一、建立数据库模型类
1.在model里创建模型类。(继承models.Model)
创建模型类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
1 class Order(models.Model): 2 TYPE_CHOICE = ( 3 (0, u"普通运单"), 4 (1, u"绑定关系"), 5 (2, u"库房读取") 6 ) 7 mac = models.CharField(max_length=TEXT_LEN, blank=True) 8 device = models.ForeignKey(IotDevice, related_name='device_orders', blank=True, null=True)#外键 9 operation = models.SmallIntegerField(choices=TYPE_CHOICE, null=True, blank=True)#存贮信息对应的关系10 is_abnormal = models.BooleanField(default=0, verbose_name=u"是否超温") |
模型里数据可用字段类型
4)字段类型
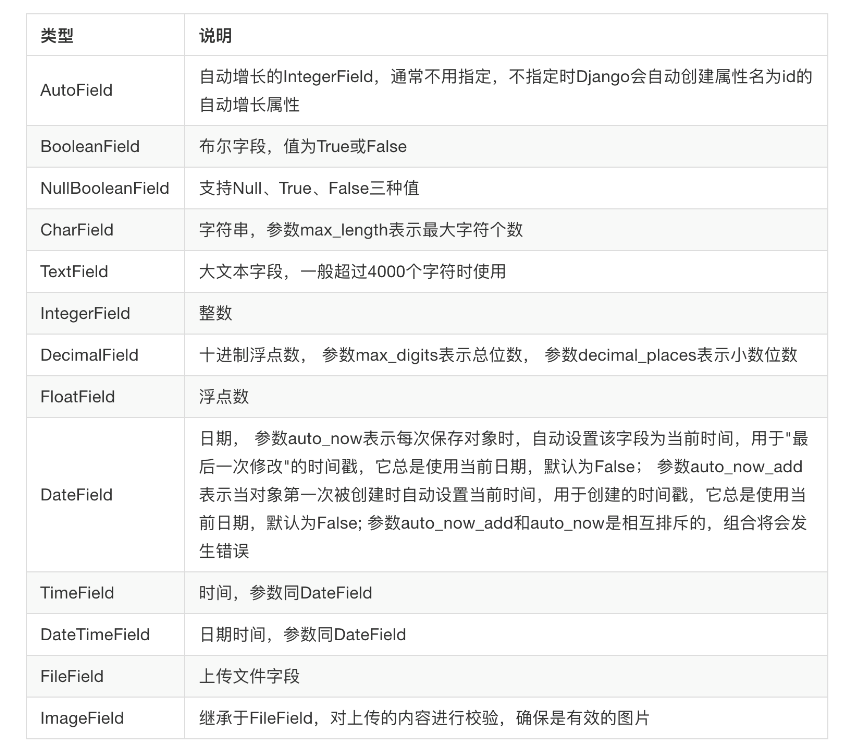
5)选项
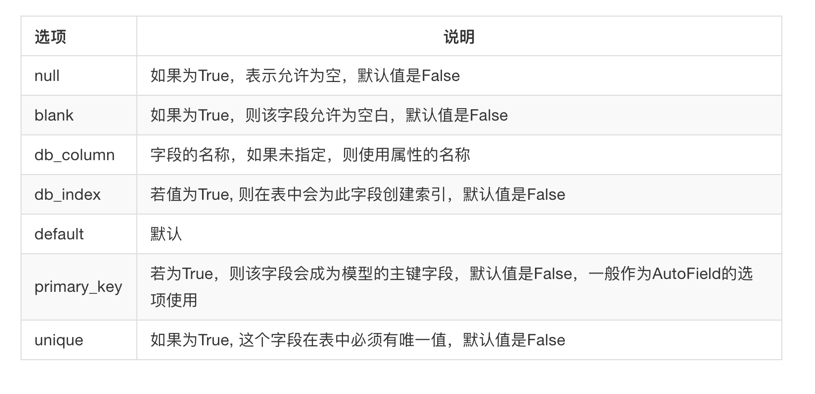

同步模型类的数据到数据库
python manage.py makemigration
python manage.py migrate
二:数据的增加
一:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
1 book = BookInfo(2 btitle='西游记',3 bput_date=date(1988,1,1),4 bread=10,5 bcomment=106 )7 book.save()方法一 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
1 HeroInfo.objects.create(2 hname='沙悟净',3 hgender=0,4 hbook=book)方法二 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#组成列表,列表里各元素的格式为:列表名(字段=值)list= []for i in temp: list.append(IotTemp(time=_time,temp=_temp))#批量导入IotTemp.objects.bulk_create(list)批量增加 |
三:数据的删除
方法一
|
1
2
|
1 hero = HeroInfo.objects.get(id=13)2 hero.delete() |
方法二
|
1
|
1 HeroInfo.objects.filter(id=14).delete() |
四:数据的修改
方法一
|
1
2
3
|
1 hero = HeroInfo.objects.get(hname='猪八戒')2 hero.hname = '猪悟能'3 hero.save() |
方法二
|
1
|
1 HeroInfo.objects.filter(hname='沙悟净').update(hname='沙 |
五:数据库的查询
1.基本查询:
book = BookInfo.objects.get(btitle='西游记') #单一查询,如果结果不存在报错
book = BookInfo.objects.all(btitle='西游记') #查询多个结果,有多少返回多少,不存在返回None
book = BookInfo.objects.count(btitle='西游记' #查询结果的数量
book = BookInfo.objects.exclude(btitle='西游记') #查询结果取反
2.模糊查询:
a.contains 是否包含
book = BookInfo.objects.filter(btitle__contains='记') #查询结果包含‘记’的
b.startswith,endswith 以指定值开头或结尾
book = BookInfo.objects.filter(btitle__startswith='西') #查询以‘西’开头的
book = BookInfo.objects.filter(btitle__endswith='记') #查询以‘记’结尾的
3.空查询:
isnull 是否为空
book = BookInfo.object.filter(bititle__isnull=Flase) #查询bititle不为空
4.范围查询:
in 在范围内
range 相当于between...and...
