http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-01/139950.htm
http://blog.csdn.net/spch2008/article/details/9338923
红黑树
红黑树是一棵二叉搜索树,它在每个节点上增加了一个存储位来表示节点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。通过对任何一条从根到叶子简单路径上的颜色来约束,红黑树保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,因而近似于平衡。
红黑树是满足下面红黑性质的二叉搜索树:
1. 每个节点,不是红色就是黑色的;
2. 根节点是黑色的;
3. 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点是黑色的;(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
4. 对每个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点;
5. 每个叶子节点都是黑色的(这里的叶子节点是指的空节点)
思考:为什么满足上面的颜色约束性质,红黑树能保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍?
如图:所能增加的红节点数最多和黑节点数目一样多,故红黑树能保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍。
这些约束强制了红黑树的关键性质: 从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长。结果是这个树大致上是平衡的。因为操作比如插入、删除和查找某个值的最坏情况时间都要求与树的高度成比例,这个在高度上的理论上限允许红黑树在最坏情况下都是高效的,而不同于普通的二叉查找树。
要知道为什么这些特性确保了这个结果,注意到性质4导致了路径不能有两个毗连的红色节点就足够了。最短的可能路径都是黑色节点,最长的可能路径有交替的红色和黑色节点。因为根据性质5所有最长的路径都有相同数目的黑色节点,这就表明了没有路径能多于任何其他路径的两倍长。
一、判断是否是红黑树:
//判断是否是红黑树
bool isRBTree()
{
int BlackNodeNum = 0;
int curBlackNodeNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
BlackNodeNum++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _isRBTree(_root, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum);
}
bool _isRBTree(Node* root, int BlackNodeNum, int curBlackNodeNum)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
curBlackNodeNum++;
}
if (BlackNodeNum == curBlackNodeNum)
{
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else if (root->_col == RED && root->_col == root->_parent->_col)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return _isRBTree(root->_left, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum)
&& _isRBTree(root->_right, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum);
} //左单旋 右边过多 红黑树放弃了追求完全平衡,追求大致平衡
void RotateL(Node* &root)
{
Node* subR = root->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
root->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = root;
}
subR->_left = root;
subR->_parent = root->_parent;
root->_parent = subR;
root = subR;
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
_root = root;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key > root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_left = root;
}
else if ( root->_parent->_key < root->_key )
{
root->_parent->_right = root;
}
}四、右单旋 左边过多
//右单旋 左边过多 红黑树放弃了追求完全平衡,追求大致平衡
void RotateR(Node*& root)
{
Node* subL = root->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
root->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = root;
}
subL->_right = root;
subL->_parent = root->_parent;
root->_parent = subL;
root = subL;
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
_root = parent;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key > root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_left = root;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key < root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_right = root;
}
}五、插入的三种情况
