一、概述
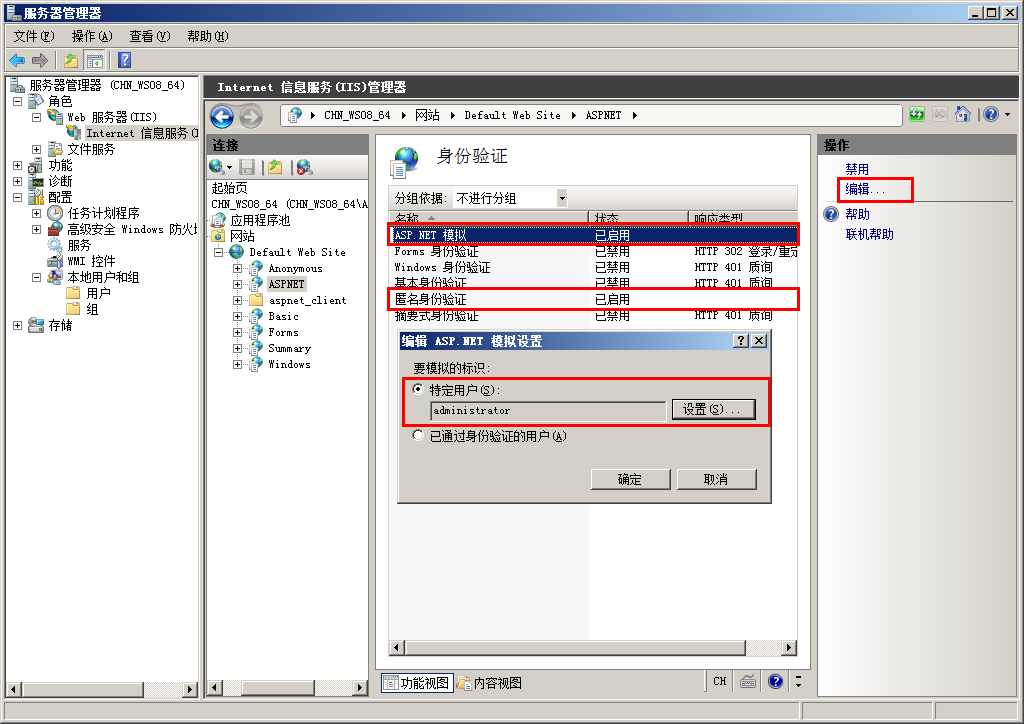
在实际的项目开发中,我们可能会需要调用一些非托管程序,而有些非托管程序需要有更高的身份权限才能正确执行。本文介绍了如何让IIS承载的ASP.NET网站以特定的账户执行,比如Administrator。
默认情况下禁用 ASP.NET 模拟。如果对某 ASP.NET 应用程序启用了模拟,该应用程序将运行在标识上下文中,其访问标记被 IIS 传递给 ASP.NET。
- 该标记可以是已通过身份验证的用户标记(如已登录的 Windows 用户的标记)【IIS上配置“集成Widows身份验证”且不勾选“匿名访问”的情况下】
- 该标记也可以是 IIS 为匿名用户提供的标记(通常为 IUSR_MACHINENAME 标识)。 【IIS上配置勾选“匿名访问”的情况下】
二、读取被模拟用户的标识
注意:可以使用以下代码来确定线程作为哪个用户执行:
WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name
三、模拟 IIS 验证的帐户或用户
若要在收到 ASP.NET 应用程序中每个页的每个请求时模拟 Microsoft Internet 信息服务 (IIS) 身份验证用户,必须在此应用程序的 Web.config 文件中包含 <identity> 标记,并将 impersonate 属性设置为 true。例如:
<identity impersonate="true" />
四、为 ASP.NET 应用程序的所有请求模拟特定用户
若要为 ASP.NET 应用程序的所有页面上的所有请求模拟特定用户,可以在该应用程序的 Web.config 文件的 <identity> 标记中指定 userName 和 password 属性。例如:
<identity impersonate="true" userName="accountname" password="password" />
五、在代码中模拟身份验证用户
若要仅在运行代码的特定部分时模拟身份验证用户 (User.Identity),您可以使用以下代码。此方法要求身份验证用户标识的类型为 WindowsIdentity。
WindowsImpersonationContext impersonationContext = ((WindowsIdentity)User.Identity).Impersonate(); //Insert your code that runs under the security context of the authenticating user here. impersonationContext.Undo();
六、在代码中模拟特定用户
若要仅在运行代码的特定部分时模拟特定用户,请使用以下代码(使用Windows API):
<%@ Page Language="C#"%> <%@ Import Namespace = "System.Web" %> <%@ Import Namespace = "System.Web.Security" %> <%@ Import Namespace = "System.Security.Principal" %> <%@ Import Namespace = "System.Runtime.InteropServices" %> <script runat=server> public const int LOGON32_LOGON_INTERACTIVE = 2; public const int LOGON32_PROVIDER_DEFAULT = 0; WindowsImpersonationContext impersonationContext; [DllImport("advapi32.dll")] public static extern int LogonUserA(String lpszUserName, String lpszDomain, String lpszPassword, int dwLogonType, int dwLogonProvider, ref IntPtr phToken); [DllImport("advapi32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto, SetLastError=true)] public static extern int DuplicateToken(IntPtr hToken, int impersonationLevel, ref IntPtr hNewToken); [DllImport("advapi32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto, SetLastError=true)] public static extern bool RevertToSelf(); [DllImport("kernel32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto)] public static extern bool CloseHandle(IntPtr handle); public void Page_Load(Object s, EventArgs e) { if(impersonateValidUser("username", "domain", "password")) { //Insert your code that runs under the security context of a specific user here. undoImpersonation(); } else { //Your impersonation failed. Therefore, include a fail-safe mechanism here. } } private bool impersonateValidUser(String userName, String domain, String password) { WindowsIdentity tempWindowsIdentity; IntPtr token = IntPtr.Zero; IntPtr tokenDuplicate = IntPtr.Zero; if(RevertToSelf()) { if(LogonUserA(userName, domain, password, LOGON32_LOGON_INTERACTIVE, LOGON32_PROVIDER_DEFAULT, ref token) != 0) { if(DuplicateToken(token, 2, ref tokenDuplicate) != 0) { tempWindowsIdentity = new WindowsIdentity(tokenDuplicate); impersonationContext = tempWindowsIdentity.Impersonate(); if (impersonationContext != null) { CloseHandle(token); CloseHandle(tokenDuplicate); return true; } } } } if(token!= IntPtr.Zero) CloseHandle(token); if(tokenDuplicate!=IntPtr.Zero) CloseHandle(tokenDuplicate); return false; } private void undoImpersonation() { impersonationContext.Undo(); }