saveAnswer保存所有答案及分数,并显示所有考题的正确答案和考生所选答案,以及考试分数,然后方法结束。如果不确认,则继续答题。 2.在Exam类的main方法中调用 ExamView类的testExam方法,验证程序是否正确运行。 第9步 — 进阶业务功能 1.添加以下功能:程序启动时,显示主菜单,菜单包含以下两项: 1.进入考试 2.显示上次考试成绩 2.当用户选择1时,进入考试过程;当用户选择2时,显示上次考试成绩,按n键后回到主菜单。
package com.Exam; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ItemService { private static final String ITEM_FILENAME = "./item.txt"; private static final String ANSWER_FILENAME = "./answer.txt"; public final int ITEM_NUMS;//一共有多少题 private final int LINE = 6; public Item[] items; public ItemService() { //将所有的本地文件读取到items中 List<String> list = readTextFile(); ITEM_NUMS = list.size()/6; items = new Item[ITEM_NUMS]; for(int i=0;i<ITEM_NUMS;i++) { String question = list.get(i*LINE); String[] options = {list.get(i*LINE+1),list.get(i*LINE+2),list.get(i*LINE+3),list.get(i*LINE+4)}; char answer = list.get(i*LINE+5).charAt(0); Item item = new Item(question,options,answer); items[i] = item; } System.out.println(items); } public List<String> readTextFile() { //读取文件到List集合中,方便读取到item到items数组 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); BufferedReader buffReader = null; try { buffReader= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(ITEM_FILENAME)); String str = null; while((str=buffReader.readLine())!=null) { if(!str.trim().equals("")) { list.add(str); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(buffReader!=null) { try { //关闭I/O流,好习惯 buffReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return list; } //获取一个item条目 public Item getItem(int index) { System.out.println(index); if(index<1||index>ITEM_NUMS) { return null; } //itemS里存放的是所有题目的集合,方便提取 return items[index-1]; } //将学生答题的答案序列化到本地 public void saveAnswer(char[] arr) { ObjectOutputStream obj = null; try { obj= new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(ANSWER_FILENAME)))); obj.writeObject(arr); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { if(obj!=null) { try { obj.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //读取序列化到本地的学生答题答案 public char[] readAnswer() { char[] arr = null; ObjectInputStream obj = null; try { FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(ANSWER_FILENAME); BufferedInputStream buff = new BufferedInputStream(in); obj = new ObjectInputStream(buff); arr = (char[]) obj.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { if(obj!=null) { try { obj.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } return arr; } }
package com.Exam; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Arrays; public class Item implements Serializable{ private String question;//题干 private String[] options;//四个选项 private char answer;//答案 public Item(String question, String[] options, char answer) { super(); this.question = question; this.options = options; this.answer = answer; } public Item() { super(); } public String getQuestion() { return question; } public void setQuestion(String question) { this.question = question; } public String[] getOptions() { return options; } public void setOptions(String[] options) { this.options = options; } public char getAnswer() { return answer; } public void setAnswer(char answer) { this.answer = answer; } }
package com.Exam; import java.util.Scanner; public class ExamView { private ItemService item = new ItemService(); private char[] answer; public ExamView() { answer = new char[item.ITEM_NUMS]; } public static void main(String[] args) { ExamView e = new ExamView(); e.enterMainMenu(); } public void enterMainMenu() { displayMainMenu(); char key = getUserAction(); switch (key) { case '1': //进入考试 textExam(); break; case '2': //查看成绩 reviewAnswer(); break; case '3': System.out.println("退出系统"); return; default: break; } } public void textExam() { welcomeExamInfo(); int currItemNum = 1; while(true) { Item i = item.getItem(currItemNum); System.out.println(i.getQuestion()); String[] options = i.getOptions(); for(int f=0;f<options.length;f++) { System.out.println(options[f]); } System.out.println("请选择:"); char c = getUserAction(); switch (c) { case 'A': case 'B': case 'C': case 'D': answer[currItemNum-1] = c; if(currItemNum>=item.ITEM_NUMS) { resultAnswer(answer); return; } currItemNum++; break; case 'N': if(currItemNum>=item.ITEM_NUMS) { System.out.println("已经是最后一个题了!"); }else { currItemNum++; } break; case 'P': if(currItemNum<=1) { System.out.println("已经达到第一个题了!"); }else { currItemNum--; } break; case 'F': System.out.println("确认是否结束考试(Y/N)"); char k = getUserAction(); if(k=='Y') { //保存答案 item.saveAnswer(answer); //自动判分 resultAnswer(answer); //将答案序列化到本地 item.saveAnswer(answer); return;//结束考试 }else if(k=='N'){ currItemNum--; } break; default: break; } } } //进入项目提示信息 public void welcomeExamInfo() { System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("---欢迎进入考试----"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("---请按照一下要求进行考试----"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("---A-D 选择指定答案---"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("---P 显示上一题--"); System.out.println("---N 显示下一题--"); System.out.println("---F 考试结束--"); System.out.println("--请按N键进入考试-"); System.out.println("-------------------"); while(true) { char c = getUserAction(); if(c=='N') { return; } } } //传入用户的答案, public void resultAnswer(char[] answer) { int score = 0; Item[] items = item.items; for(int i=0;i<item.ITEM_NUMS;i++) { Item it =items[i]; //获取准确答案an,和用户的答案进行对比 char an = it.getAnswer(); if(an==answer[i]) { score+=10; } } System.out.println("您的最终得分是:"+score); } //获取本地用户答案 public void reviewAnswer() { //调用对答案方法,获取成绩 resultAnswer(item.readAnswer()); } //获取输入,规定对应的输入 public char getUserAction() { char[] arr = {'1','2','3','A','B','C','D','N','P','F','Y'}; while(true) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String s = scan.next().toUpperCase(); char c = s.charAt(0); for(char r:arr) { if(c==r) { return c; } } System.out.println("请继续输入:"); } } //显示功能,提示 public void displayMainMenu() { System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("----欢迎使用在线考试系统--------------------"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println(" 1 进入考试"); System.out.println(" 2 查看成绩"); System.out.println(" 3 退出系统"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("--------------------------"); System.out.println("--请选择:--"); } }