在上一篇中,我们已经讲了,SpringBoot 如何构建项目,和SpringBoot的HelloWorld,
那这一节我们继续讲 Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf

官网: Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是跟Velocity、FreeMarker类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代JSP,相较与其他的模板引擎,它主要有以下几个优势:
-
Thymeleaf在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以thymeleaf的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
-
Thymeleaf开箱即用的特性。它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、改jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
-
Thymeleaf提供spring标准方言和一个与SpringMVC完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
简单点说:就是为我们要渲染的界面
自动配置
自动给我们默认分配了模版的前缀和后缀,我们只需要按部就班的将模版丢进去即可,
SpringBoot天生就带自动配置,这也是为什么,我们直接丢进去就可以了,
相比于SpringMVC,他会自动拼接到templates页面

Thymeleaf整合SpringBoot
- 在pom.xml文件引入thymeleaf1
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 在application.properties(application.yml)文件中配置thymeleaf
spring.thymeleaf.
prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
- 新建编辑控制层代码HelloController,在request添加了name属性,返回到前端hello.html再使用thymeleaf取值显示。
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "springboot-thymeleaf") String name) {
request.setAttribute("name", name);
return "hello";
}
}
- 新建编辑模板文件,在resources文件夹下的templates目录,用于存放HTML等模板文件,在这新增hello.html,添加如下代码。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>springboot-thymeleaf demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'hello, ' + ${name} + '!'" />
</body>
</html>
以后,我们所有的 代码 都是上面 这三板斧 ,这也是SpringBoot的优势
- 写 pom
- 写配置
- 业务类
切记:使用Thymeleaf模板引擎时,必须在html文件上方添加该行代码使用支持Thymeleaf。
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
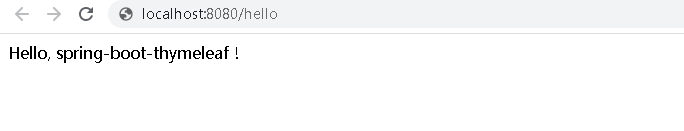
- 启动项目,访问http://localhost:8080/hello,看到如下显示证明SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf成功。
Thyemeleaf 的常用语法
Thymeleaf的主要作用是把model中的数据渲染到html中,因此其语法主要是如何解析model中的数据。从以下方面来学习:
- 变量、方法、条件判断、循环、运算 [ 逻辑运算、布尔运算、比较运算、条件运算 ]
- 其他 大家可以去官网: Thymeleaf详解
变量_变量案列
我们先新建一个实体类:User
public class User {
String name;
int age;
User friend;// 对象类型属性
}
然后在Controller中添加数据
@GetMapping("test2")
public String test2(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(21);
user.setName("Jackson");
user.setFriend(new User("李小龙", 30));
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "hello2";
}
·语法解释·
Thymeleaf通过
${}来获取model中的变量,注意这不是el表达式,而是ognl表达式,但是语法非常像。
我们在页面获取user数据:
<h1>
你好:<span th:text="${user.name}">请跟我来</span>
</h1>
感觉跟el表达式差不多的。区别在于,我们的表达式写在一个名为:th:text的标签属性中,这个叫做指令
向下兼容
但是要注意,如果浏览器不支持Html5怎么办?
如果不支持这种th:的命名空间写法,那么可以把th:text换成 data-th-text,Thymeleaf也可以兼容。
如果想要不进行格式化输出,而是要输出原始内容,则使用th:utext来代替.
变量_ognl表达式的语法
刚才获取变量值,我们使用的是经典的对象.属性名方式。但有些情况下,我们的属性名可能本身也是变量,怎么办?
ognl提供了类似js的语法方式:
例如:${user.name} 可以写作${user['name']}
看下面案例
<h2>
<p>Name: <span th:text="${user.name}">Jack</span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="${user.age}">21</span>.</p>
<p>friend: <span th:text="${user.friend.name}">Rose</span>.</p>
</h2>
我们获取用户的所有信息,分别展示。
当数据量比较多的时候,频繁的写user.就会非常麻烦。
因此,Thymeleaf提供了自定义变量来解决:
示例
<h2 th:object="${user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{name}">Jack</span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="*{age}">21</span>.</p>
<p>friend: <span th:text="*{friend.name}">Rose</span>.</p>
</h2>
- 首先在 h2上 用 th:object="${user}"获取user的值,并且保存
- 然后,在h2内部的任意元素上,可以通过 *{属性名}的方式,来获取user中的属性,这样就省去了大量的user.前缀了
循环遍历
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎访问thymeleaf页面</h1>
<h4>
<span th:each="user:${user}"> [[${user}]] </span>
</h4>
</body>
</html>
欧克 ,好了,就总结到这里 ,喜欢的话,记得点个关注哦!