if
单分支if语句
if [ expression ]
then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true
fi
- [ expression ]expression和方括号之前必须有空格,否则会有语法错误
- [ expression ]条件表达式结果为true时,执行then后面的语句,fi结束
- 反之,直接fi结束
- ;标识着一条语句结束,不用分号则以换行符表示语句结束,如果使用分号可以将多行语句并为一行
if [ expression ] ; then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true
fi
if else
双分支if语句
if [ expression ] ; then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true
else
Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true
fi
- [ expression ]条件表达式结果为true执行时执行then后面的语句,fi结束
- 反之执行else后面的语句,fi结束
if elif
多分支if语句
if [ expression1 ] ; then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression1 is true
elif [ expression2 ] ; then
Statement(s) to be executed elif expression2 is true
elif [ expression3 ] ; then
Statement(s) to be executed elif expression3 is true
...
else
Statement(s) to be executed when any if and elif expression is not true
fi
- 从上往下执行,前面的if或者elif条件表达式为true则执行then后面的语句,fi结束
- 即便之后的条件表达式也是成立的,但只要前面成立的条件表达式,后面的条件表达式不再进行判断
- 如果所有的条件表达式都不成立则执行else后的语句,fi结束
case
shell中的case语句与其他语言中的switch/case语句类似,是一种多分支选择结构
case $var in
pattern1)
Statement(s) to be executed when $var match pattern 1
;;
pattern2)
Statement(s) to be executed when $var match pattern 3
;;
...
patternn)
Statement(s) to be executed when $var match pattern n
;;
*)
Default,statement(s) to be executed when $var not match all patterns
;;
esac
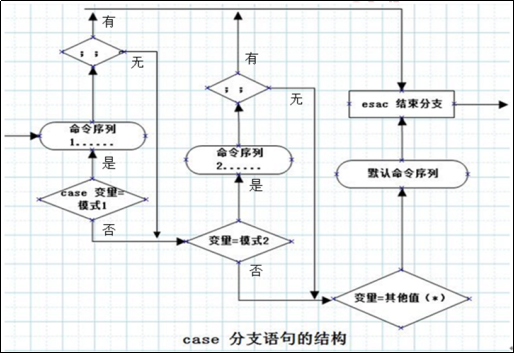
- 首先使用$var与pattern1进行比较,若取值相同则执行模式1后的命令序列,直到遇见双分号后esac结束分支
- 若$var与pattern1不匹配,则继续与pattern2进行比较,若取值相同则执行pattern2后的命令序列,直到遇见双分后esac结束分支
- 依次类推,若找不到任何匹配的值,则执行默认模式*)后的命令序列,直到遇见esac后结束分支
- 取值后面必须为单词in,每一模式必须以右括号结束
- 取值可以为变量或常数,匹配发现取值符合某一模式后,其间所有命令开始执行直至;;
- 取值将检测匹配的每一个模式,一旦模式匹配,则执行完匹配模式相应命令后不再继续其他模式
- 如果无一匹配模式,使用星号*捕获该值,再执行后面的命令
- 它需要一个esac(就是case反过来)作为结束标记,每个case分支用右圆括号,用两个分号表示break
util.sh
最后通过一个小工具脚本来练习下,功能为根据输入的值执行对应的操作
1:Copy
2:Delete
3:Backup
4:Quit
#author: mapros
#date: 2016/11/7
#description: copy delete backup
function copy()
{
read -p "Please enter a source file or directory path: " src
if [ -n "$src" ] && [ -f $src ]
then
echo "This is a file path"
read -p "Please enter a dest directory path: " dest
if [ -n "$dest" ]
then
[ ! -e $dest ] && mkdir -p $dest
cp -f $src $dest && echo "copy success" || "copy failed"
else
echo "Dest directory path can not be null"
fi
elif [ -n "$src" ] && [ -d $src ]
then
echo "This is a directory path"
read -p "Please enter a dest directory path: " dest
if [ -n "$dest" ]
then
[ ! -e $dest ] && mkdir -p $dest
cp -R -f $src $dest && echo "copy success" || echo "copy failed"
else
echo "Dest directory path can not be null"
fi
else
echo "Source file or directory not exists"
fi
}
del()
{
read -p "Please enter a file or directory path which do you want to delete: " src
([ -n "$src" ] && [ -f $src ]) || ([ -n "$src" ] && [ -d $src ])
[ $? -eq 0 ] && rm -rf $src || echo "The path of file or directory which do you want to delete is not exist !"
}
bak()
{
echo "This operate will backup your file with .bak suffix in special directory !"
read -p "Please enter a soure file path: " src
if [ -n "$src" ] && [ -f $src ]
then
read -p "Please enter a backup directory: " dest
[ -n "$dest" ] && [ ! -e $dest ] && mkdir -p $dest
cp -f $src{,.bak} && mv -f ${src}.bak $dest
[ $? -eq 0 ] && echo "back up success" || echo "back up file failed"
else
echo "Source file path is null or is not exist or file path is a directory path !"
fi
}
function print()
{
cat<<EOF
This is a util script of copy delete backup file opts.
There are 4 options for choose.
************************************************
1 Copy:copy file or directory
2 Delete:delete file or directory
3 Backup:backup file or directory
4 Quit:quit this util
************************************************
EOF
read -p "Please choose a number and continue your operation: " number
case $number in
"1")
echo "Your selection is copy"
copy
;;
"2")
echo "Your selection is delete"
del
;;
"3")
echo "Your selection is backup"
bak
;;
"4")
echo "Your selection is quit,see u again"
break
;;
*)
echo "Error number of selection,please choose a correct sellection"
;;
esac
}
while true
do
print
done