继续文档的第二章
(一)pytest中可以在命令行中静态/动态添加option,这里没什么好讲的,略过...
这里面主要讲下如何试用skip/xfail,还有incremental(包含一些列的测试步骤,如果某一步出错后,该步骤之后的所有步骤都没有任何意义了,xfail掉)
1)首先来看下怎样通过命令行来skip一些case,首先要添加个option,然后使用@pytest.mark.skipif( condition) , xfail使用@pytest.mark.xfail( condition,reson,run,raise),这里不详细介绍了
import pytest def test_func_fast(): print 'fast' @pytest.mark.skipif(not pytest.config.getoption("--runslow")) def test_func_slow_1(): print 'skip slow' @pytest.mark.xfail(not pytest.config.getoption("--runslow")) def test_func_slow_2(): print 'xfail slow'
2)然后来看下如何实现incremental,首先在测试文件的目录下创建conftest.py, 代码如下:
# content of conftest.py import pytest def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call): if "incremental" in item.keywords: if call.excinfo is not None: parent = item.parent parent._previousfailed = item def pytest_runtest_setup(item): if "incremental" in item.keywords: previousfailed = getattr(item.parent, "_previousfailed", None) if previousfailed is not None: pytest.xfail("previous test failed (%s)" %previousfailed.name)
然后创建test_steps.py
# content of test_step.py import pytest @pytest.mark.incremental class TestUserHandling: def test_login(self, fix_err): pass def test_modification(self): assert 0 def test_deletion(self): pass def test_normal(): assert 0
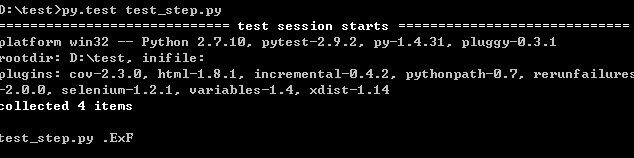
执行结果,在test_modification后的test_deletion 执行为x

3)由于pytest中的Error也划分到Fail中,而Unittest中是单独讲Error独立出来,说明由于case中存在异常或错误导致case未能正常运行,其实在pytest中也可以做到这样,只需要加上一点儿代码,如下:
# content of test_step.py import pytest @pytest.fixture def fix_err(x): raise x @pytest.mark.incremental class TestUserHandling: def test_modification(self): pass def test_login(self, fix_err): try: raise RuntimeError("error") except AssertionError,e: pass except: fix_err(e) def test_deletion(self): pass def test_normal(): assert 0
其执行效果如下:
(二)、这里讲下关于fixture,fixture是pytest特有的功能,它用pytest.fixture标识,定义在函数前面。在你编写测试函数的时候,你可以将此函数名称做为传入参数,pytest将会以依赖注入方式,将该函数的返回值作为测试函数的传入参数。例如上面的例子fix_err.
1)准备函数usefixtures
@pytest.fixture() def cleandir(): newpath = tempfile.mkdtemp() os.chdir(newpath) @pytest.mark.usefixtures("cleandir") class TestDirectoryInit: def test_cwd_starts_empty(self): assert os.listdir(os.getcwd()) == [] with open("myfile", "w") as f: f.write("hello")
2)销毁函数addfinalizer
@pytest.fixture() def smtp(request): smtp = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com") def fin(): print ("teardown smtp") smtp.close() request.addfinalizer(fin) return smtp # provide the fixture value
获取调用函数信息: request 使用fixture标记函数后,函数将默认接入一个request参数,它将包含使用该fixture函数的函数信息
3)fixture的参数,有时我们需要全面测试多种不同条件下的一个对象,功能是否符合预期。我们可以通过params参数来指定传入的参数。
class SMTP: def __init__(self, smtp, sender, receiver): self.smtp = smtp self.sender = sender self.receiver = receiver def __del__(self): self.smtp.close() @pytest.fixture(params=[["smtp.gmail.com", "from@domain.com", "to@doamin.com"], ["mail.python.org", "from@python.org", "to@python.org"]) def smtp(request): return SMTP(#param) def test_mail(smtp): message = "hello" assert smtp.sendmail(message)
4)fixture的作用域:function、module、session ,autouse=True使得函数将默认执行
work_dir = "/tmp/app" @pytest.fixture(session="session", autouse=True) def clean_workdir(): shutil.rmtree(work_dir) os.mkdir(work_dir) os.chrdir(work_dir)
fixture的存在使得我们在编写测试函数的准备函数、销毁函数或者多个条件的测试提供了更加灵活的选择。py.test --fixtures 可以查看所有的fixtures,包含目录下及子目录下的conftest.py
pytest.hookimpl这个没太看明白,应该就是个钩子函数,以后弄明白了再说,今天就到这儿了,下一节再说这个参数化的问题