book = BookInfo.object.filter(id__in = [1,5,13,24]) #查询id为1或5或13或24
book = BookInfo.object.filter(id__range = [10,20]) #查询范围为10-20的id
5.比较查询:
gt 大于
gte 大于等于
lt 小于
lte 小于等于
exclude 不等于
book = BookInfo.object.filter(id__gt =10) #查询id大于10的
book = BookInfo.object.exclude(id = 10) #查询id不等于的10的
6.日期查询
year、month、day、week_day、hour、minute、second:对日期时间类型的属性进行运算。
book = BookInfo.object.filter(bpub_date__year = 1977) #查询1977年出版的书
book = BookInfo.object.filter(bpub_date__gt =date(1977,1,1)) #查询1977年1月1日以后出版的书
7.F对象和Q对象
比较两个字段对象之间的关系用F对象。(F对象可以进行运算)
book = BookInfio.Object.filter(bread__gte=F('bcomment')) #查询阅读量等于评论量的对象
book = BookInfio.Object.filter(bread__gte=F('bcomment') * 2 )
与逻辑运算符连用使用Q对象。 或( | ) 与( & ) 非( ~ )
book = BookInfo.Object.filter(Q(bread__gte=20) | Q(pk__lt=3)) #查询阅读量为20或者id为3的对象
8.聚合函数
使用aggregate()过滤器调用聚合函数。聚合函数包括:Avg 平均,Count 数量,Max 最大,Min 最小,Sum 求和
book = BookInfo.Object.aggregate(Sum('bread')) #求阅读量的和
9.排序
使用order_by对结果进行排序
book=BookInfo.object.all().order_by('bread') #按阅读量的升序排列
book=BookInfo.object.all().order_by('-bread') #按阅读量的降序排列
10.关联查询
一对多模型
一到多的访问语法:一对应的模型类对象.多对应的模型类名小写_set
b = BookInfo.object.filter(id = 1)
b.heroinfo_set.all() #查询book_id = 1的书里的所有英雄
(一本书里有多个英雄,一个英雄只能存在一本书里。表关系为一对多,英雄表里外键关联书id,英雄表里的存放多个书id。英雄表为多,书表为一。)
多到一的访问语法:多对应的模型类对象.多对应的模型类中的关系类属性名
h = HeroInfo.object.filter(id = 1)
h.hbook #查询英雄id = 1的书是哪本。
方向查询除了可以使用模型类名_set,还有一种是在建立模型类的时候使用related_name来指定变量名。
hbook= model.ForeignKey(HeroInfo,on_delete=model.CACADE,null=Ture,related_name='heros')
b.herose.all()
六:多对多表操作
1.建多对多表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class Student(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 老师类class Teacher(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) stu = models.ManyToManyField(to='Student',related_name='teacher') #让django帮助建立多对多关系表model.py |
2.数据的增删改查
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
class ManyToManyTest(APIView): def get(self, request): # 方法一:在建立manytomany的models里查数据 # teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.get(id=2) # data = teacherobj.stu.all() # data_list = [] # for i in data: # data_dic={ # "student_name":i.name, # "teacher_name":teacherobj.name # } # data_list.append(data_dic) # return Response(data_list) # 方法二:在未建立manytomany的models里查数据 studentobj = models.Student.objects.get(id=2) data = studentobj.teacher_set.all() data_list = [] for i in data: data_dic = { "student_name": studentobj.name, "teacher_name": i.name } data_list.append(data_dic) return Response(data_list) def post(self, request): # 方法一:在建立manytomany的models里添加数据,(一条,一个对象) # teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.filter(id=1).first() # studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2).first() # teacherobj.stu.add(studentobj) # return Response({ # "status": 200 # }) #方法二:在未建立manytomany的models里添加数据,(一条,一个对象) teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.all() studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2).first() studentobj.teacher_set.set(teacherobj) return Response({ "status": 200 }) def put(self, request): # 方法一:在建立manytomany的models里修改数据,参数只能是可迭代对象 teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.filter(id=3).first() studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2) teacherobj.stu.set(studentobj) return Response({ "status": 200 }) #方法二:在未建立manytomany的models里修改数据,参数只能是可迭代对象 # teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.all() # studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2).first() # studentobj.teacher_set.set(teacherobj) # return Response({ # "status": 200 # }) def delete(self, request): # 方法一:在建立manytomany的models里删除数据,(一条,一个对象) # teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.filter(id=1).first() # studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2).first() # teacherobj.stu.remove(studentobj) # return Response({ # "status": 200 # }) #方法二:在未建立manytomany的models里删除数据,(多条,可迭代对象) teacherobj = models.Teacher.objects.all() studentobj = models.Student.objects.filter(id=2).first() studentobj.teacher_set.remove(*teacherobj) return Response({ "status": 200 })views.py |