ps:cur为当前节点,p为父节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
1.第一种情况
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红,则将p,u改为黑,g改为红,然后把g当成cur,继续向上调整。
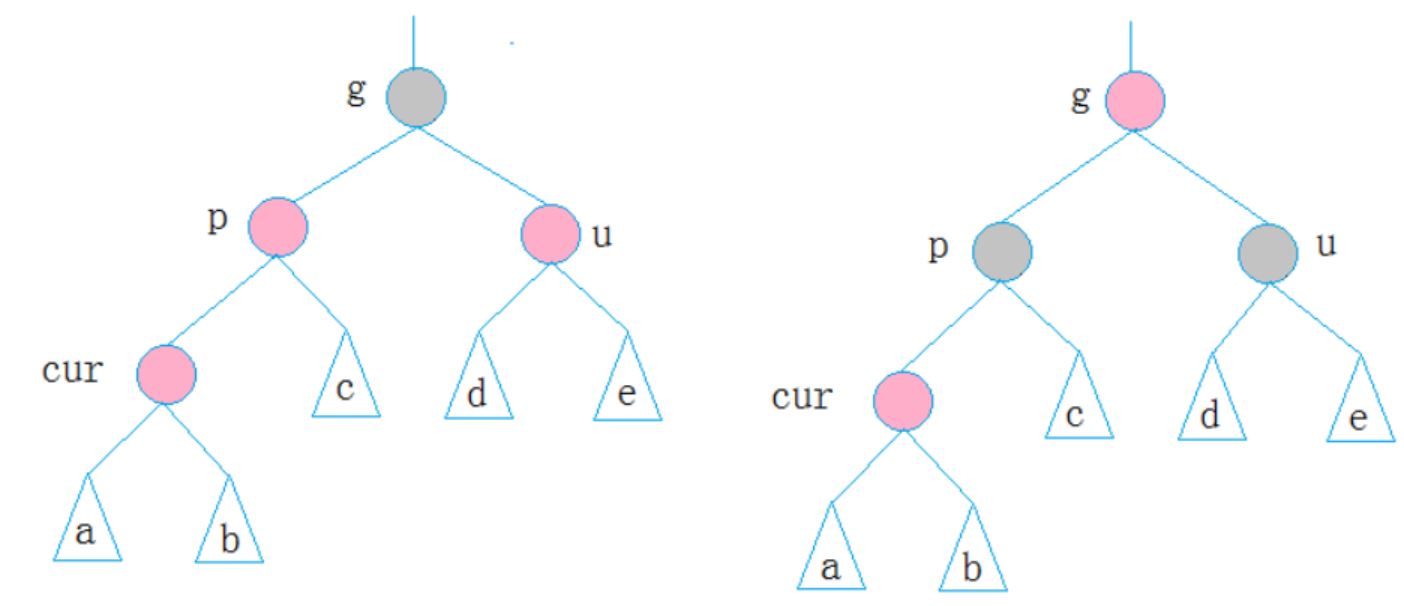
2.第二种情况
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则进行右单旋转;相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则进行左单旋转,p、g变色--p变黑,g变红
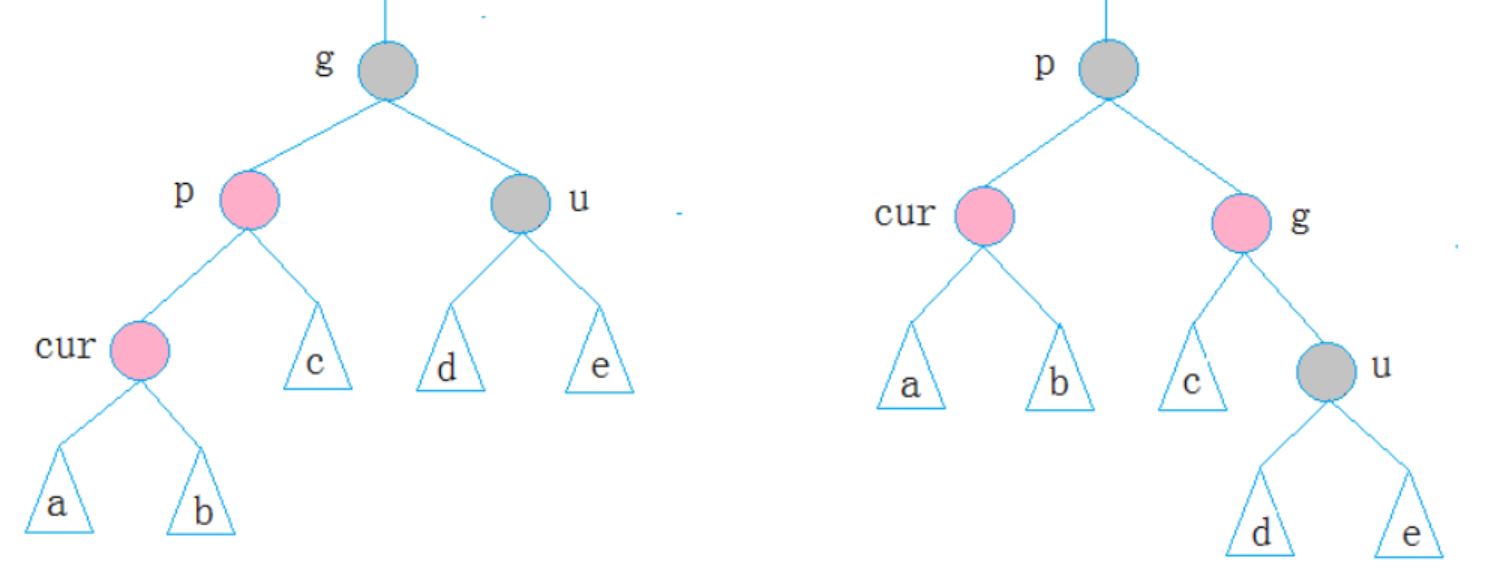
3.第三种情况
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左单旋转;相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右单旋转,则转换成了情况2
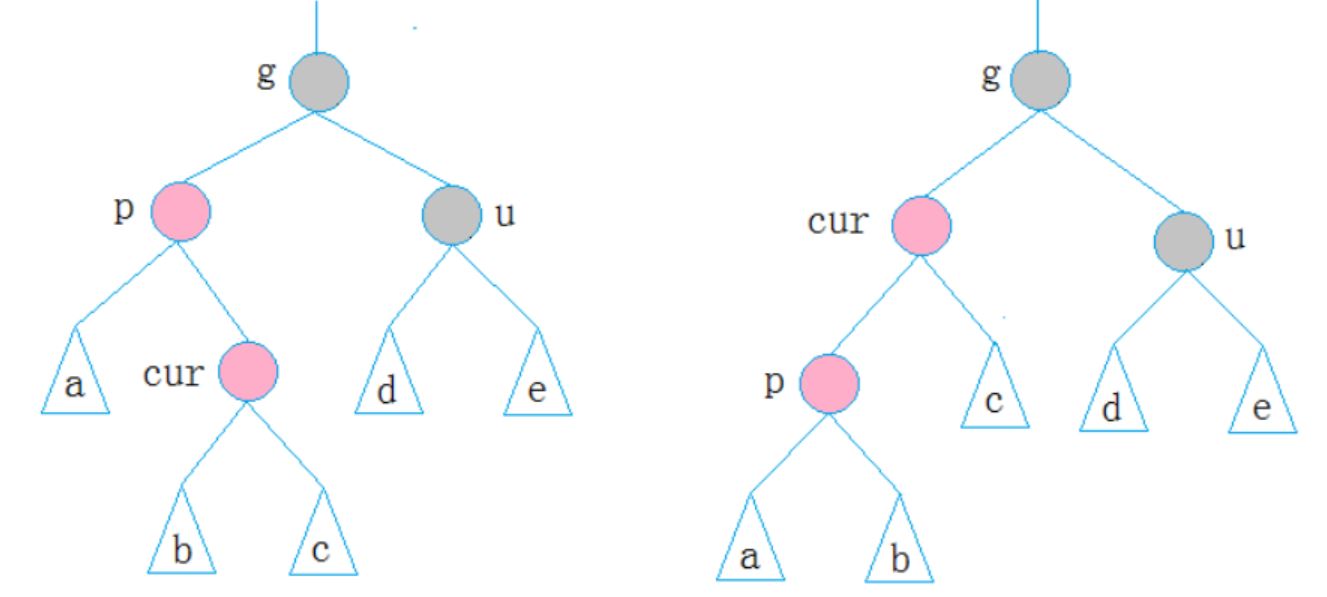
上面已经把每种情况基本列出来了,其他相反的情况类似,反过来写一下就行了,具体详细过程参考代码。
//红黑树的插入操作
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = NULL;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//插入位置
if (parent->_key >key)
{
cur = new Node(key, value);
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else if (parent->_key < key)
{
cur = new Node(key, value);
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
//插入以后,进行调整
while (cur != _root && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = NULL;
//左边的情况
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
//情况一
uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//1. 不需要旋转
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//2.需要旋转
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
}
//情况二,三
else if (uncle == NULL || (uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK))
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateR(grandfather);
break;
}
}
//右边的情况
else if (parent == grandfather->_right)
{
//情况一
uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//1.不需要旋转
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//2.需要旋转
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
}
//情况二,三
else if (uncle == NULL || (uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK))
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateL(grandfather);
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum colour
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
int _col;
K _key;
V _value;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
RBTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value) :
_key(key), _value(value), _col(RED), _left(NULL), _right(NULL), _parent(NULL)
{
}
};
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
RBTree():_root(NULL)
{
}
//红黑树的插入操作
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = NULL;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//插入位置
if (parent->_key >key)
{
cur = new Node(key, value);
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else if (parent->_key < key)
{
cur = new Node(key, value);
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
//插入以后,进行调整
while (cur != _root && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = NULL;
//左边的情况
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
//情况一
uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//1. 不需要旋转
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//2.需要旋转
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
}
//情况二,三
else if (uncle == NULL || (uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK))
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateR(grandfather);
break;
}
}
//右边的情况
else if (parent == grandfather->_right)
{
//情况一
uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//1.不需要旋转
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//2.需要旋转
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
}
//情况二,三
else if (uncle == NULL || (uncle && uncle->_col == BLACK))
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateL(grandfather);
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
//判断是否是红黑树
bool isRBTree()
{
int BlackNodeNum = 0;
int curBlackNodeNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
BlackNodeNum++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _isRBTree(_root, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrderTraverse()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
protected:
bool _isRBTree(Node* root, int BlackNodeNum, int curBlackNodeNum)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
curBlackNodeNum++;
}
if (BlackNodeNum == curBlackNodeNum)
{
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else if (root->_col == RED && root->_col == root->_parent->_col)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return _isRBTree(root->_left, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum) && _isRBTree(root->_right, BlackNodeNum, curBlackNodeNum);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root)
{
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
}
//左单旋 右边过多 红黑树放弃了追求完全平衡,追求大致平衡
void RotateL(Node* &root)
{
Node* subR = root->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
root->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = root;
}
subR->_left = root;
subR->_parent = root->_parent;
root->_parent = subR;
root = subR;
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
_root = root;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key > root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_left = root;
}
else if ( root->_parent->_key < root->_key )
{
root->_parent->_right = root;
}
}
//右单旋 左边过多 红黑树放弃了追求完全平衡,追求大致平衡
void RotateR(Node*& root)
{
Node* subL = root->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
root->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = root;
}
subL->_right = root;
subL->_parent = root->_parent;
root->_parent = subL;
root = subL;
if (root->_parent == NULL)
{
_root = parent;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key > root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_left = root;
}
else if (root->_parent->_key < root->_key)
{
root->_parent->_right = root;
}
}
protected:
Node* _root;
};
#include "Queue.h"
void TestRBtree()
{
RBTree<int, int>RBT;
int Arr[10]= { 1, 2, 5, 12, 16, 18, 26, 3, 99, 100 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
RBT.Insert(Arr[i], i);
}
RBT.InOrderTraverse();
cout << endl;
cout << "is RBTree ?: " << RBT.isRBTree() << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestRBtree();
return 0;
}


